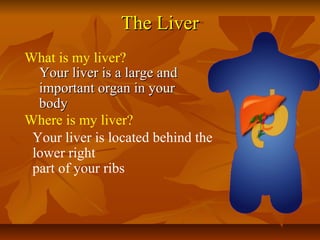
The document discusses various risk behaviors that can lead to diseases like AIDS, hepatitis, and syphilis. It identifies unprotected sex, sharing needles, lack of awareness, and unsafe blood transfusions as some of the main risk behaviors. The key diseases highlighted are HIV/AIDS, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. Prevention methods discussed include vaccination, safe sex practices like condom use, avoiding sharing personal items, and ensuring safe blood transfusions. The document emphasizes spreading awareness about risk behaviors and prevention.