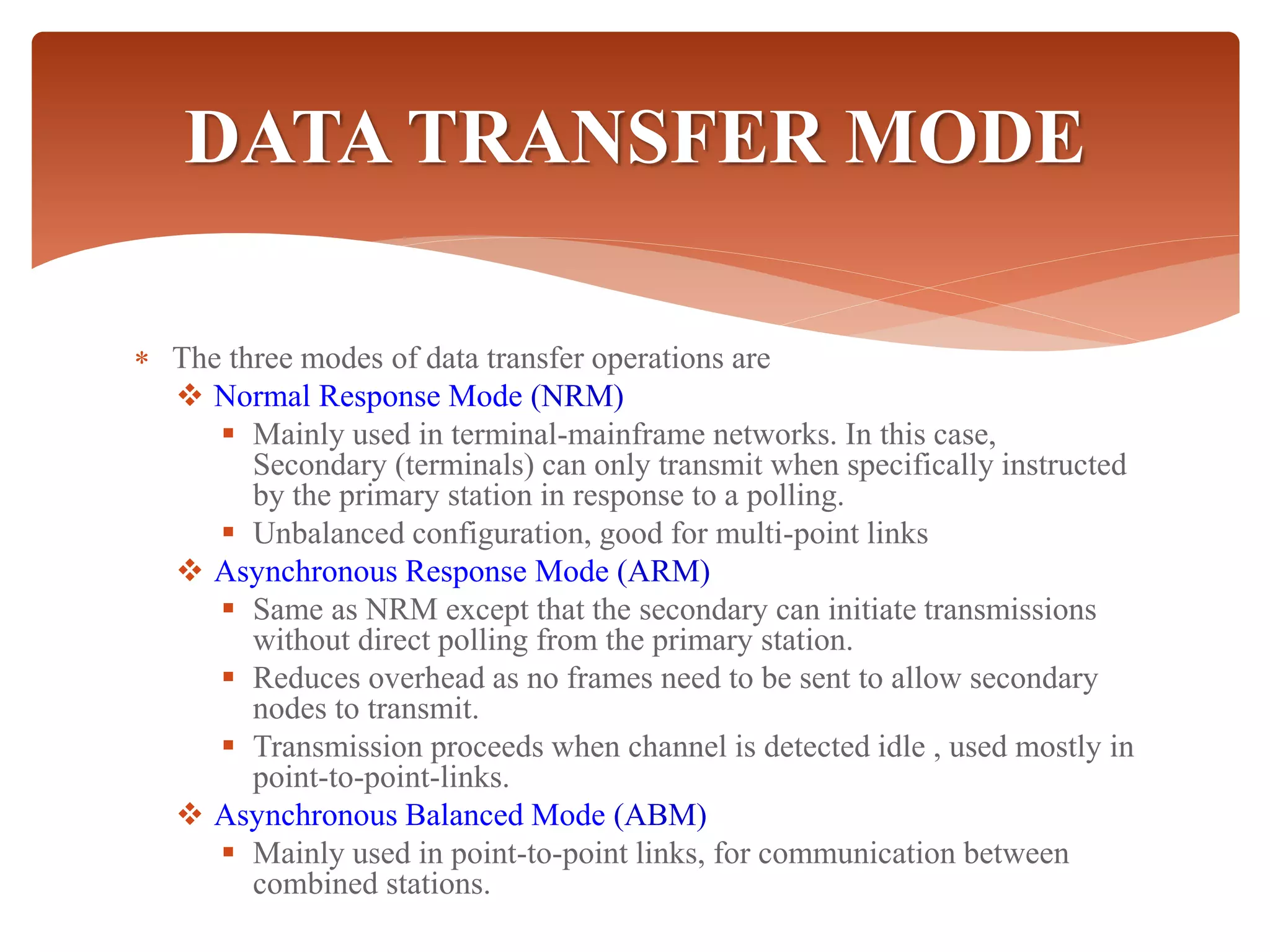
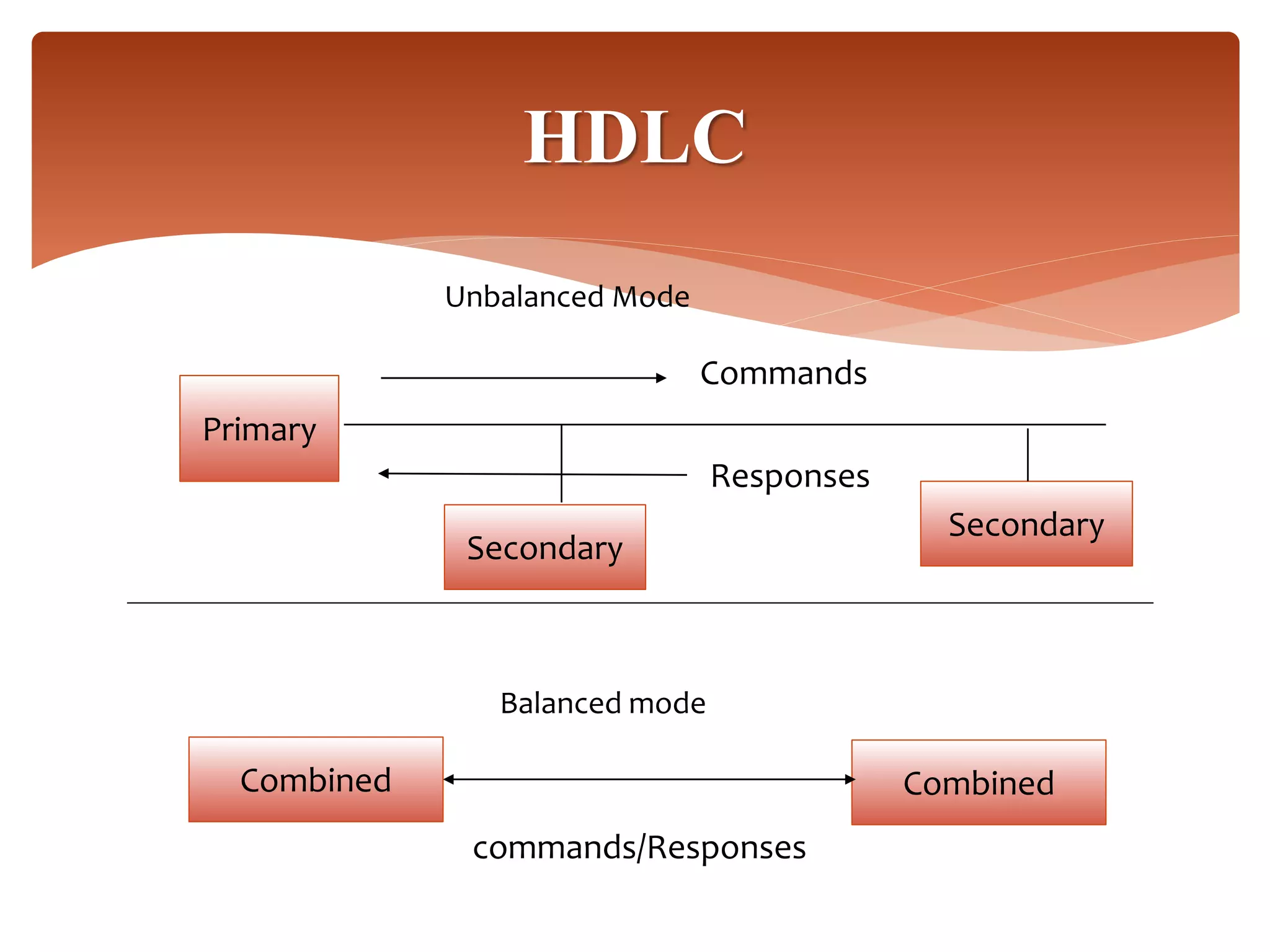
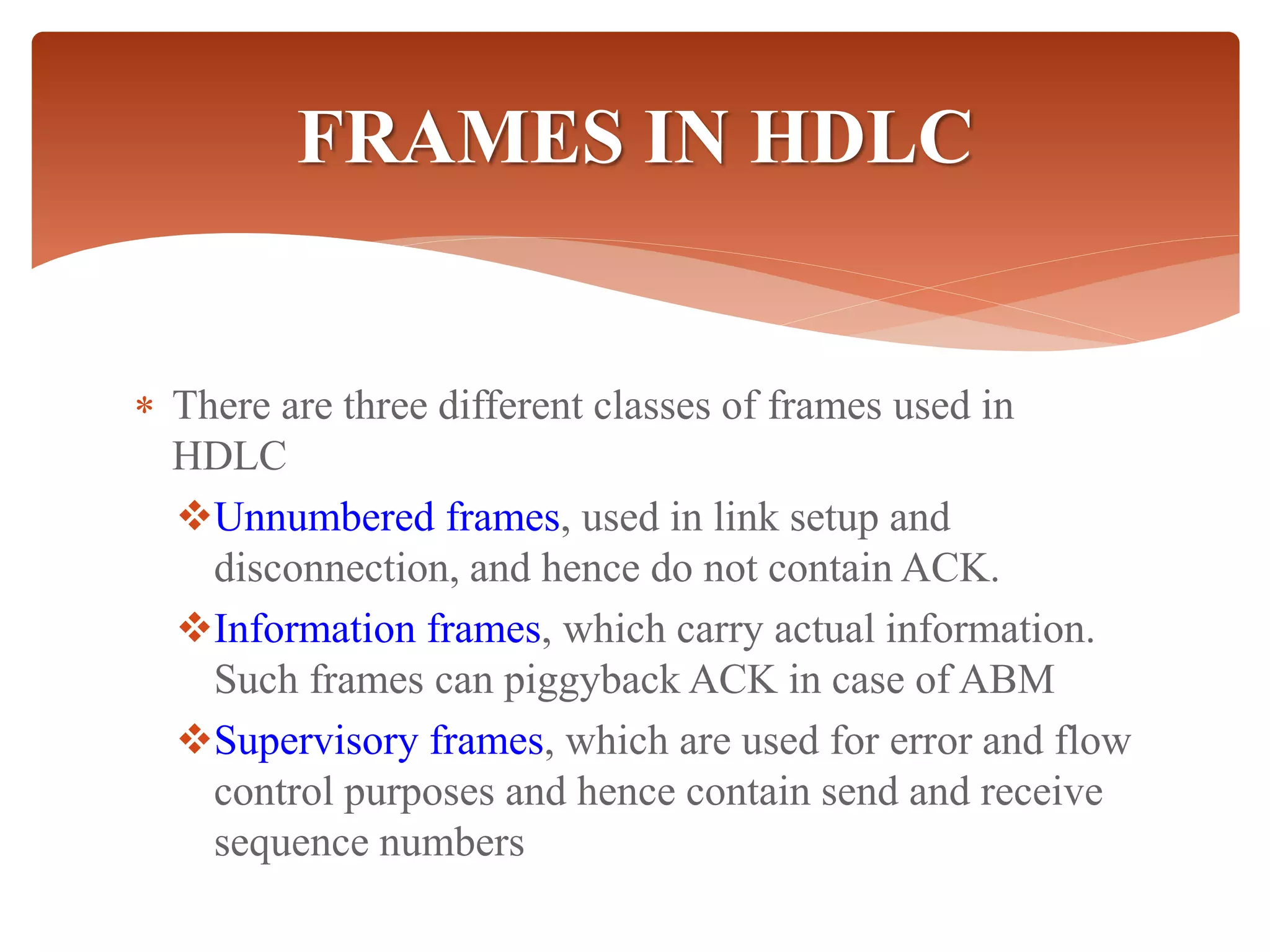
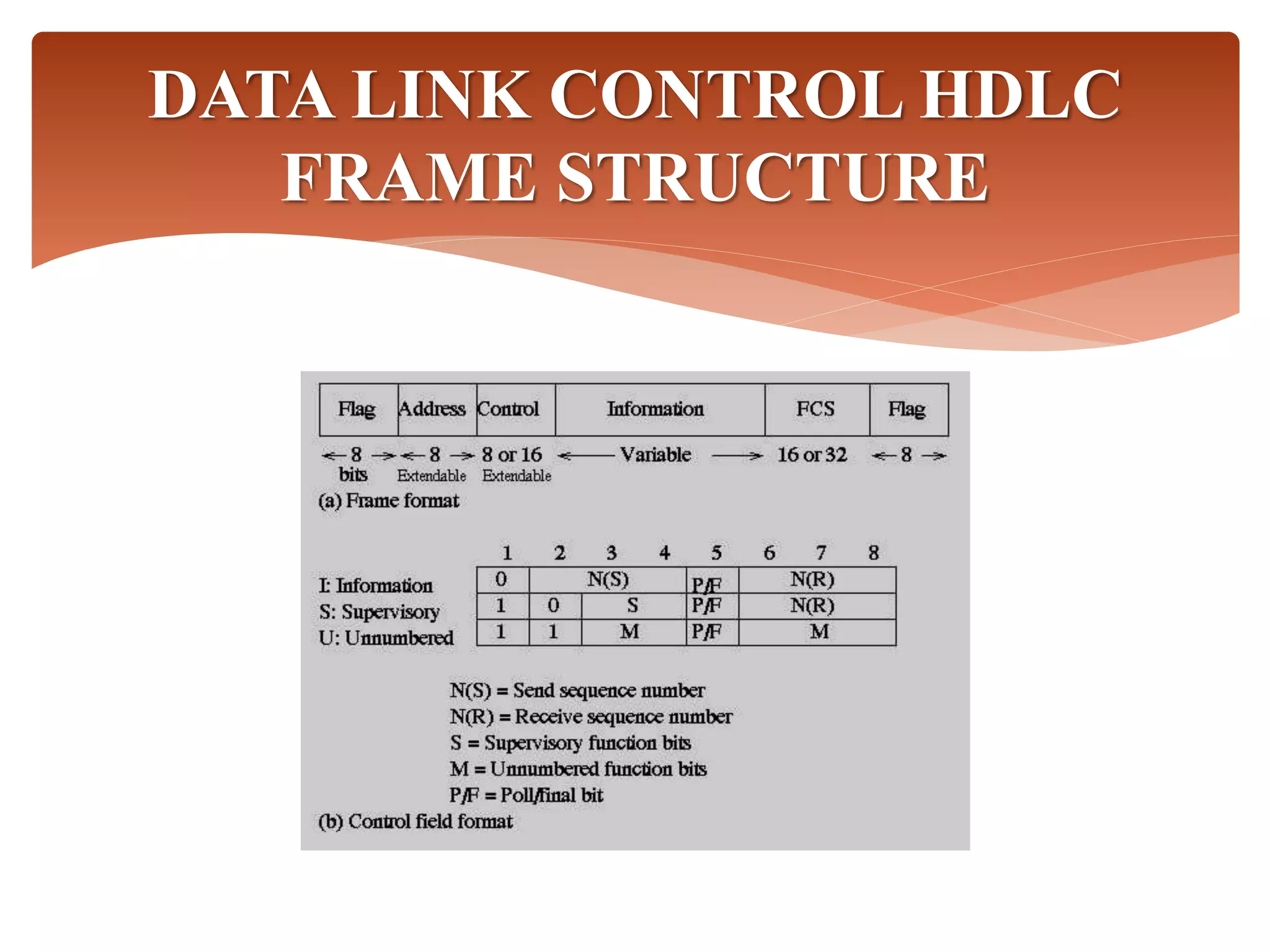
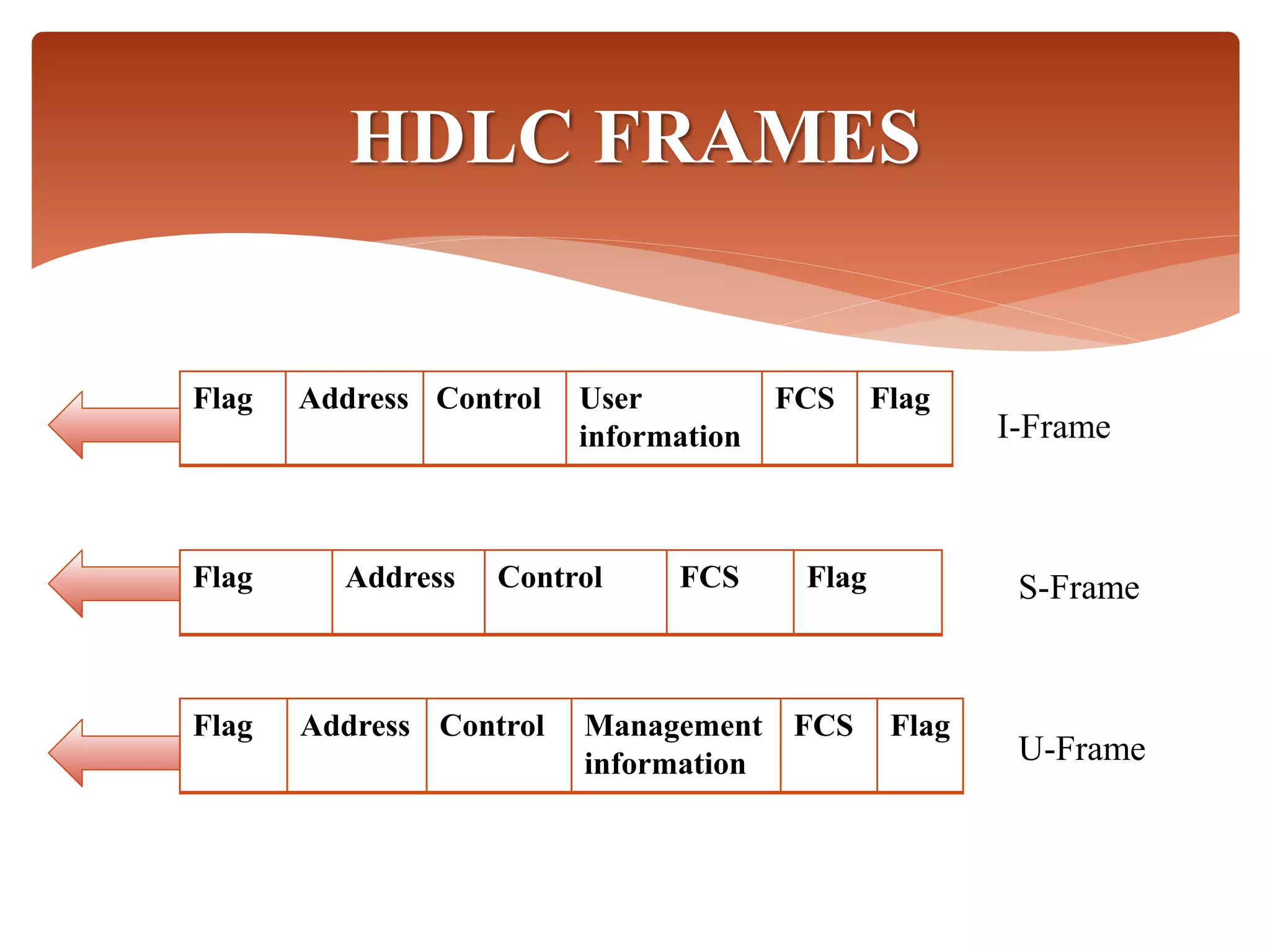
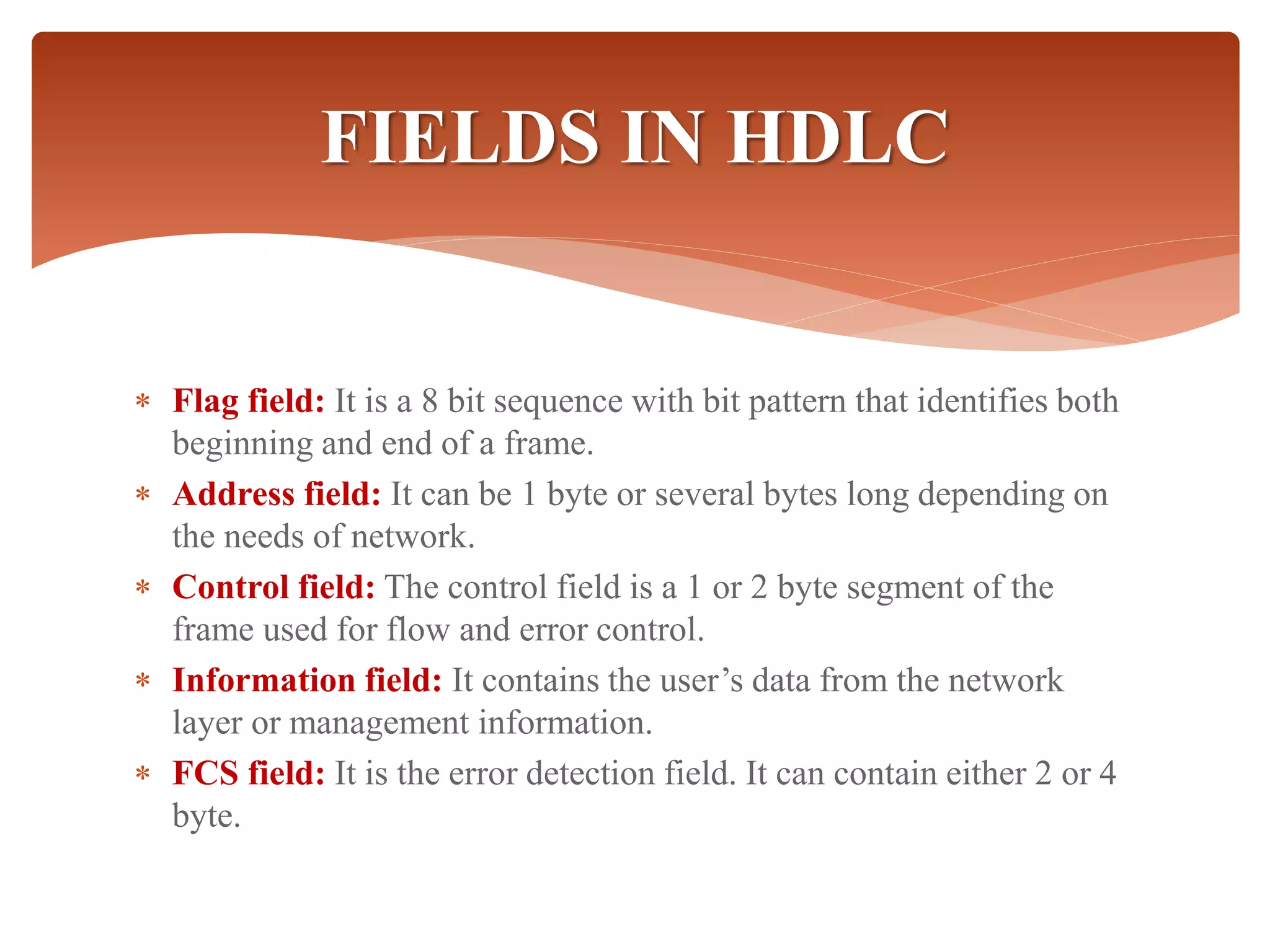
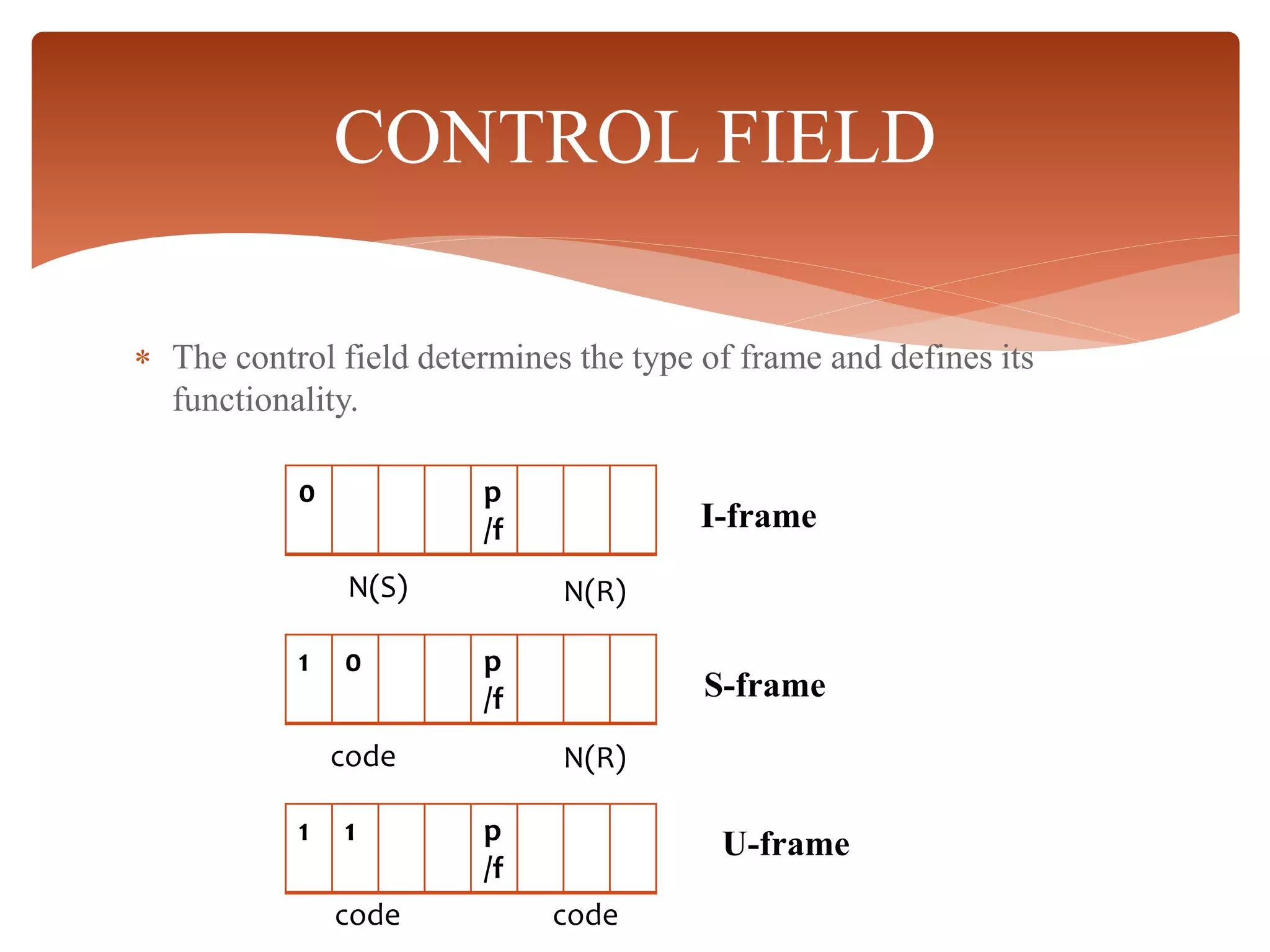
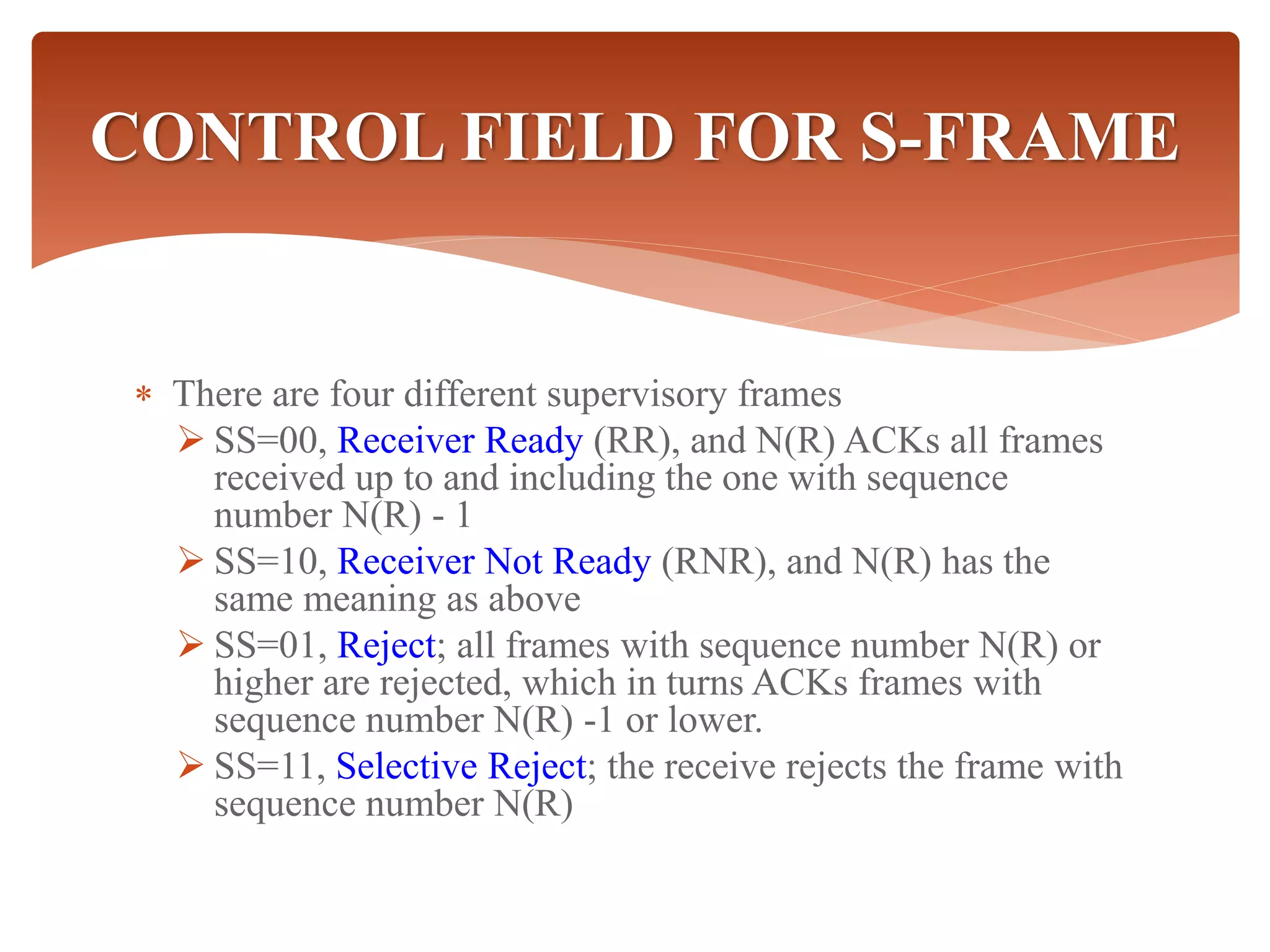
High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) is a protocol for point-to-point and multipoint communication, providing both connectionless and connection-oriented services through synchronous transmission in frame format. It features three types of stations (primary, secondary, and combined) and three modes of data transfer (normal response, asynchronous response, and asynchronous balanced modes), along with three frame types (information, supervisory, and unnumbered). HDLC frames include various fields such as address, control, information, and frame check sequence (FCS) for error detection and control.