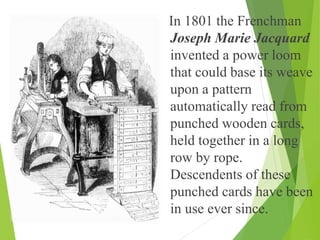
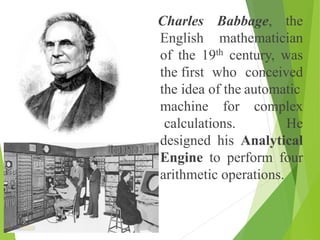
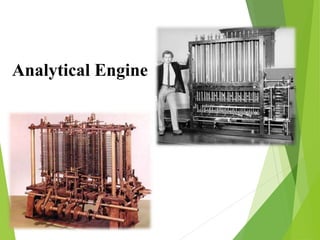
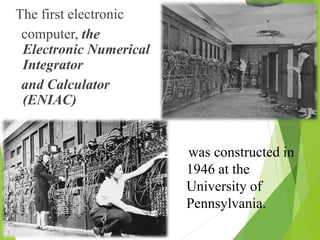
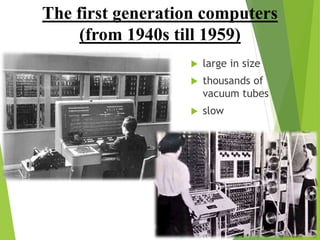
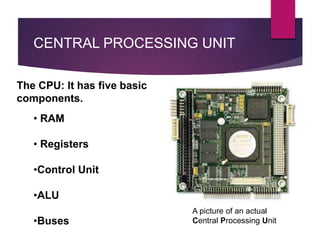
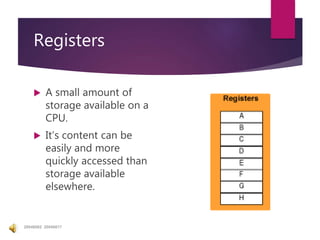
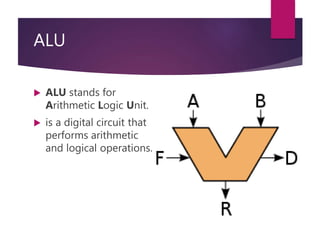
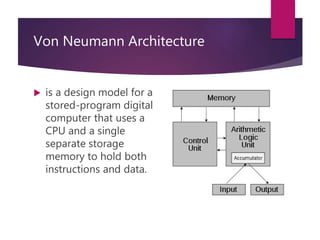
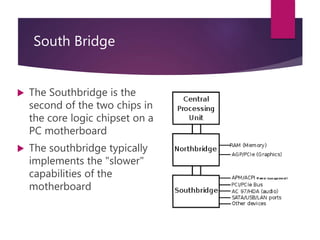
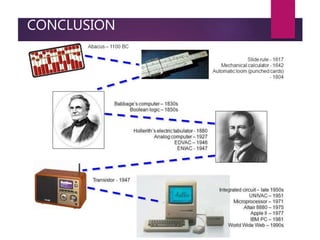
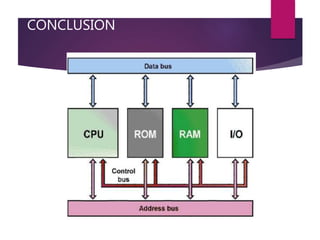
The document traces the history of computing from the term 'computer' as a job title for human calculators to the development of early mechanical and electronic devices. It discusses key inventions like logarithms, the slide rule, and various calculators, leading to Charles Babbage's analytical engine, which laid the groundwork for modern computing. Additionally, it outlines the evolution of computer generations, detailing advancements in technology, CPU architecture, and storage, illustrating the ongoing transformation of computing capabilities.