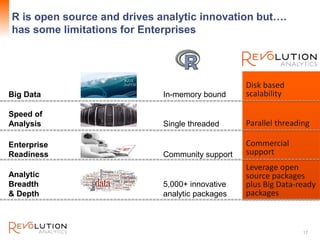
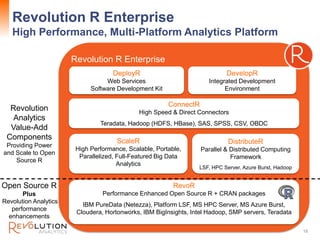
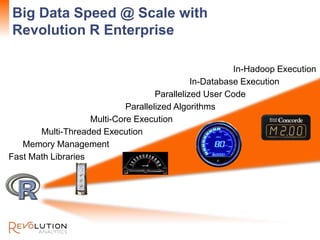
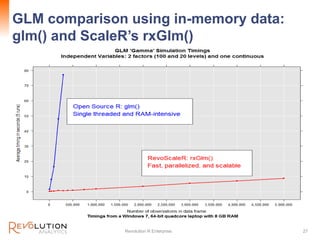
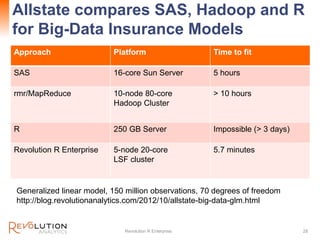
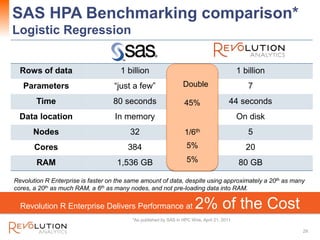
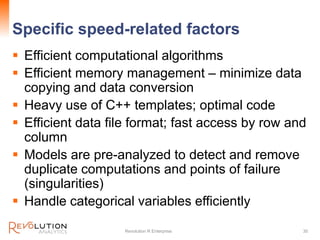
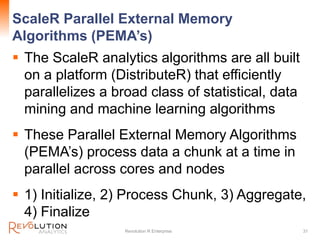
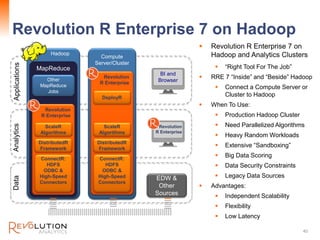
The document presents an overview of high-performance predictive analytics using R and Hadoop, emphasizing their integration for big data analysis. It introduces Revolution R Enterprise, a scalable platform that enhances R's capabilities for big data processing, while maintaining ease of use and performance. The presentation highlights the significant advantages of this integration in areas like fraud detection, mortgage default prediction, and data visualization.