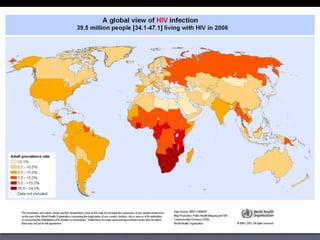
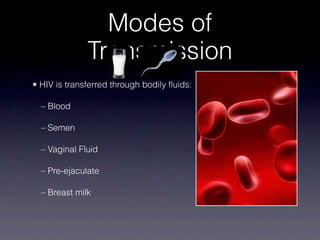
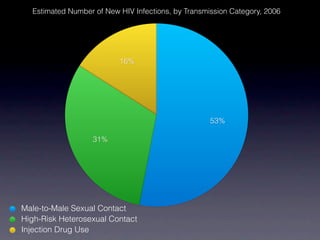
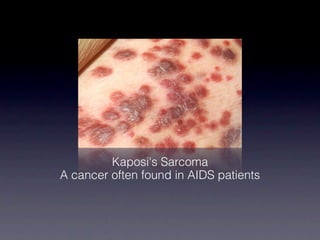
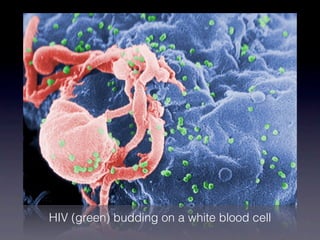
HIV attacks and kills helper T cells, weakening the immune system and leaving the body vulnerable to opportunistic infections. HIV is transmitted through bodily fluids and can develop into AIDS if not treated, as defined by a low white blood cell count. While symptoms of HIV may include fever and fatigue, diagnosis requires testing since symptoms are not reliable indicators. Prevention methods include abstinence, condom use, monogamy, needle safety, and treatment to prevent mother-to-child transmission.