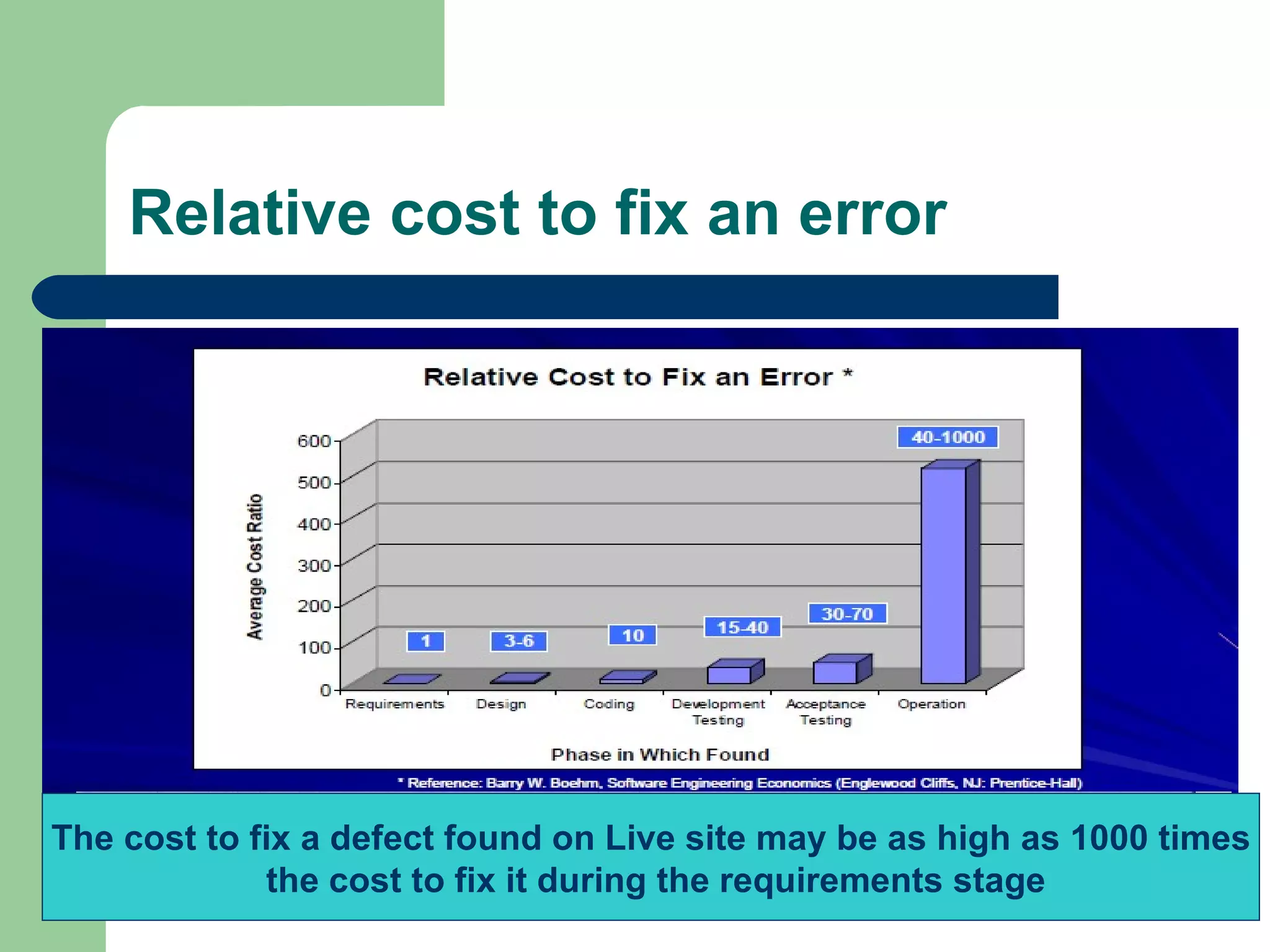
The document discusses the cost of poor quality in software development projects. It notes that the visible costs are small compared to the larger, less quantifiable costs represented by the bottom of the "quality iceberg". Fixing defects early in the requirements stage can be 1000 times cheaper than fixing them after launch. Common problems include poor requirements, feature creep, and unrealistic schedules. Small changes can require significant testing and documentation efforts across teams. The quality team aims to ensure a flawless experience for customers by analyzing defects, automating testing, and continually improving processes through defect analysis and baselining applications.














![THANK YOU [email_address] 9910699578](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/costofquality2503-12699668223376-phpapp01/75/Cost-Of-Quality-16-2048.jpg)