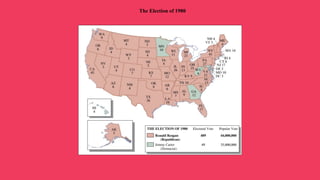
Ronald Reagan was a former actor and governor of California who ran unsuccessfully for president in 1976 before winning in 1980. His presidency ushered in a conservative realignment as evangelical Christians increasingly backed Republican policies. Reagan cut taxes and increased defense spending, which contributed to large budget deficits. His foreign policy aggressively confronted Soviet expansionism and he met with Gorbachev to sign nuclear arms treaties, helping end the Cold War. However, social programs were reduced and homelessness increased during his terms.