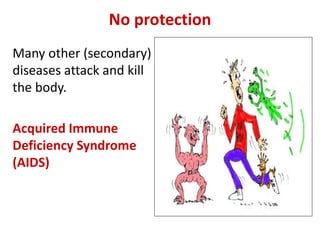
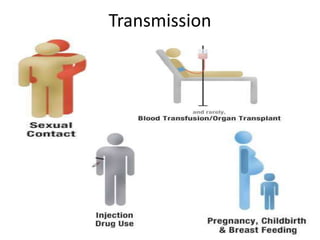
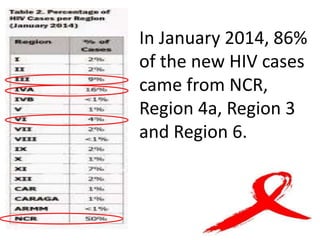
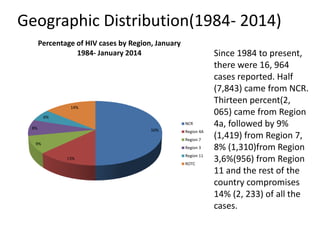
The document discusses HIV/AIDS, how HIV attacks and weakens the immune system, the progression to AIDS, signs and symptoms, transmission, risk behaviors, statistics on cases in the Philippines, and prevention strategies. HIV infects and destroys CD4 cells, progressively destroying the immune system and leaving the body vulnerable to opportunistic infections. Without treatment, HIV ultimately develops into AIDS. The A-B-C-D-E method is described as the primary prevention strategy.