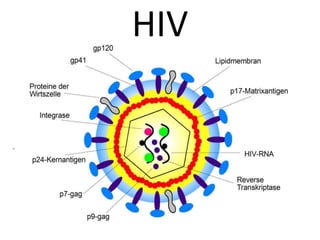
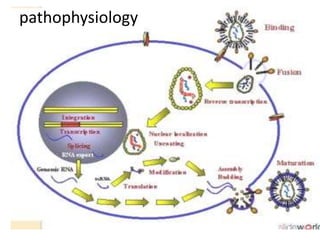
This document discusses paediatric HIV, including:
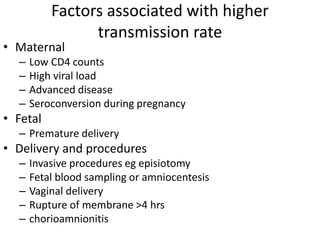
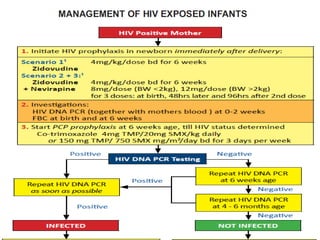
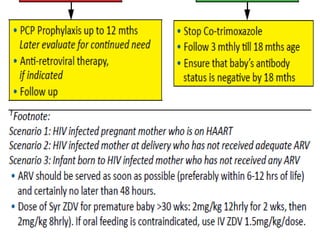
1) Over 2 million children under 15 were living with HIV by 2006, most acquiring it vertically from their mothers. Prevention of mother-to-child transmission focuses on antiretroviral prophylaxis and treatment.
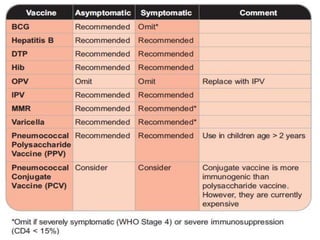
2) HIV infected children can receive routine immunizations which are generally safe and effective, though antibody response may be impaired. Live attenuated vaccines require additional precautions for immunosuppressed children.
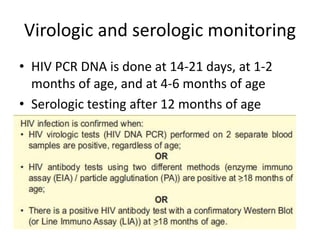
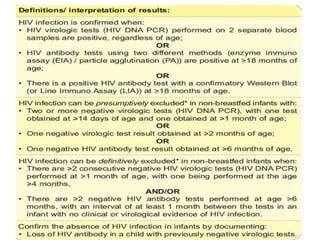
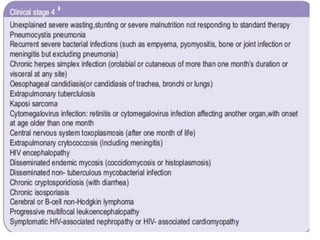
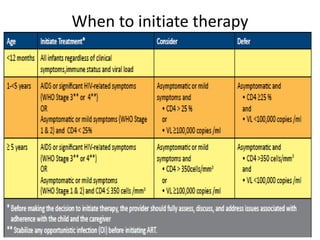
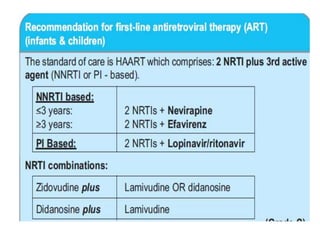
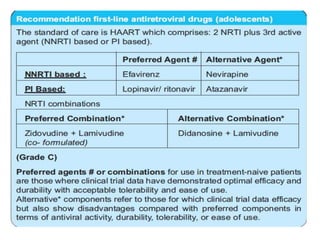
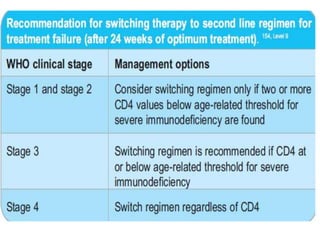
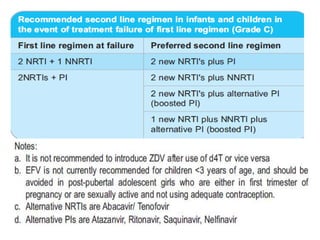
3) Clinical monitoring of perinatally exposed infants includes growth, development, and screening for opportunistic infections. HIV testing is done via PCR and serology. Antiretroviral therapy aims to suppress viral load and improve CD4 counts.