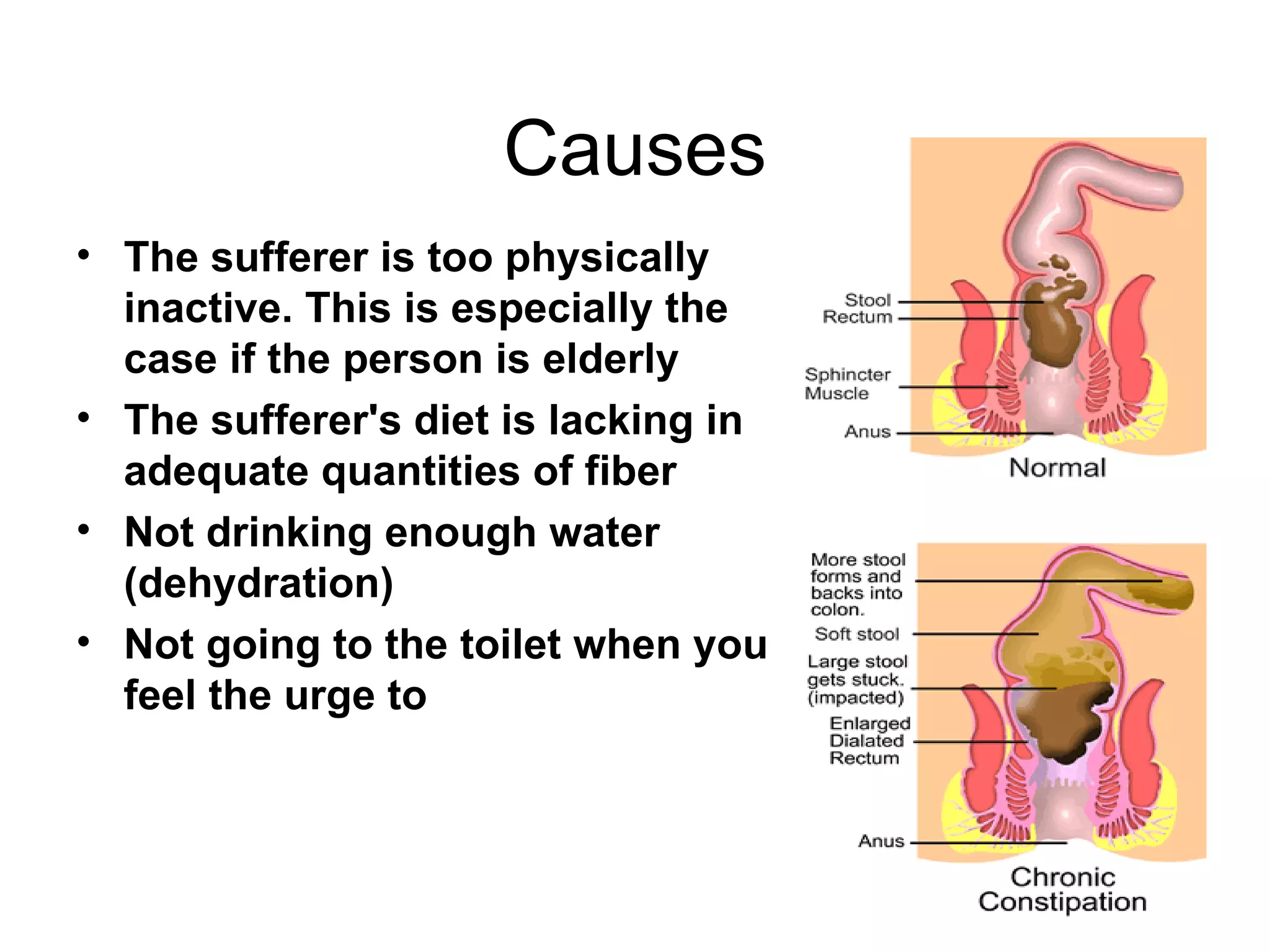
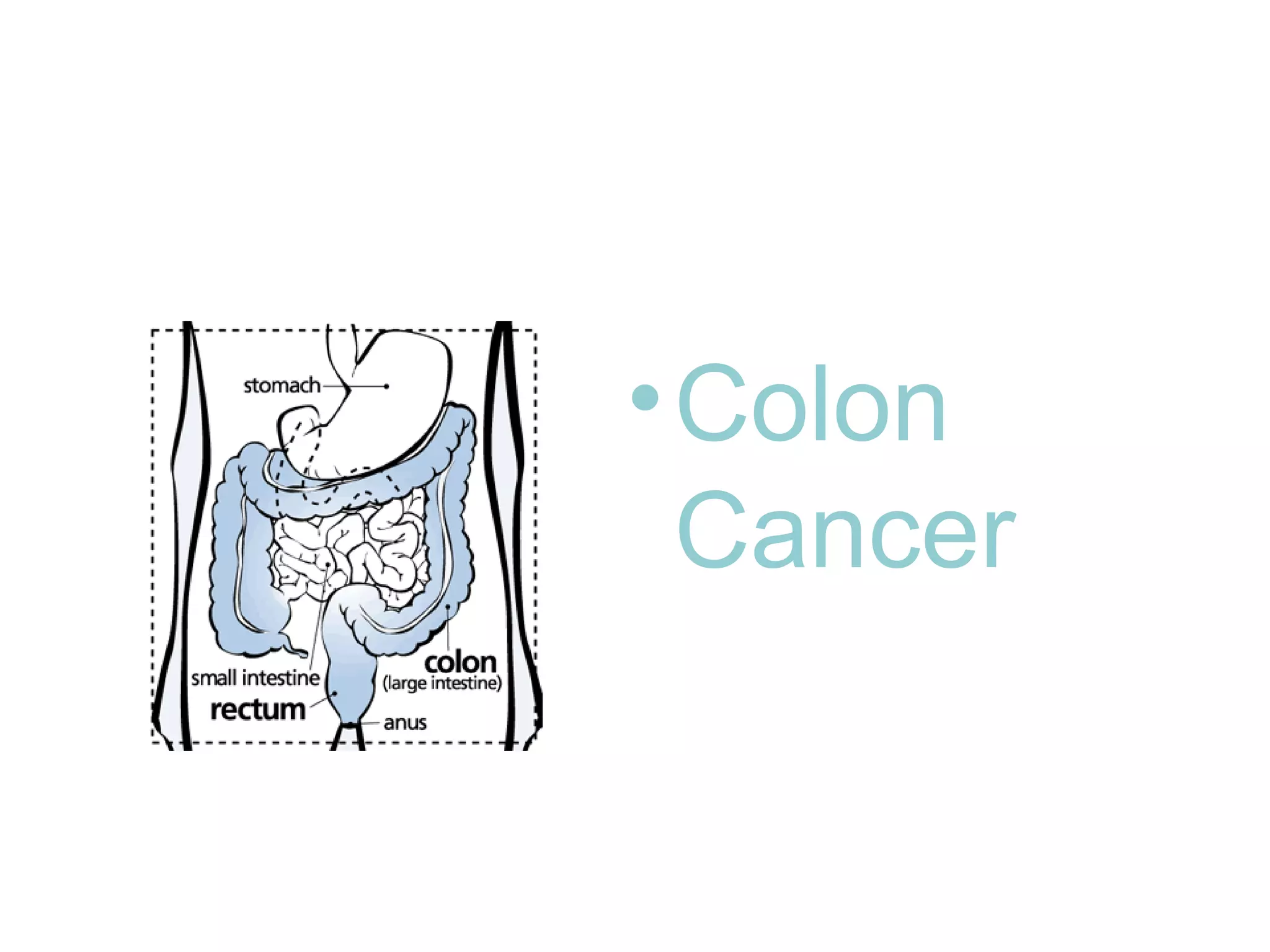
Constipation can increase the risk of colon cancer. Constipation occurs when the colon absorbs too much water from food, making feces hard to pass. It may be caused by inactivity, low fiber diet, dehydration, or not going to the toilet when needed. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes like more activity, high fiber diet, and drinking water. Constipation risk rises with age and multiple medications. Colon cancer develops slowly over years from non-cancerous polyps and risk factors include family history, diet high in fat and low in fiber, and pre-existing colon conditions. Early detection is important as colon cancer chances increase with age.