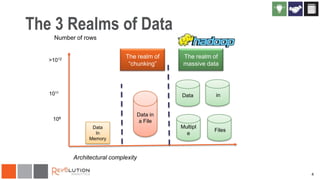
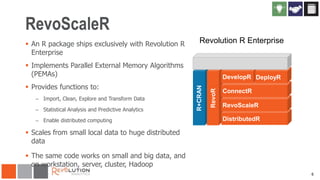
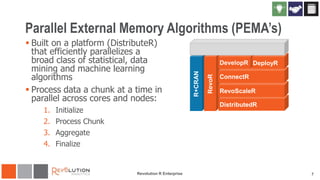
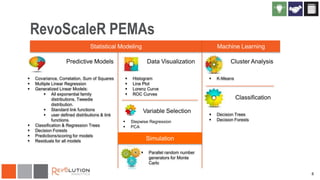
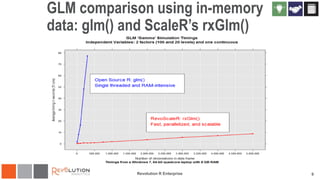
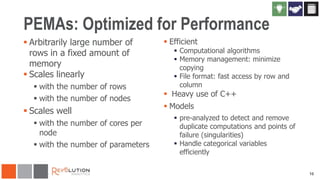
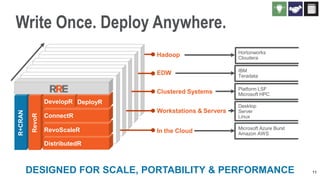
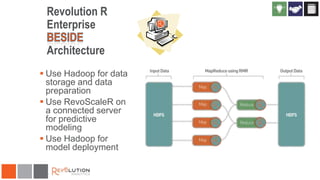
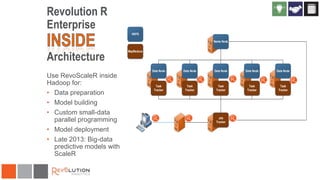
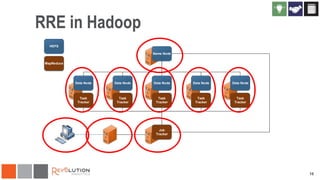
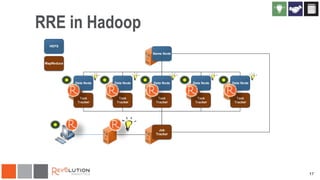
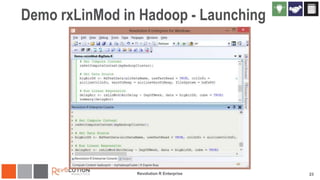
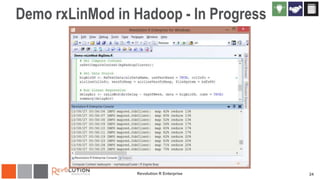
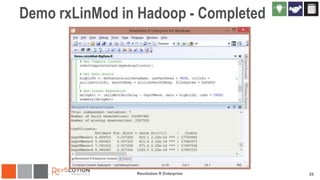
The document discusses the integration of Revoscaler with Hadoop for statistical computation, highlighting its capabilities for handling massive datasets and performing predictive modeling with parallel external memory algorithms. It outlines the architecture of Revolution R Enterprise, which facilitates data preparation, model building, and deployment, enabling users to efficiently scale their analyses from local to distributed environments. Sample code demonstrates how to implement statistical models both on local machines and within a Hadoop cluster.