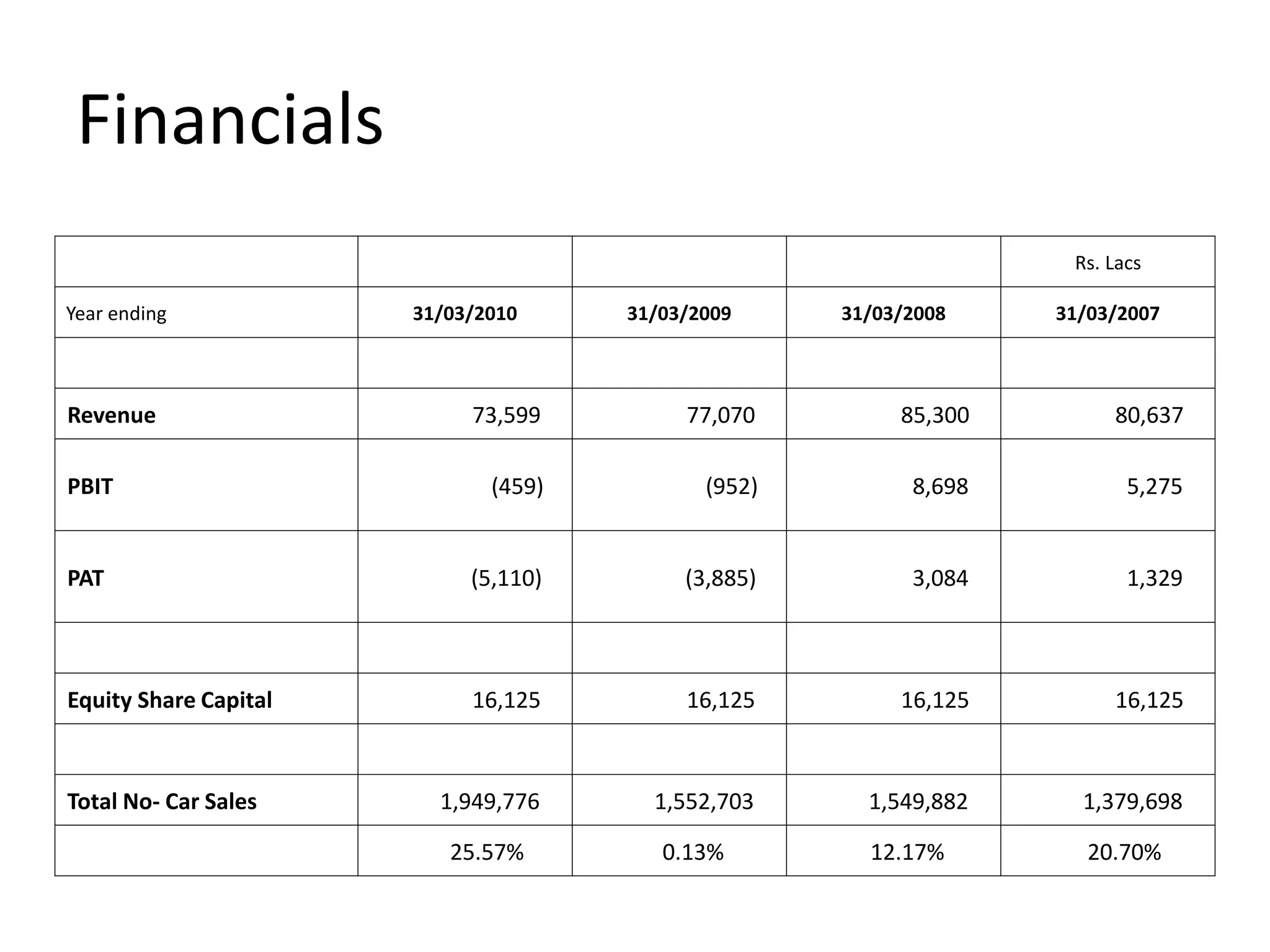
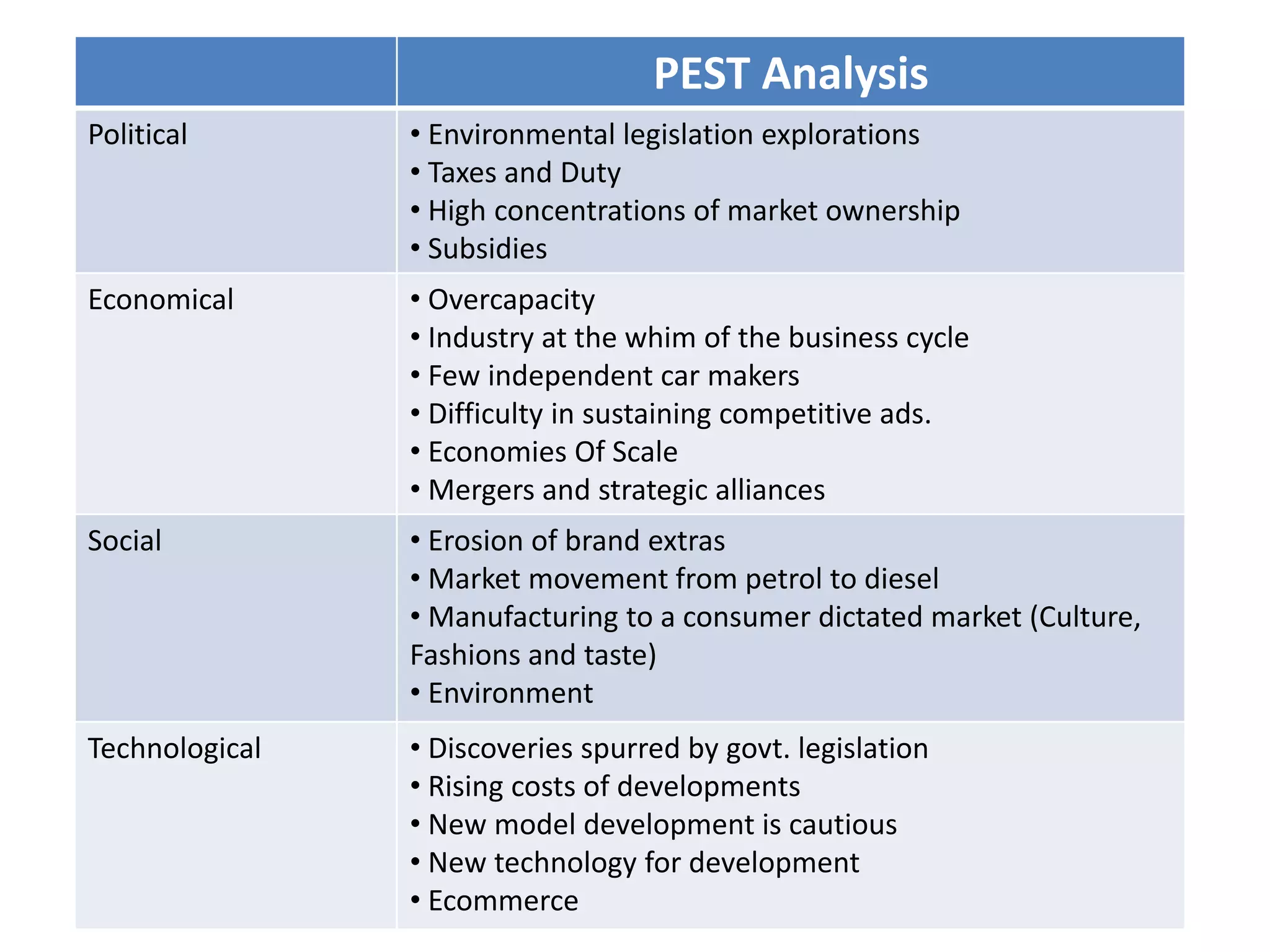
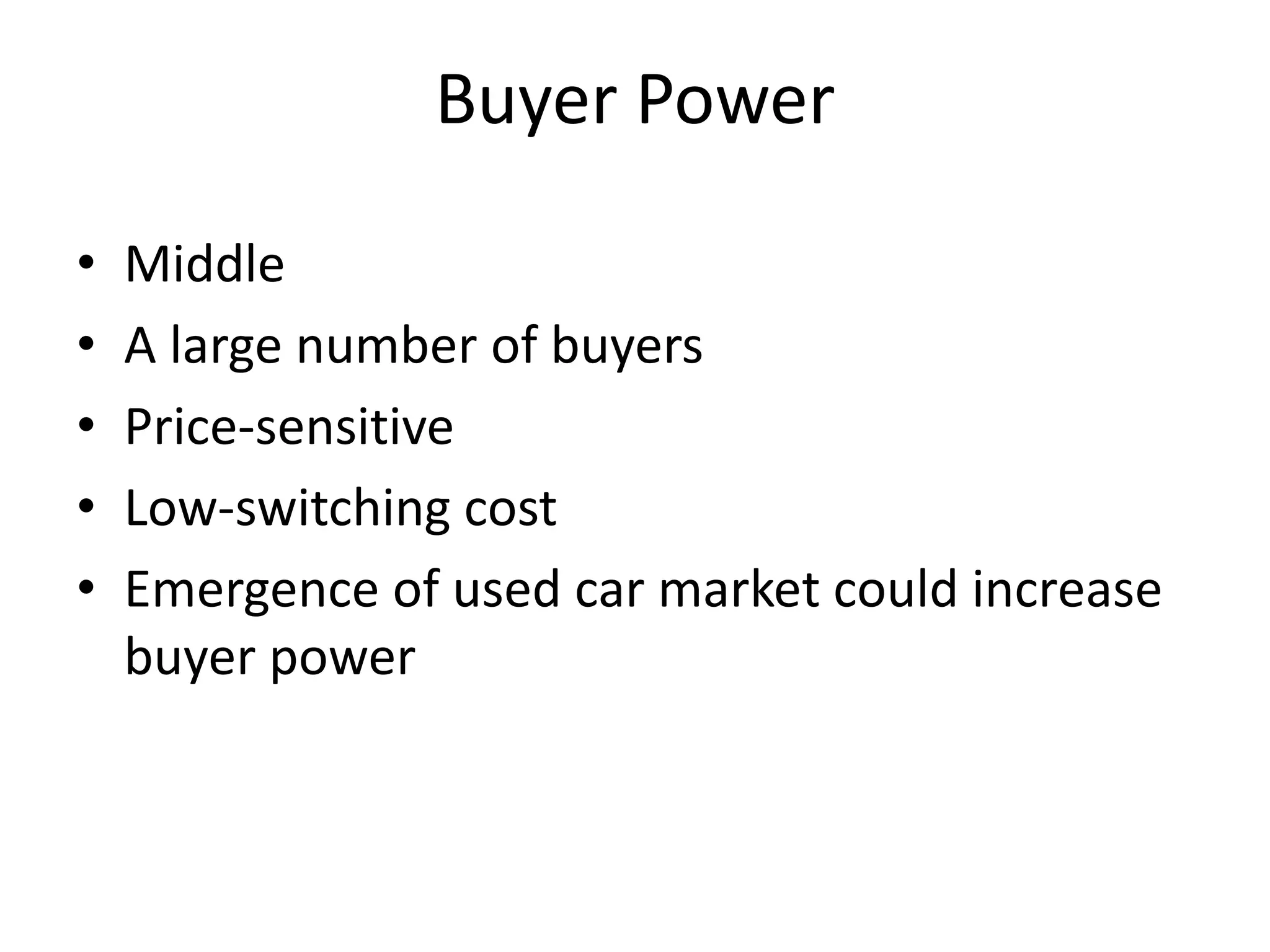
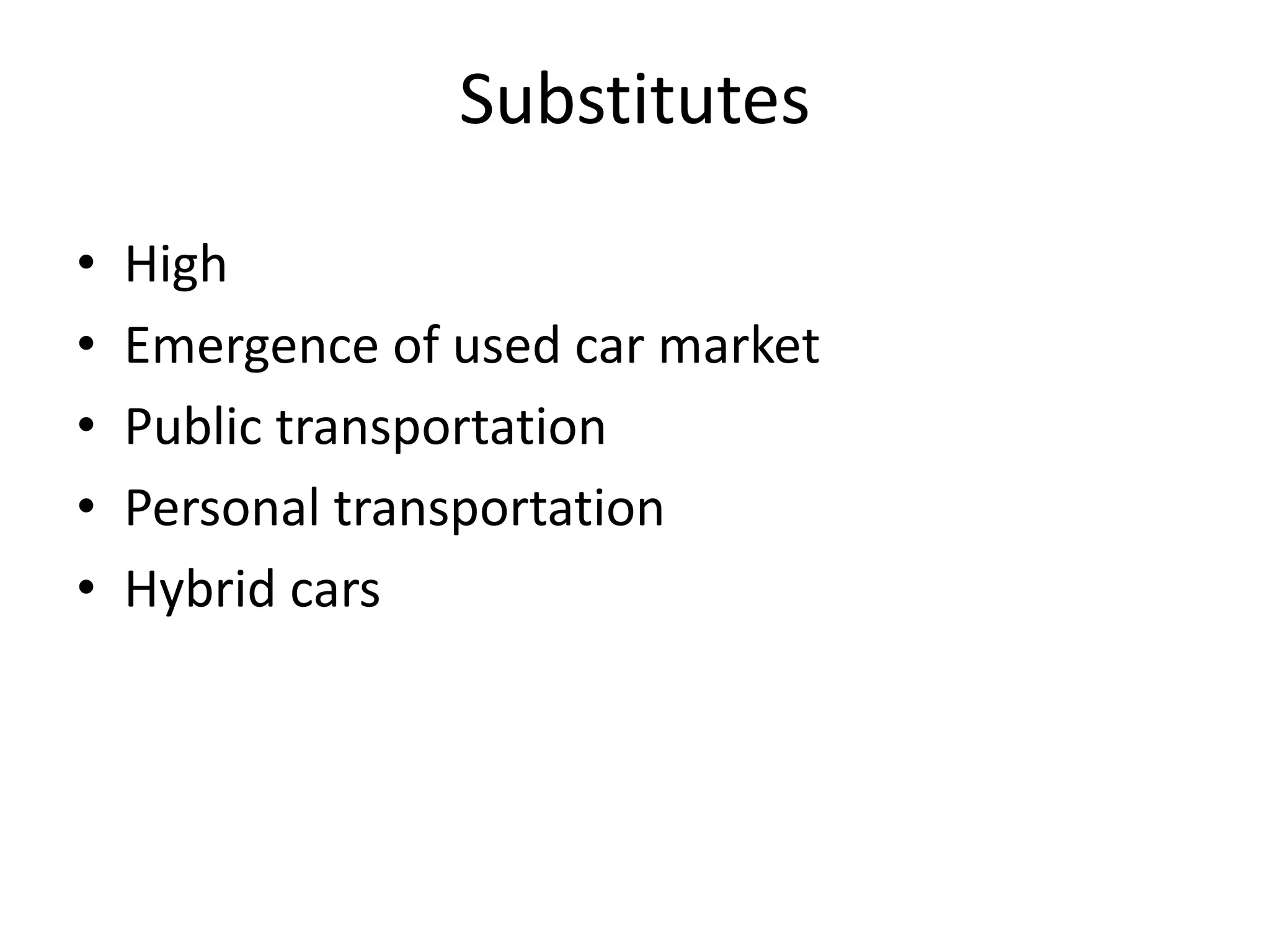
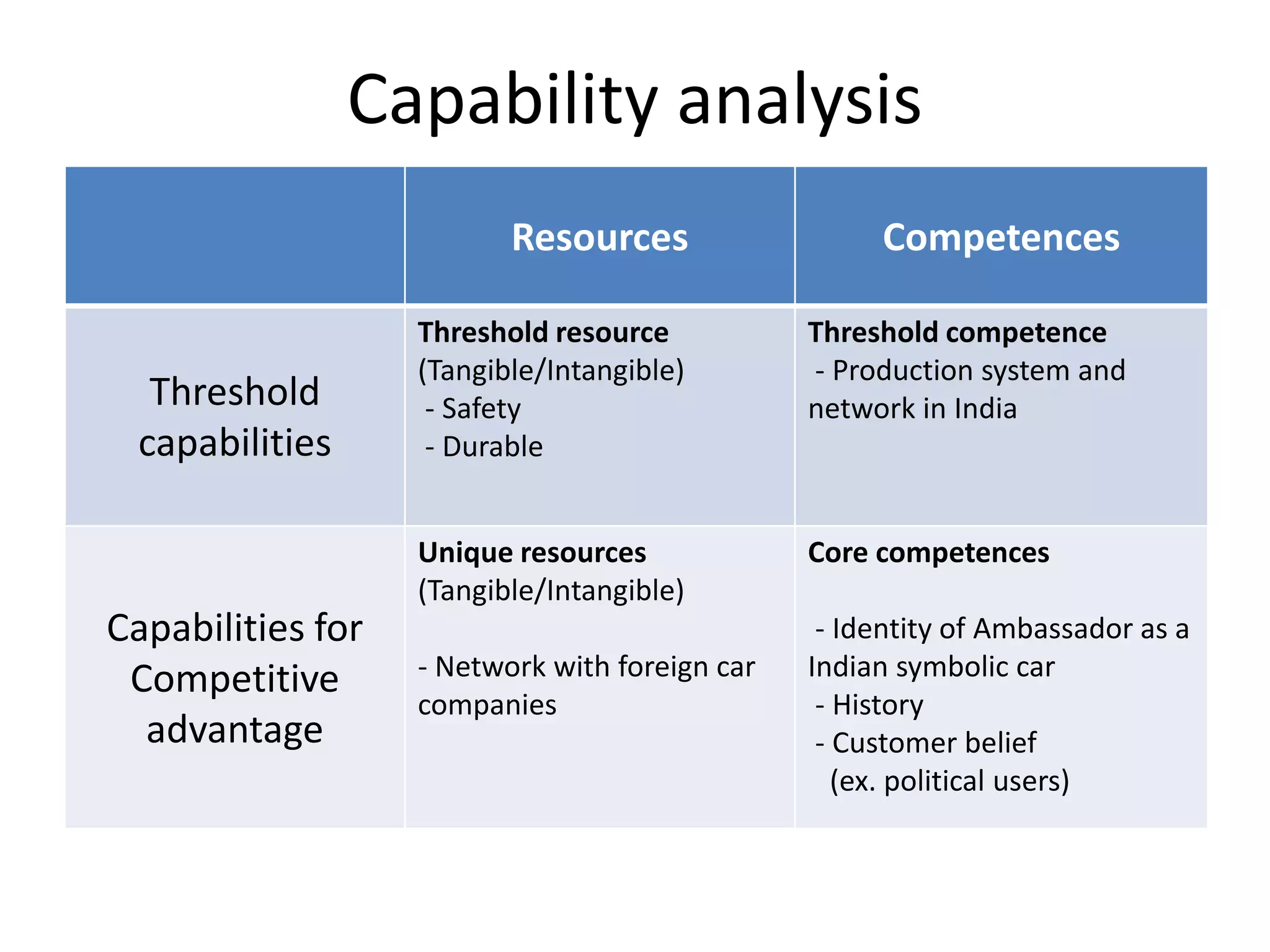
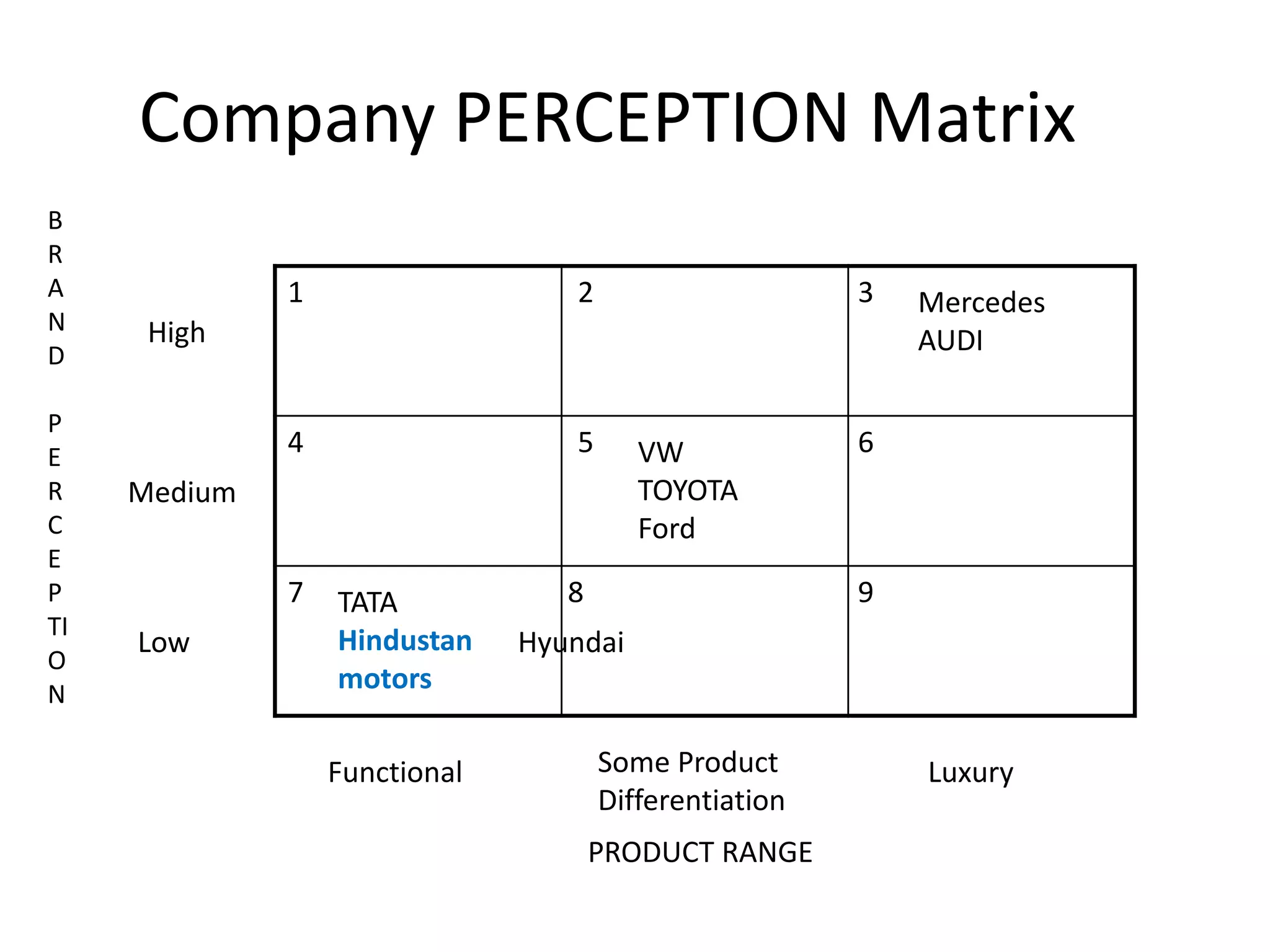
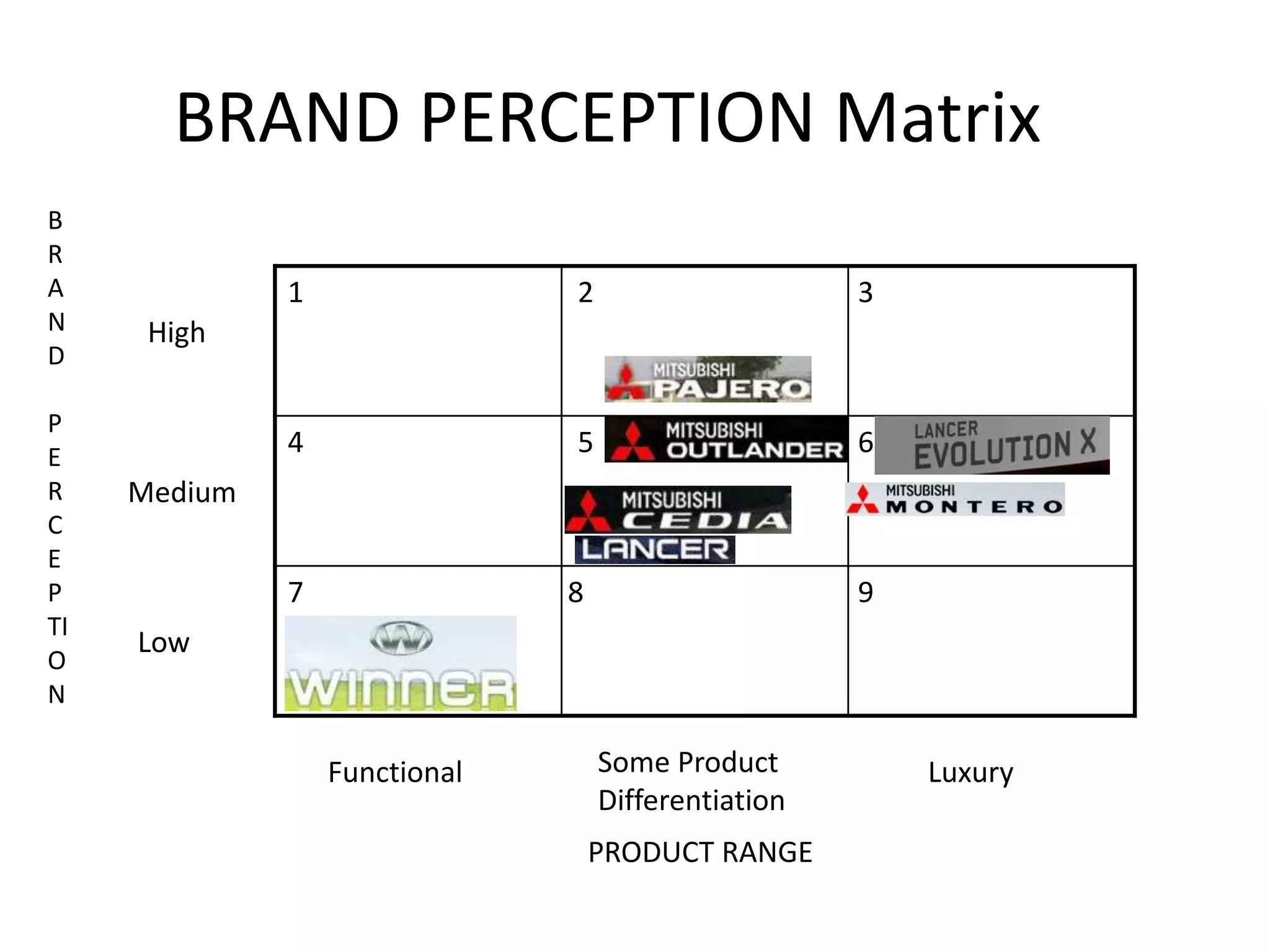
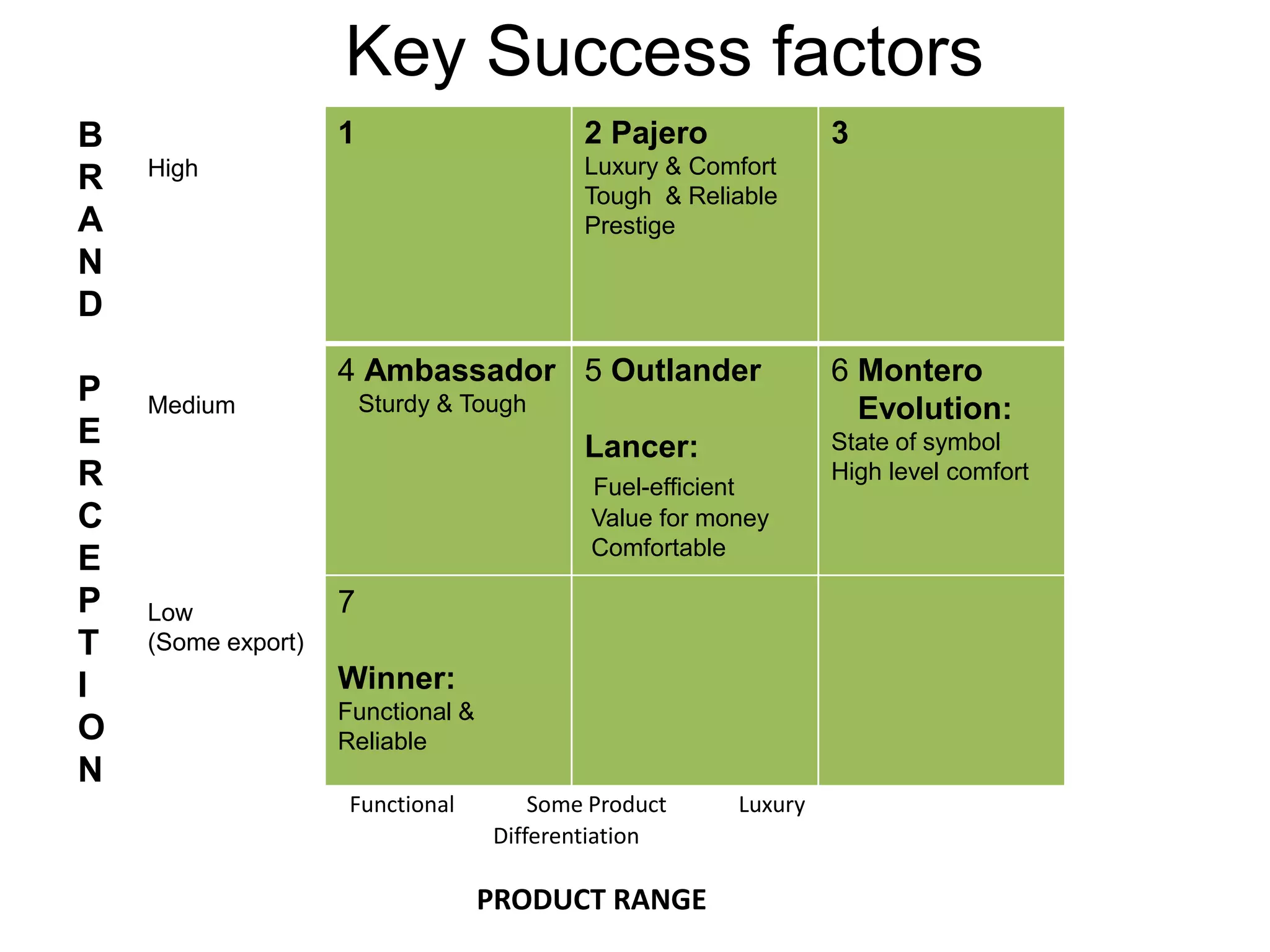
Hindustan Motors is an Indian automobile manufacturer established in 1942. It manufactured India's first car, the Ambassador, which is still in production today and is widely used as a taxi and government vehicle. The company has a joint venture with Mitsubishi and produces various models of cars, SUVs, and MUVs. While it has a long history and brand recognition in India, Hindustan Motors has experienced financial losses in recent years and faces challenges from increasing competition in the domestic automobile market.