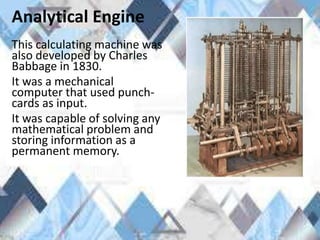
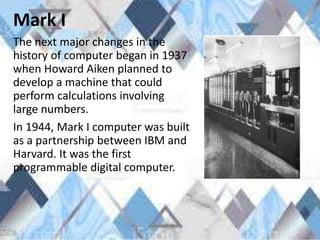
The document summarizes the history of computers from ancient counting devices like the abacus to modern computers. It describes the evolution from early mechanical computers invented by Pascal and Leibniz to electronic computers like the Analytical Engine and Mark 1. It then outlines the five generations of computers, defining each generation by the integrated circuitry and describing examples from each era, from transistor computers to modern devices using artificial intelligence.