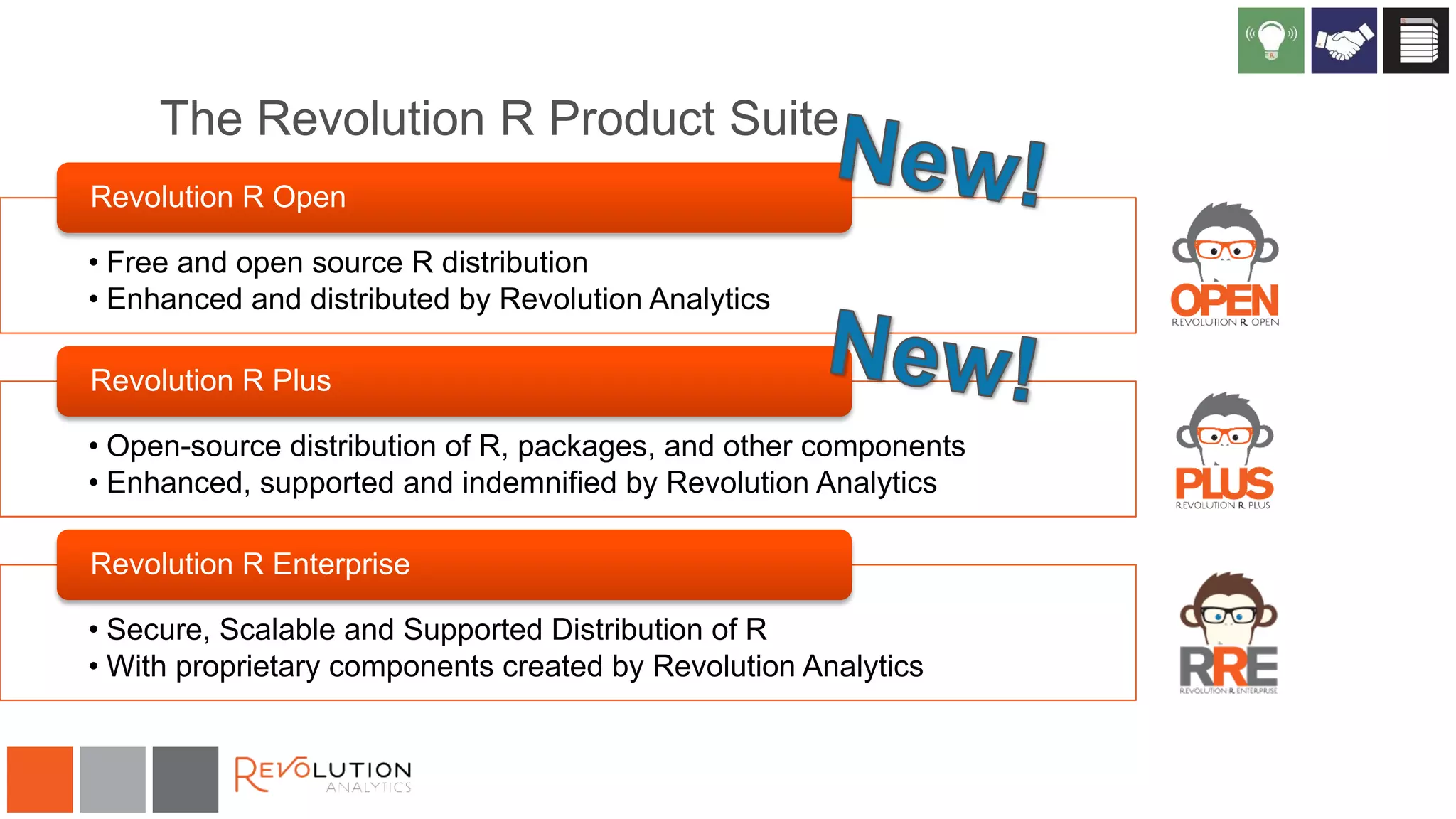
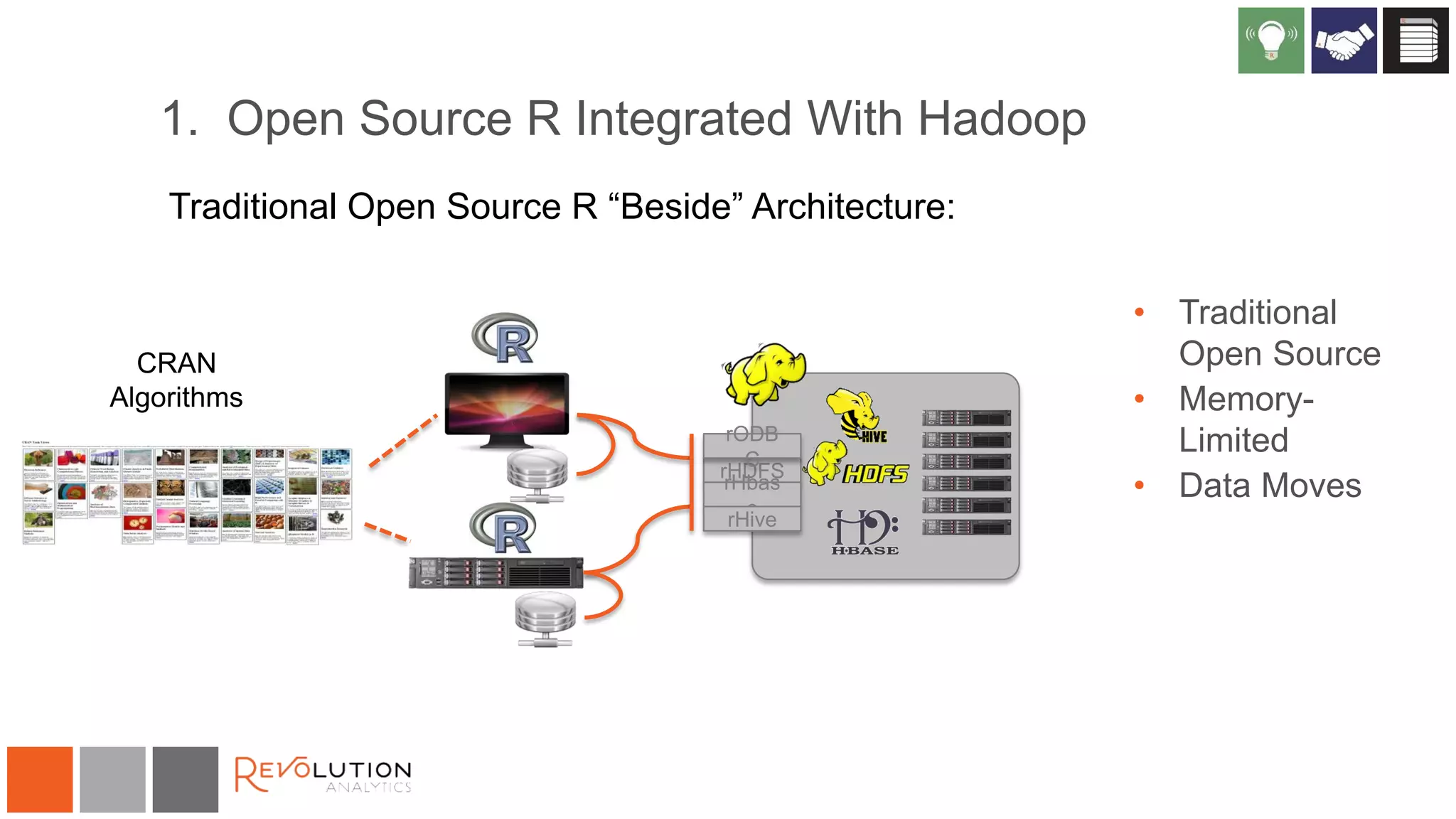
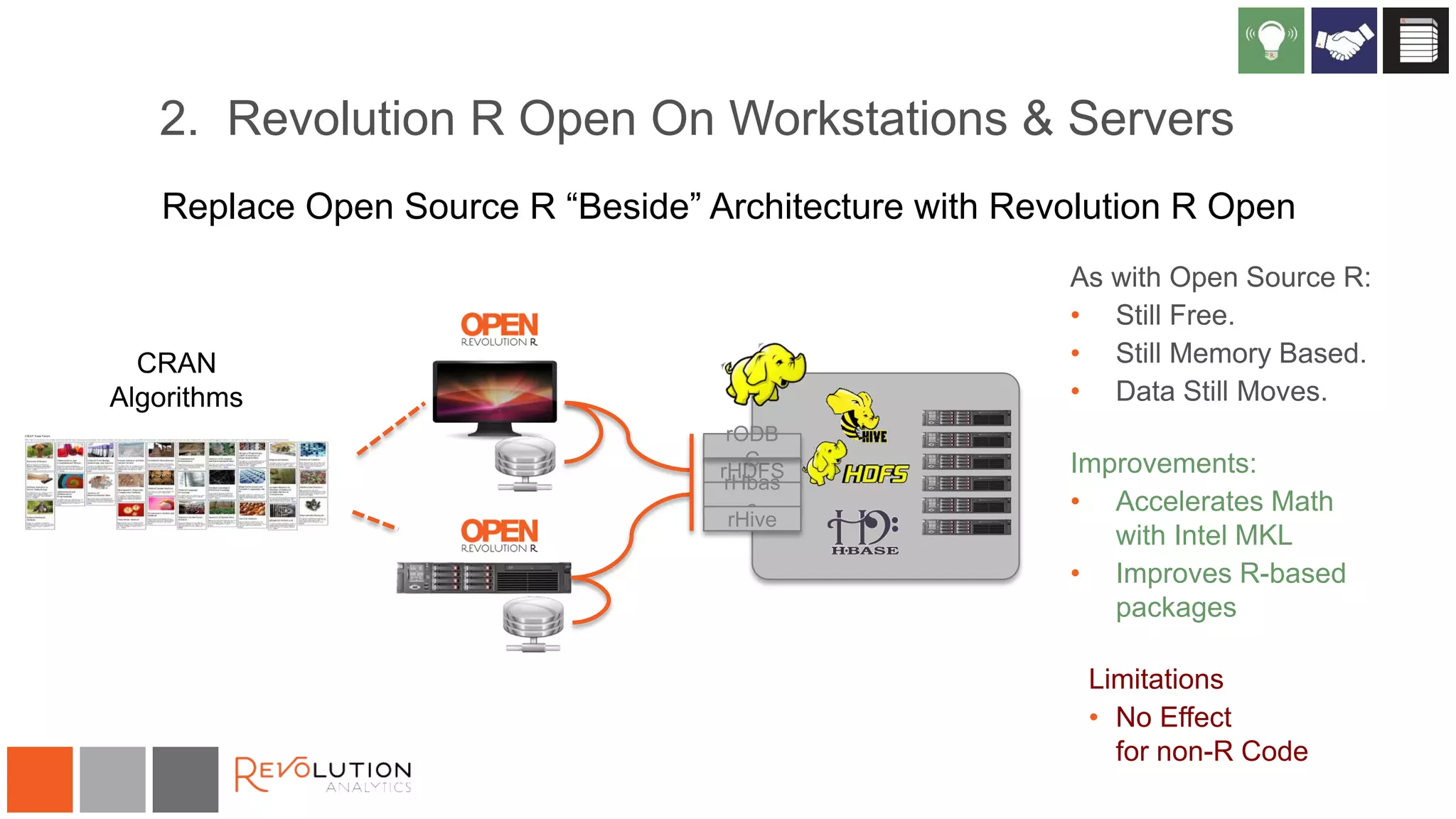
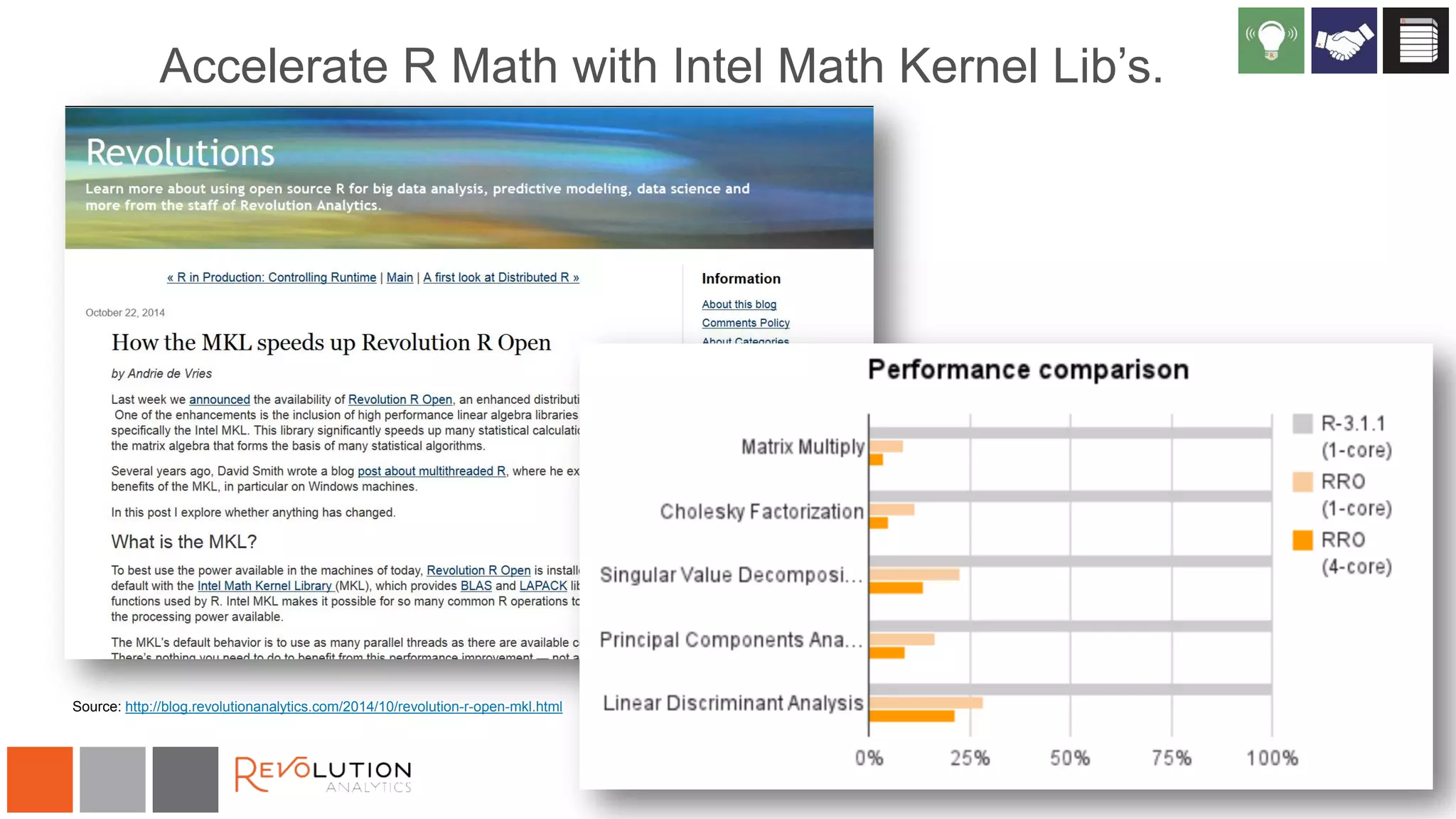
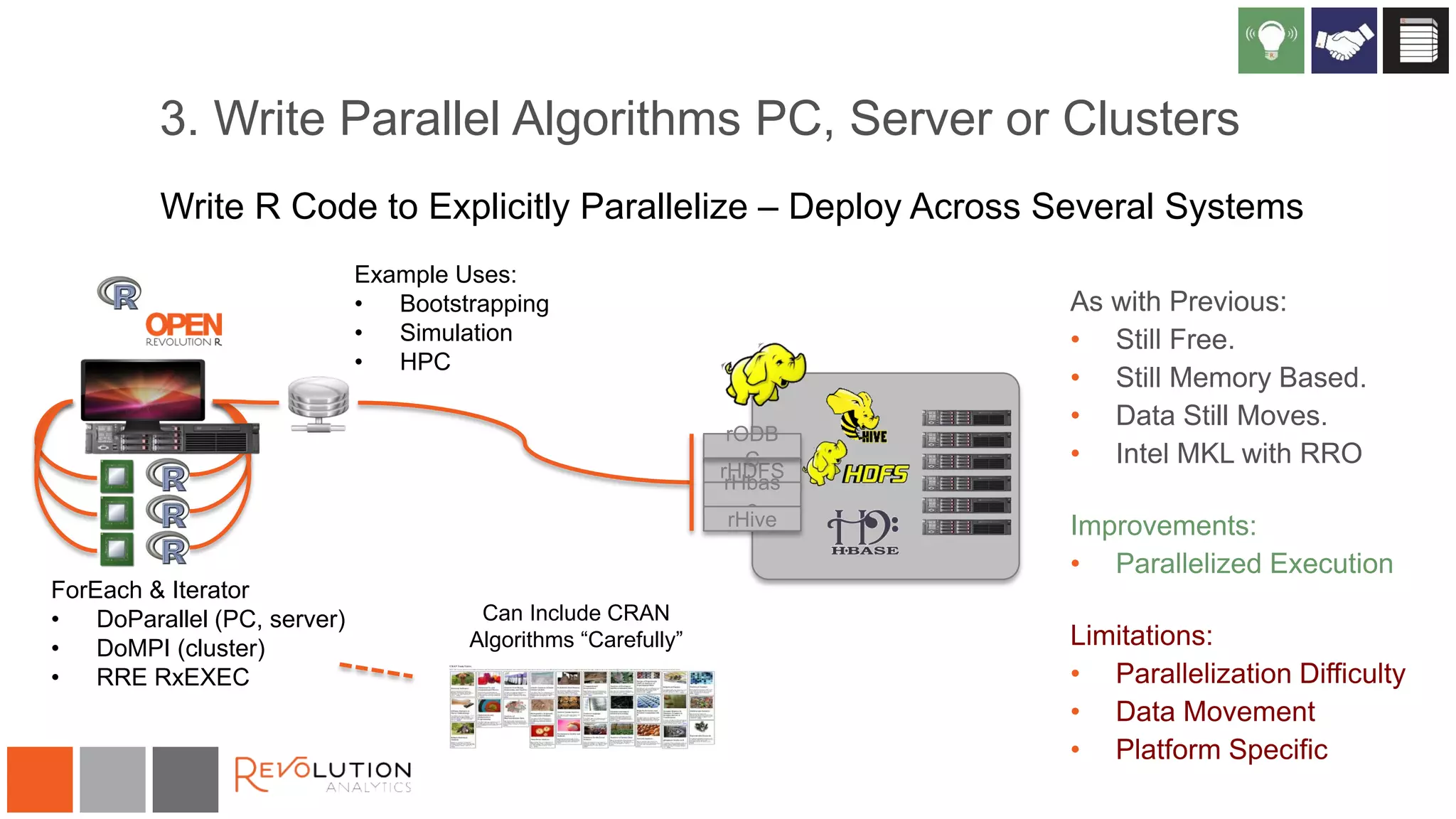
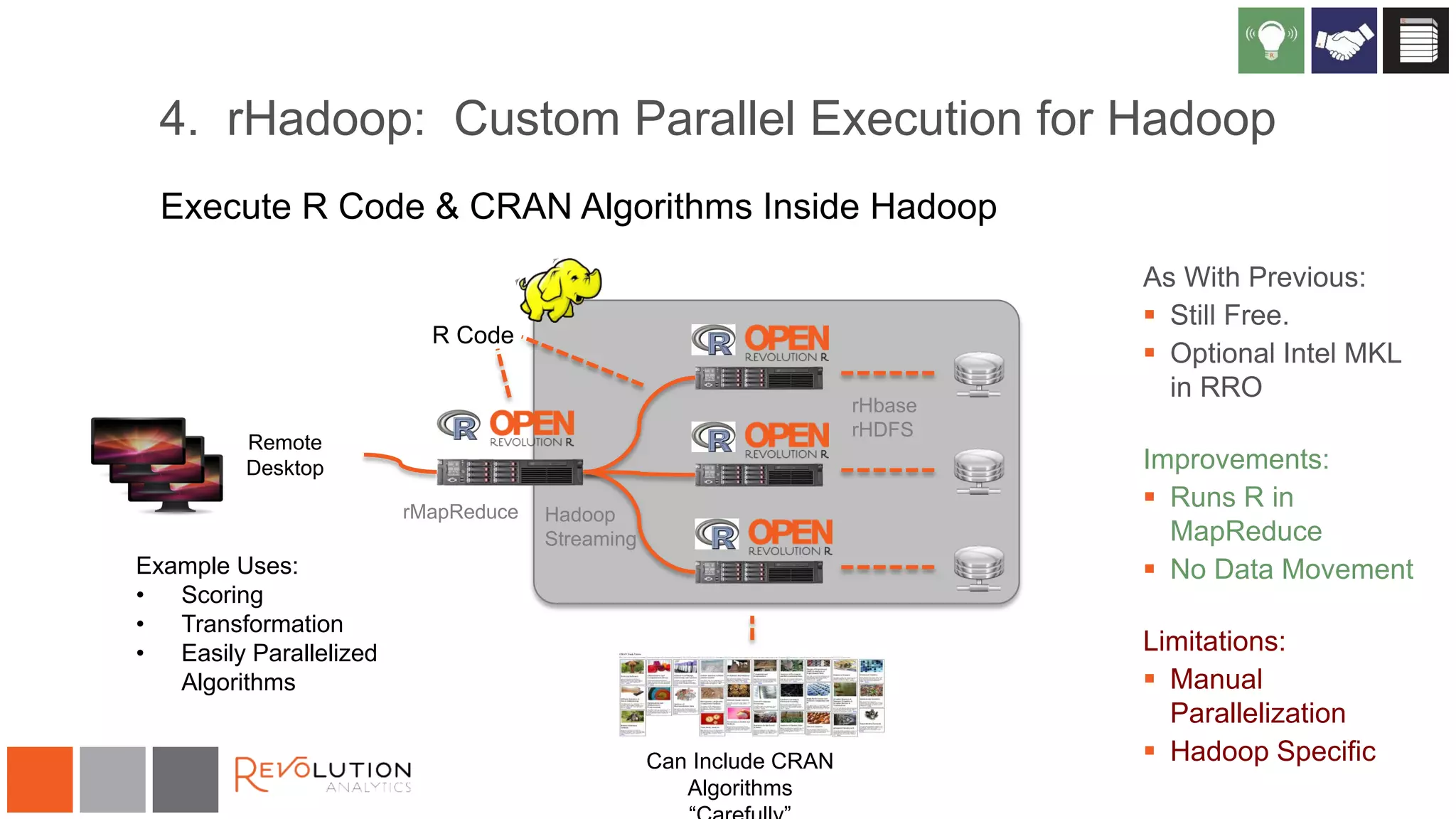
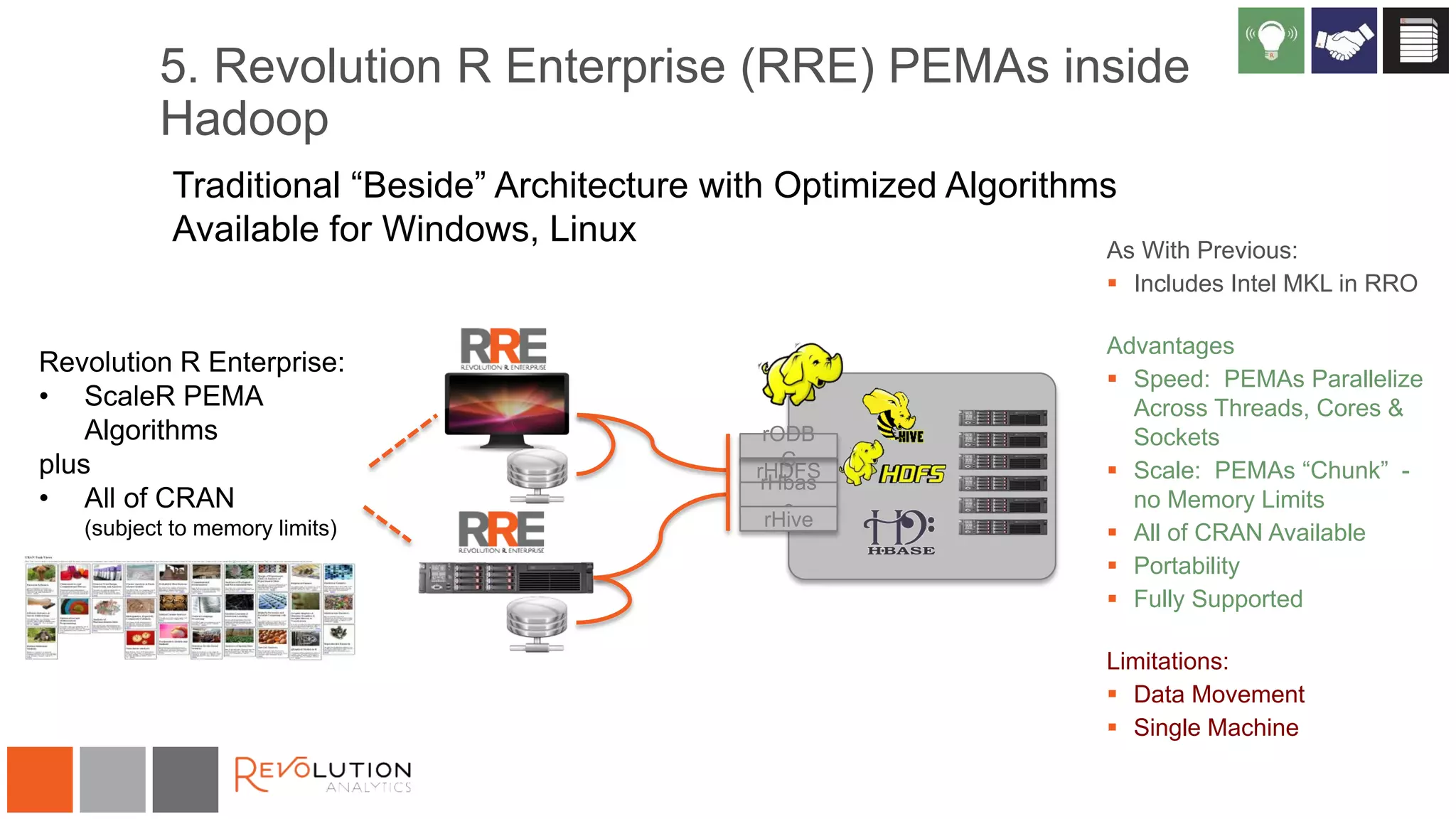
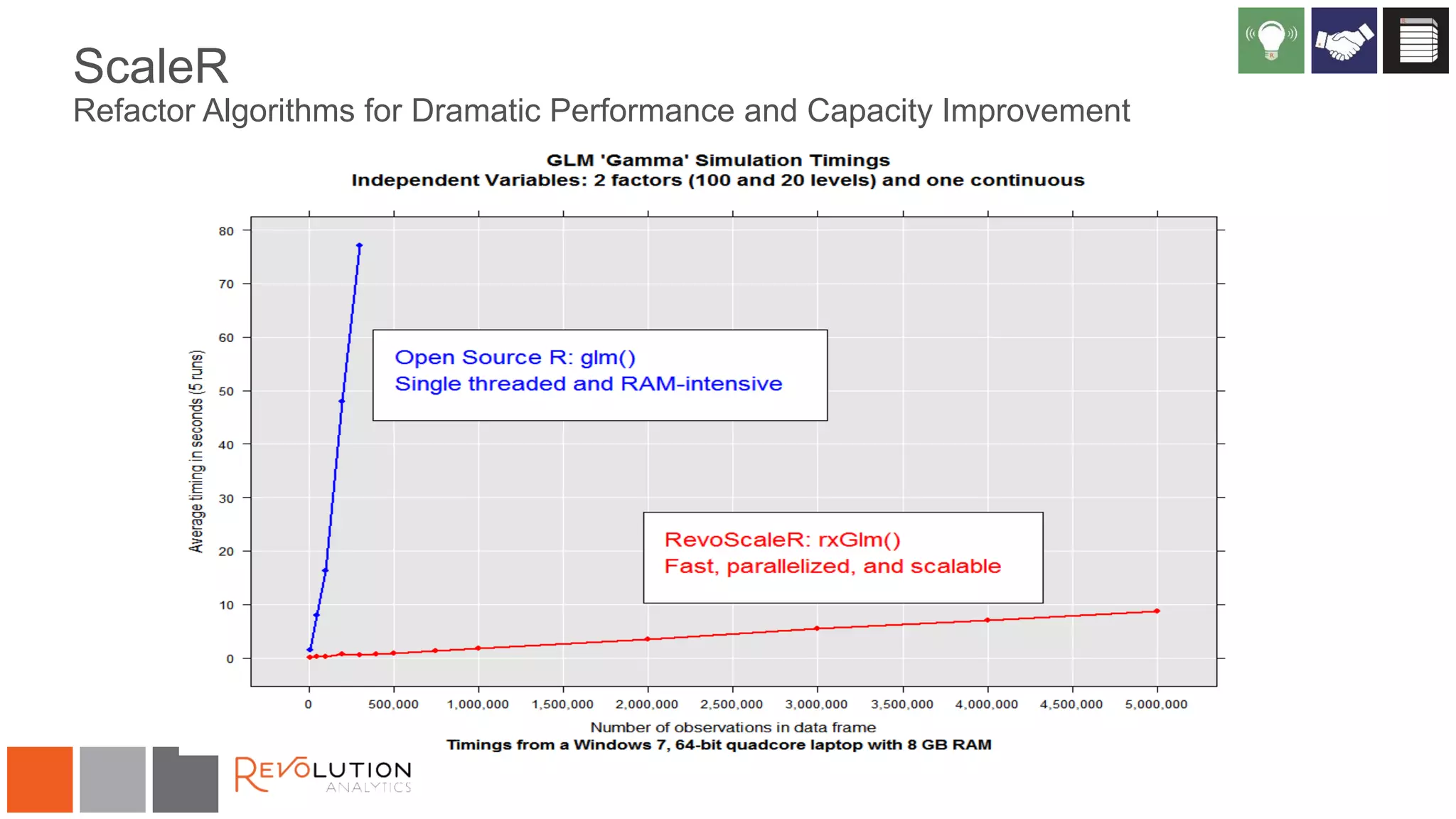
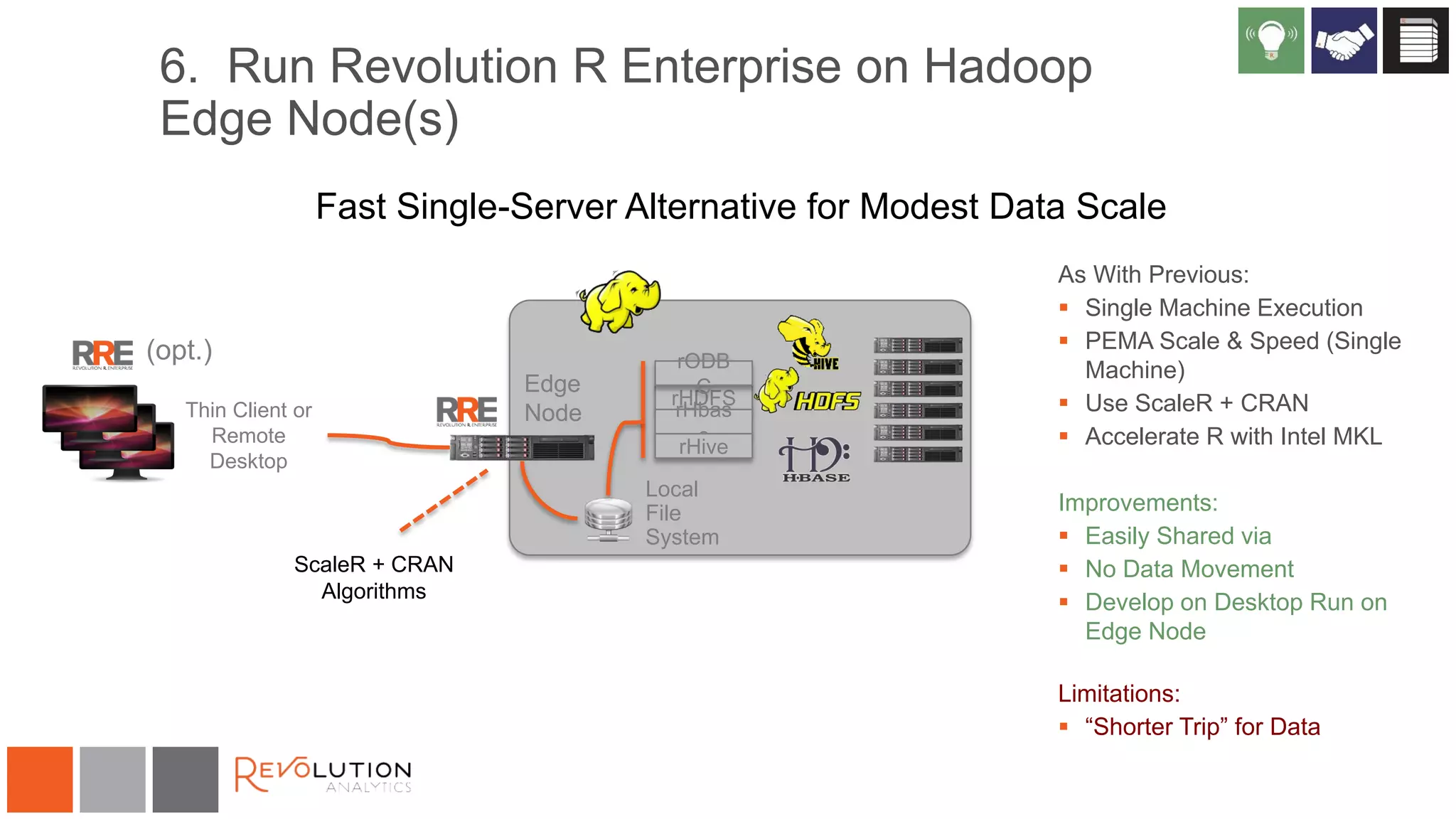
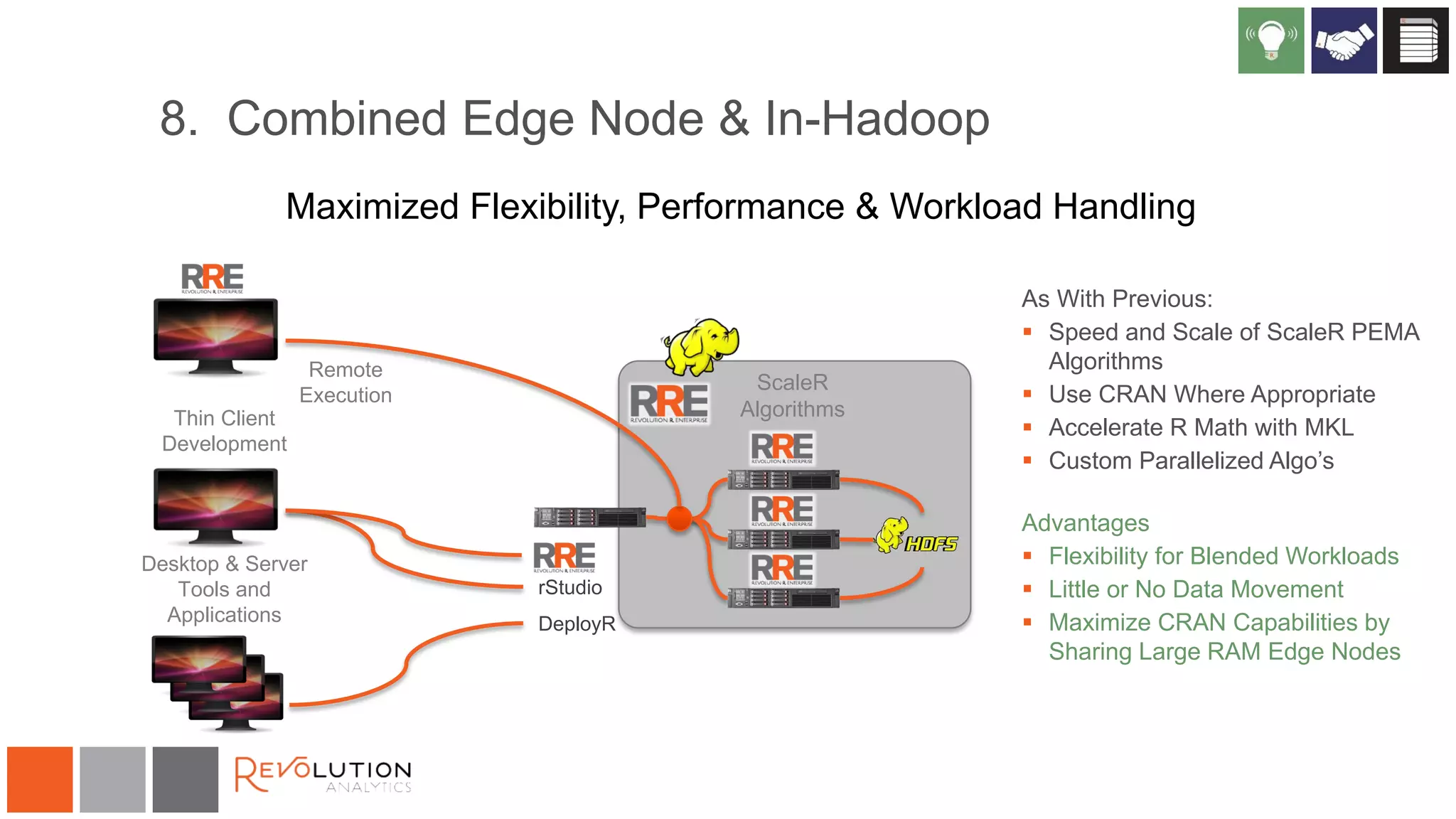
The document discusses the integration of R and Hadoop, outlining various architectural options and the use of Revolution Analytics' products to enhance analytics capabilities. It presents alternatives for integrating R with Hadoop, including open-source and commercial solutions, and emphasizes the advantages of using Revolution R Enterprise for scalable analytics. Additionally, it highlights key considerations for organizations when selecting analytical capabilities and future platform plans.