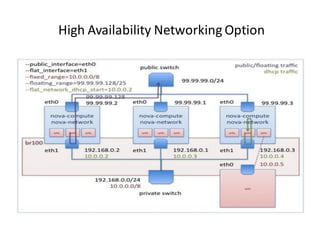
There are four main high availability networking options for OpenStack: 1) Using external hardware gateways to offload networking HA, 2) Configuring VMs with multi-NICs on separate networks for failover, 3) Enabling a 4-second failover between network hosts, and 4) Configuring each compute host to handle networking for its own VMs to eliminate single points of failure in networking hosts.