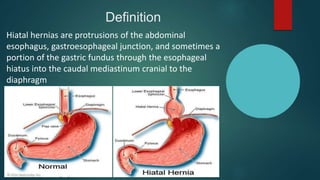
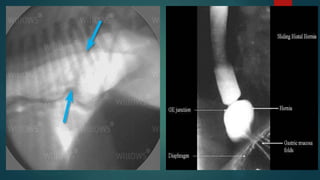
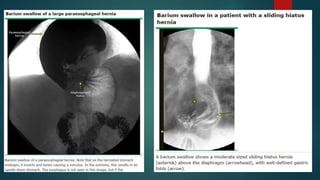
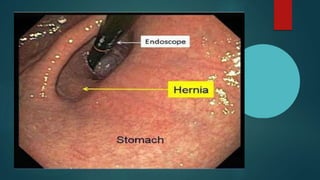
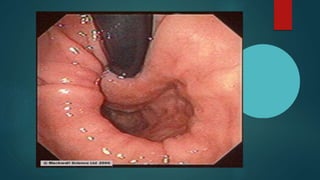
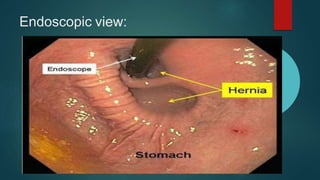
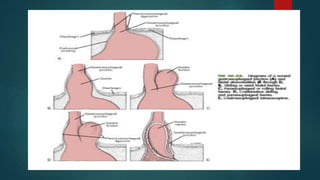
The document discusses hiatal hernia, which occurs when part of the stomach bulges through an opening in the diaphragm. It outlines the causes, symptoms, diagnosis through imaging and endoscopy, differential diagnosis, and treatment options including medication, surgery to repair the diaphragm and prevent reflux, and post-operative care. The prognosis is generally good if the hernia is repaired and complications like aspiration pneumonia are managed.