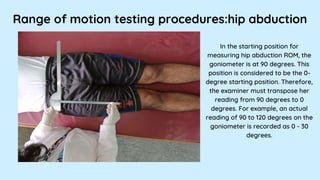
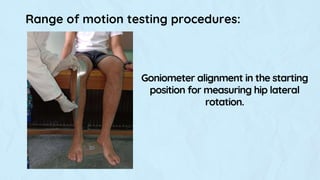
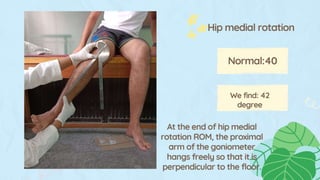
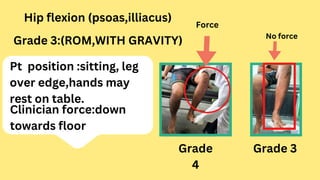
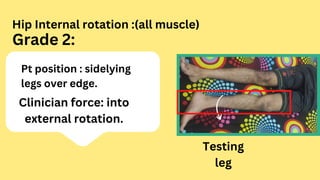
This document provides instructions for assessing range of motion and muscle strength of the hip joint. It describes patient positioning and examiner techniques for range of motion testing of hip flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and internal and external rotation. It also explains how to grade hip muscle strength on the Oxford Scale from grades 0 to 5 during motions like extension, flexion, abduction, and adduction. References for more information on goniometry and pelvic floor physical therapy are provided at the end.