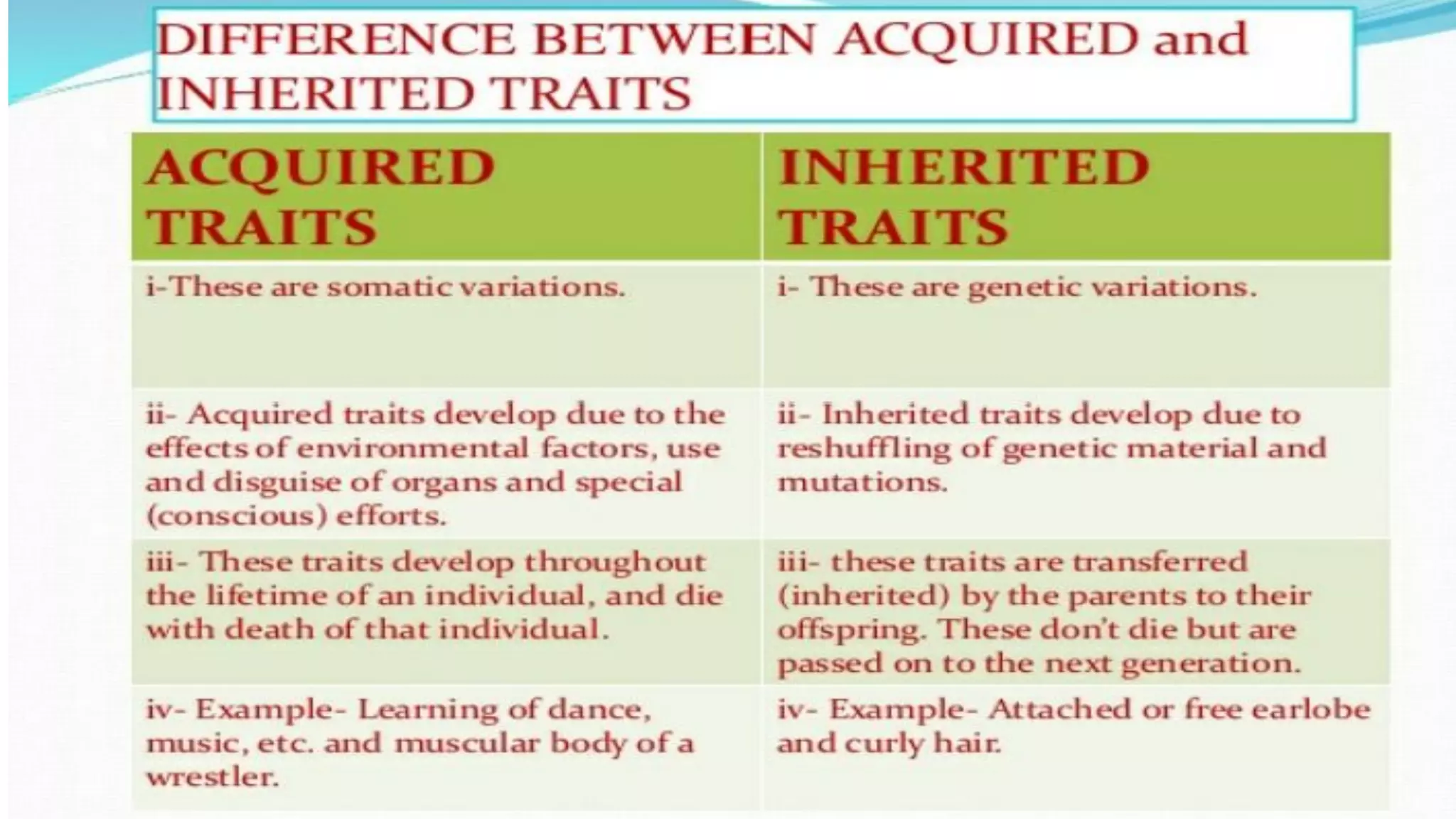
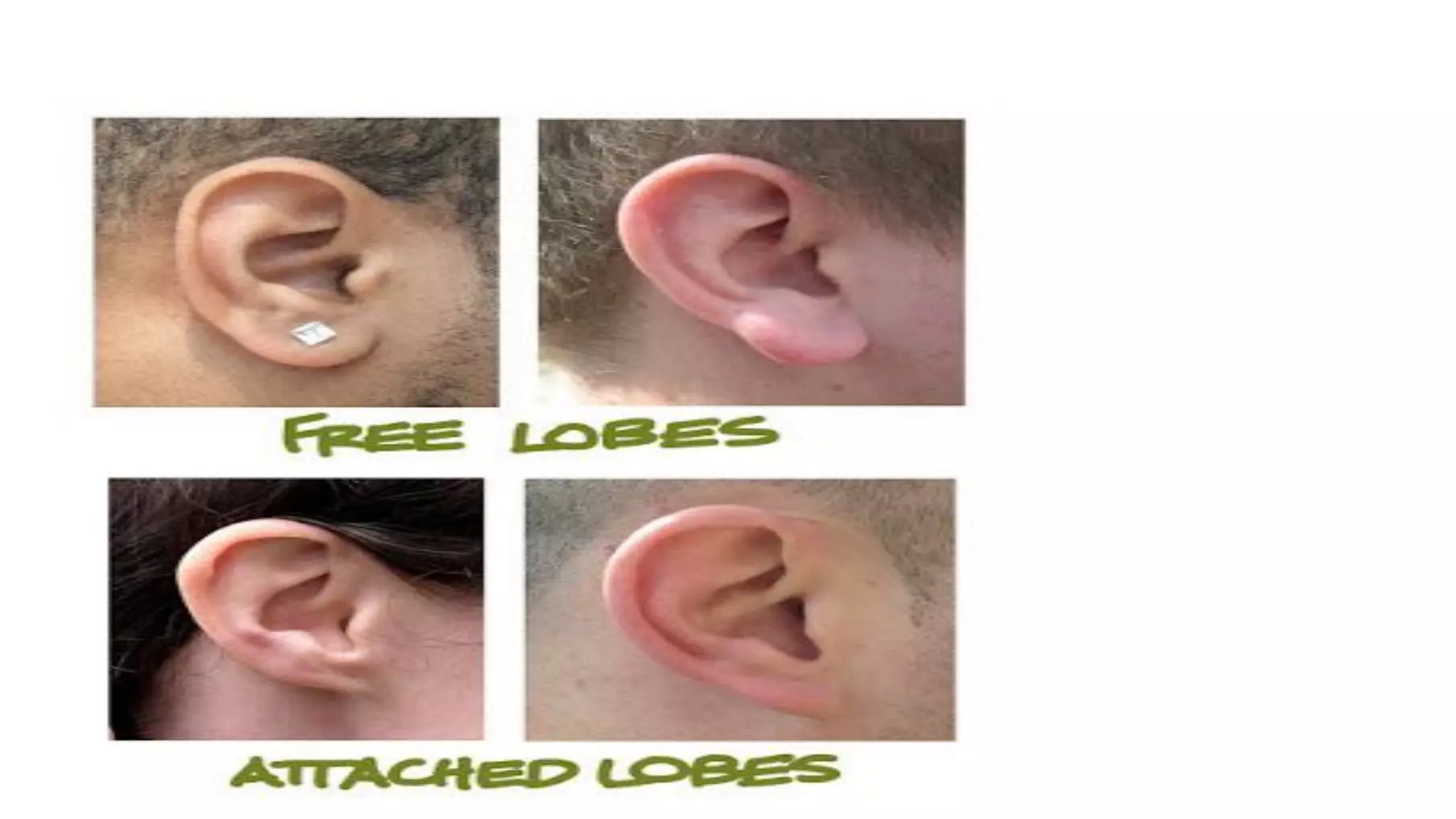
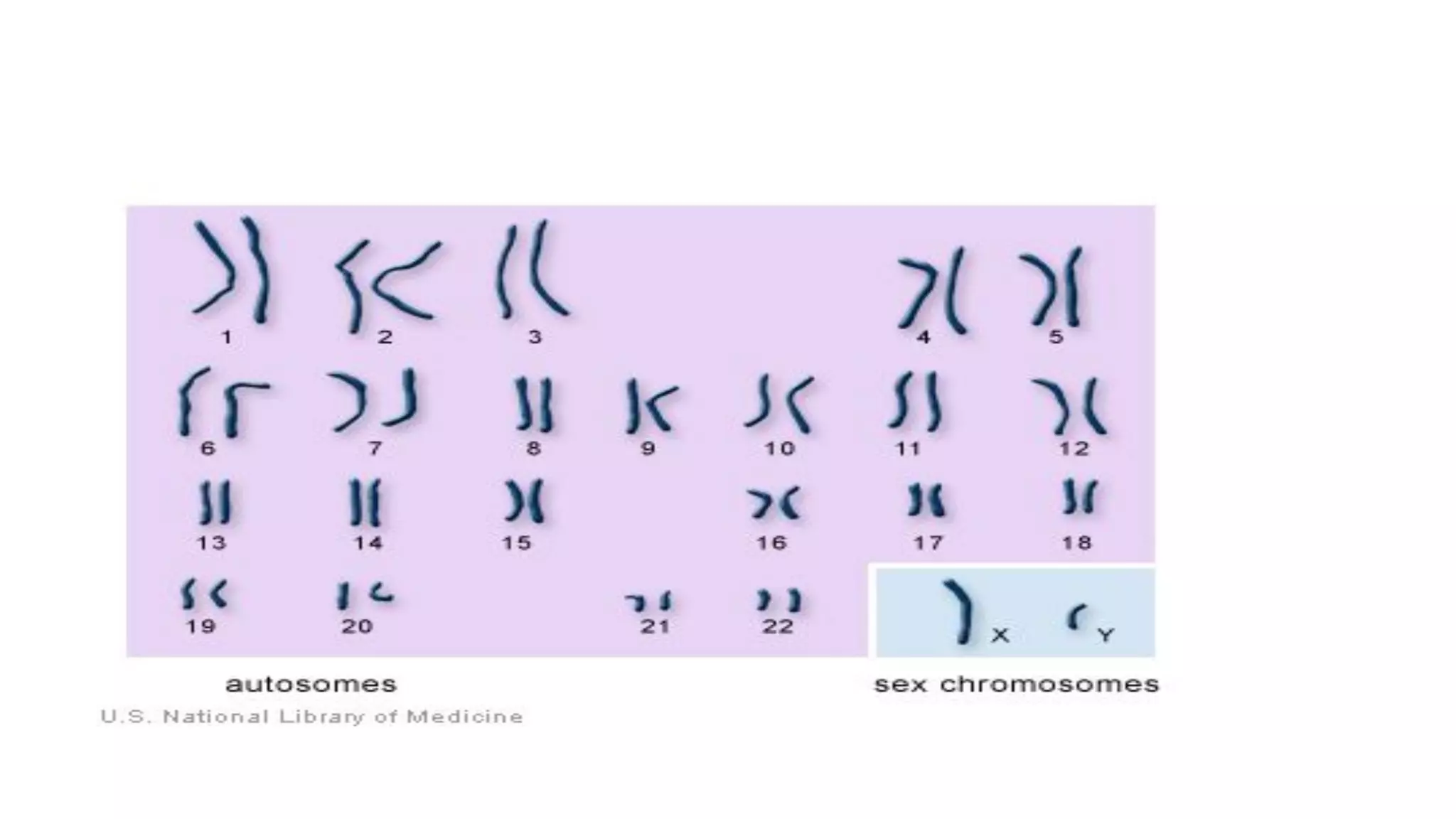
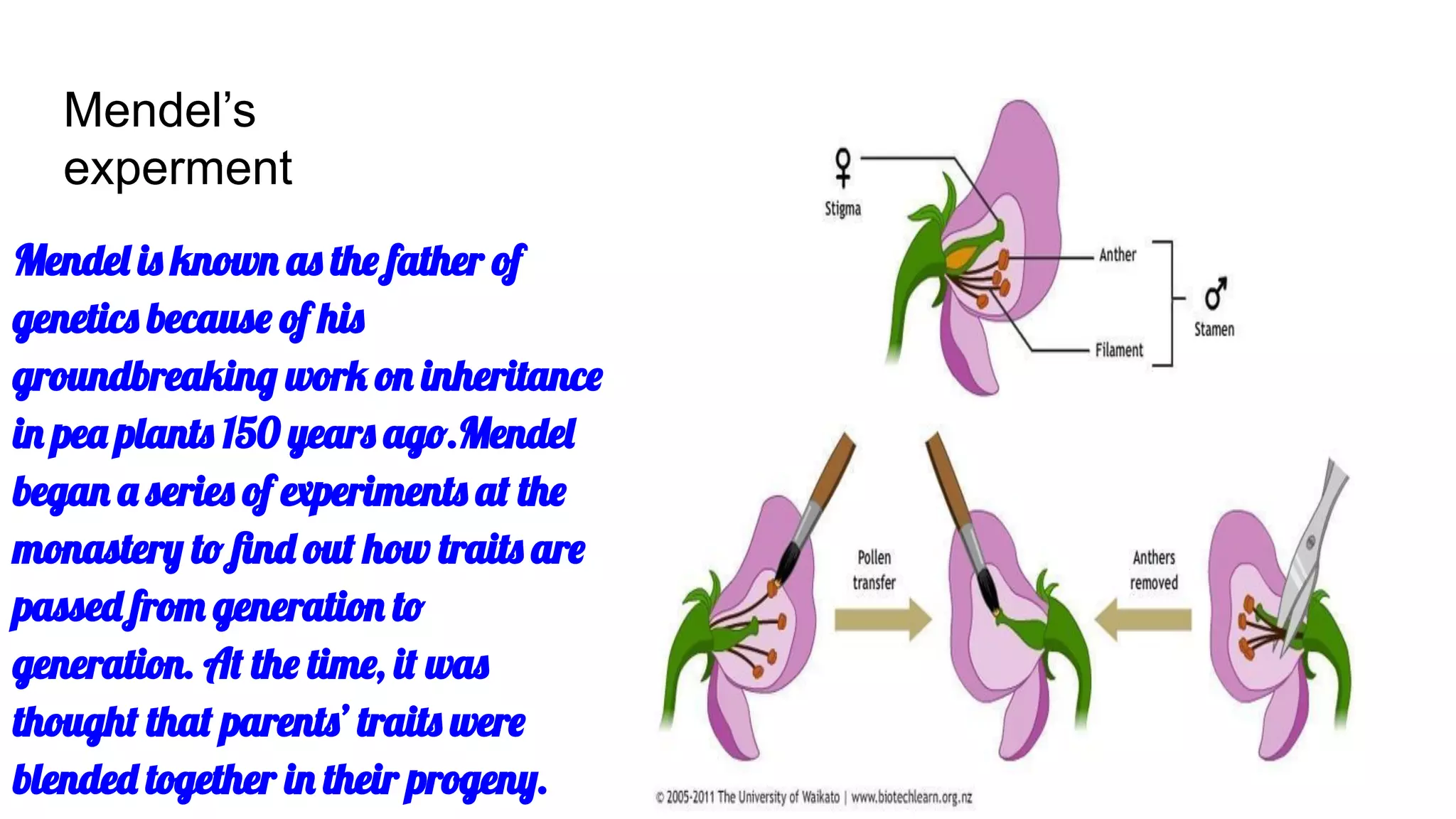
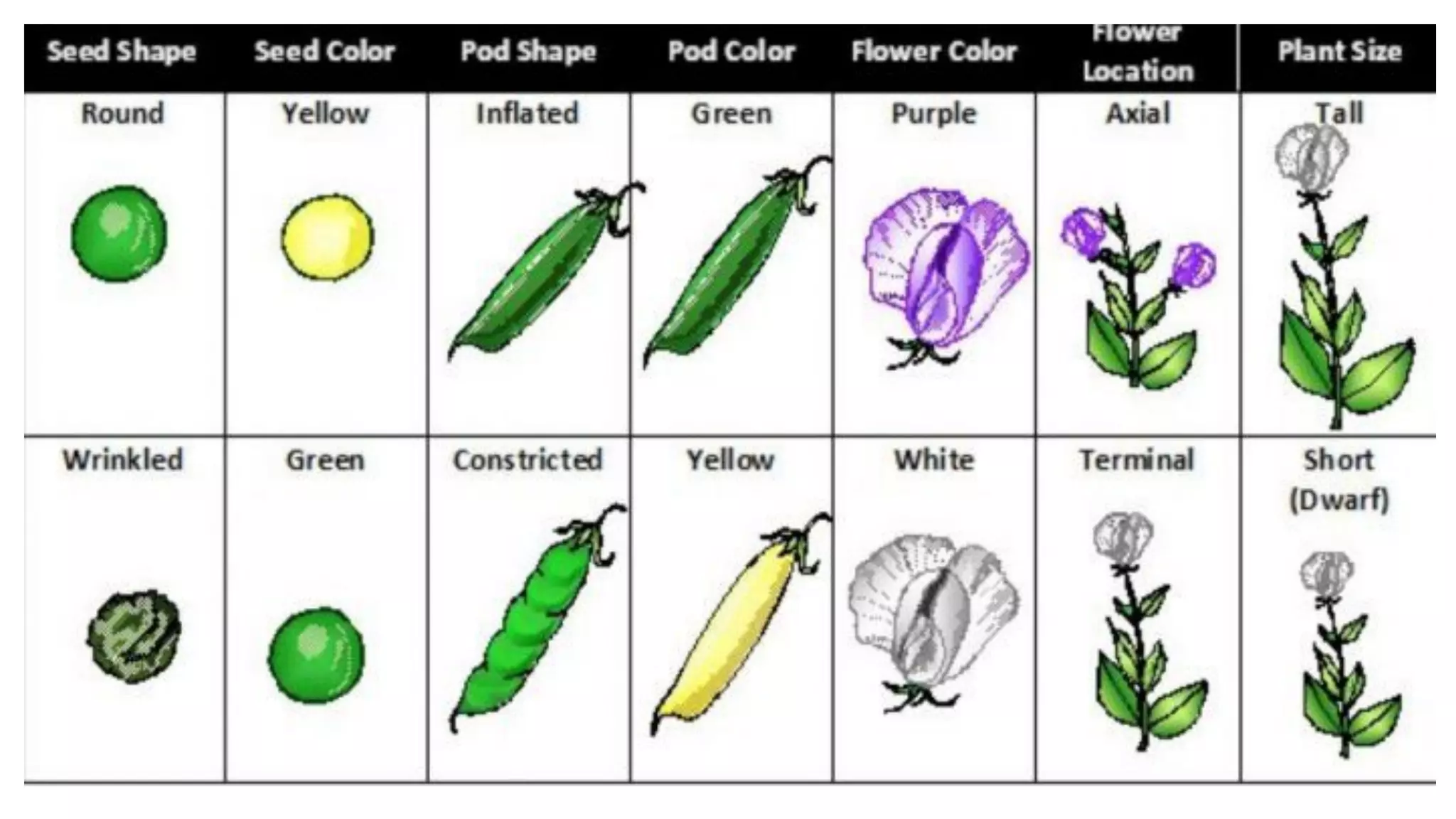
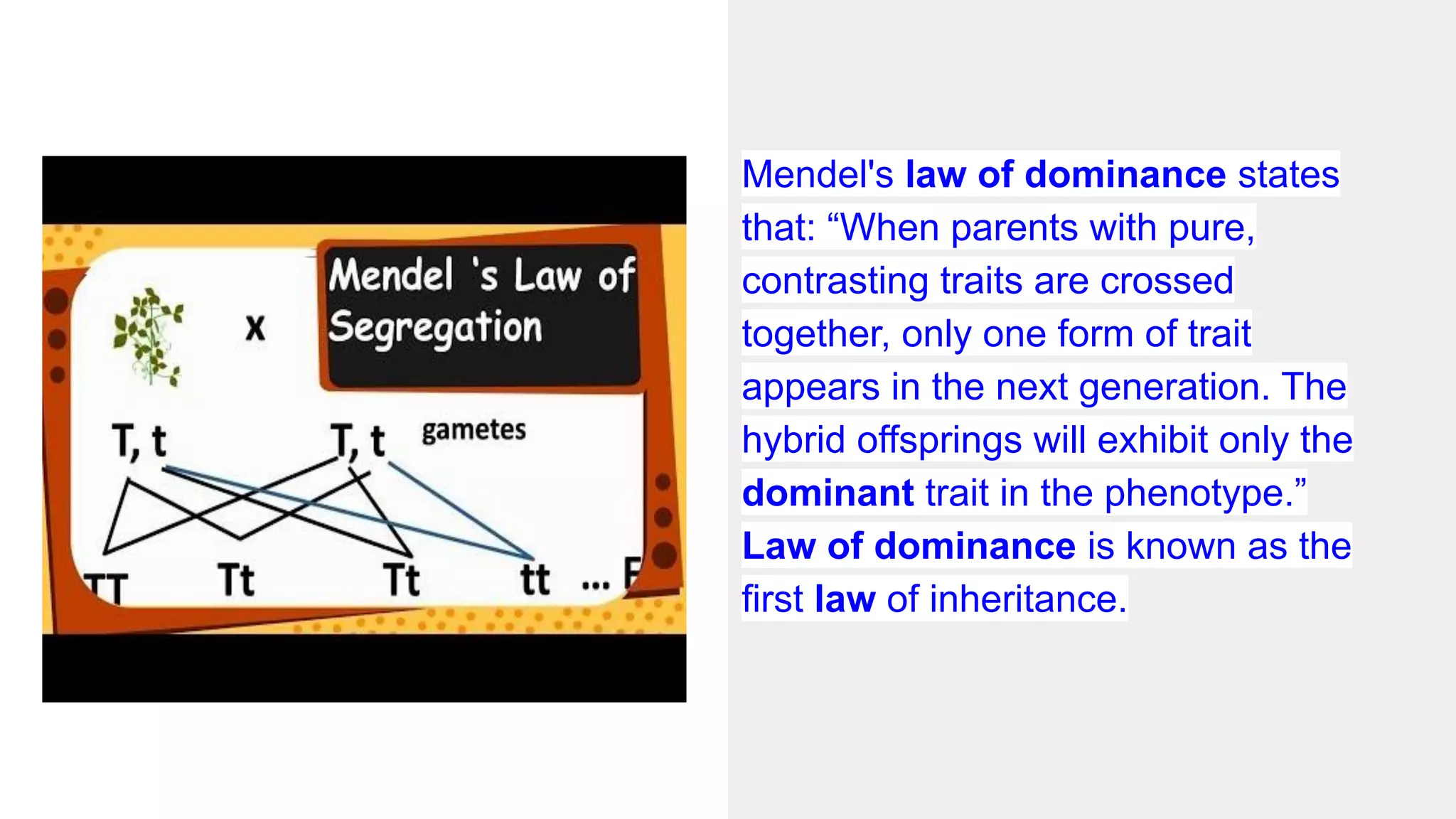
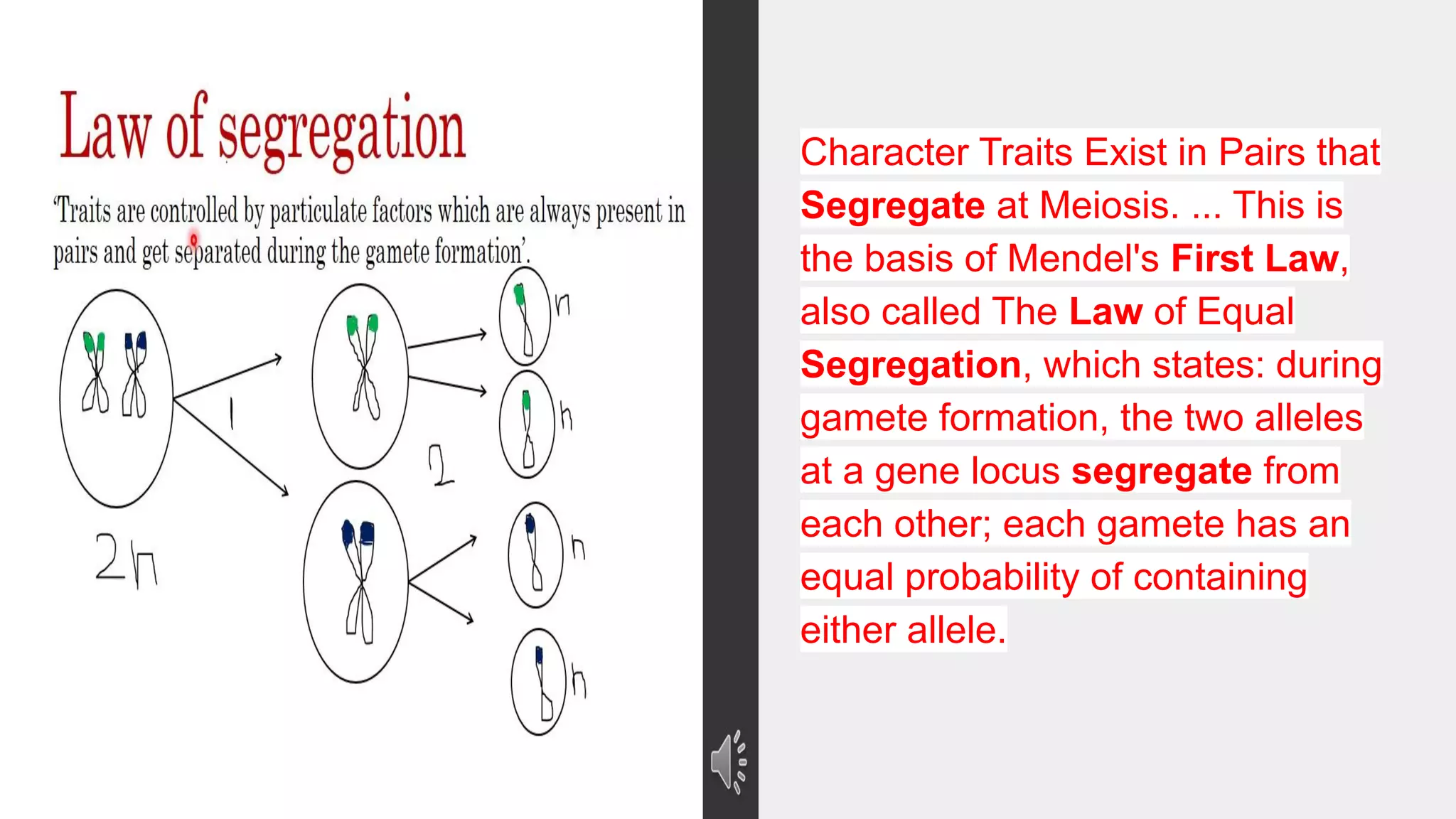
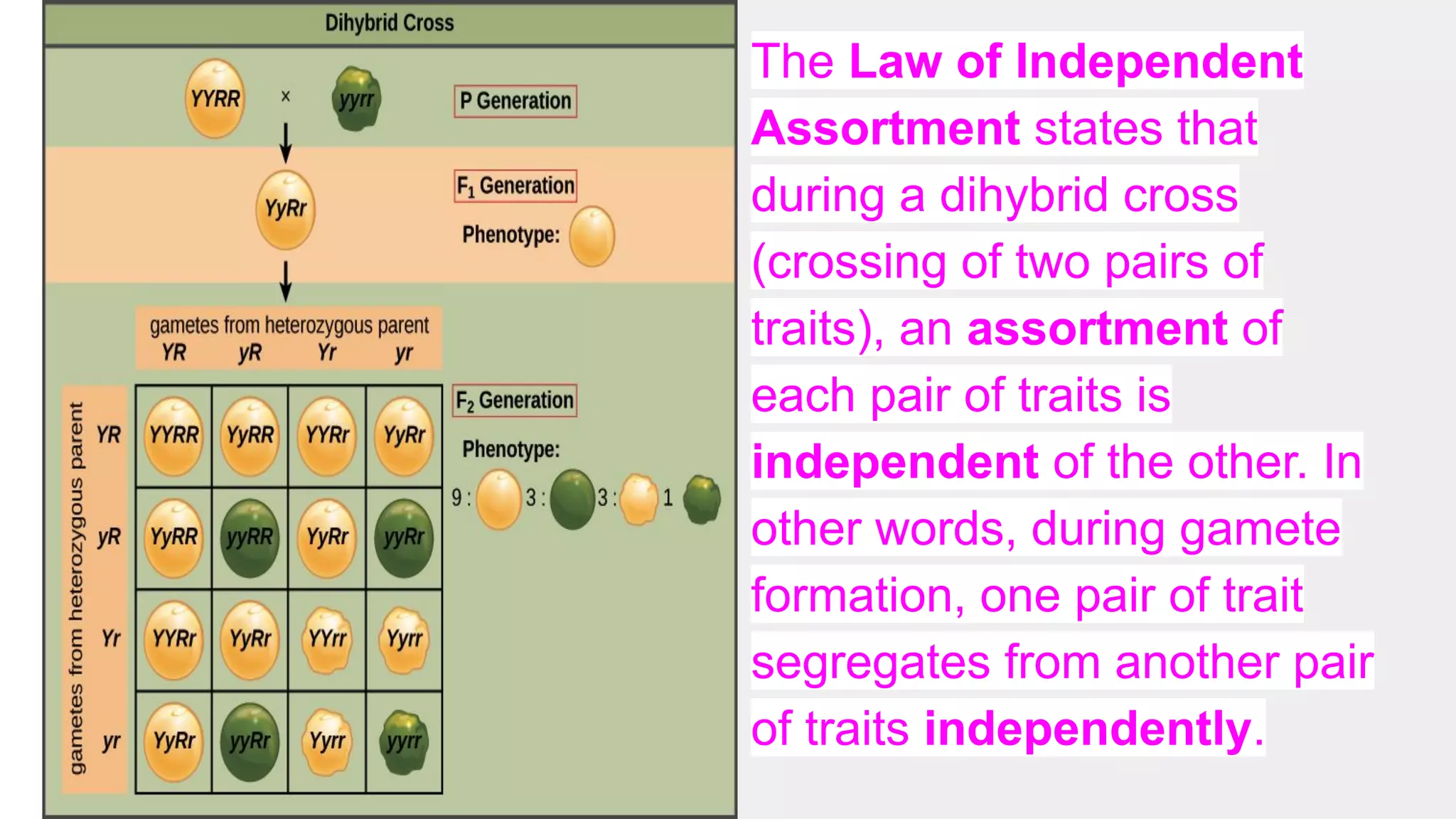
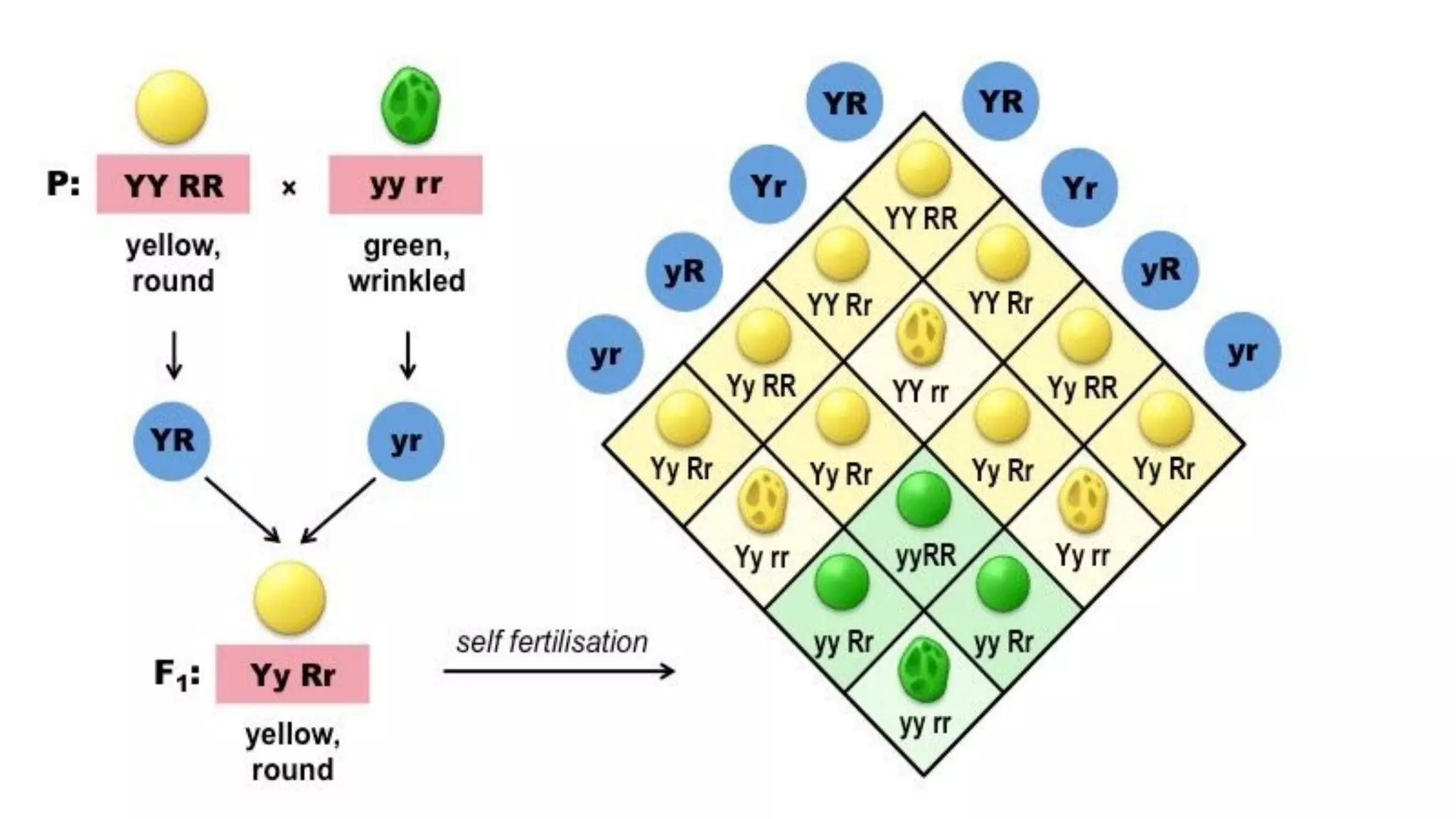
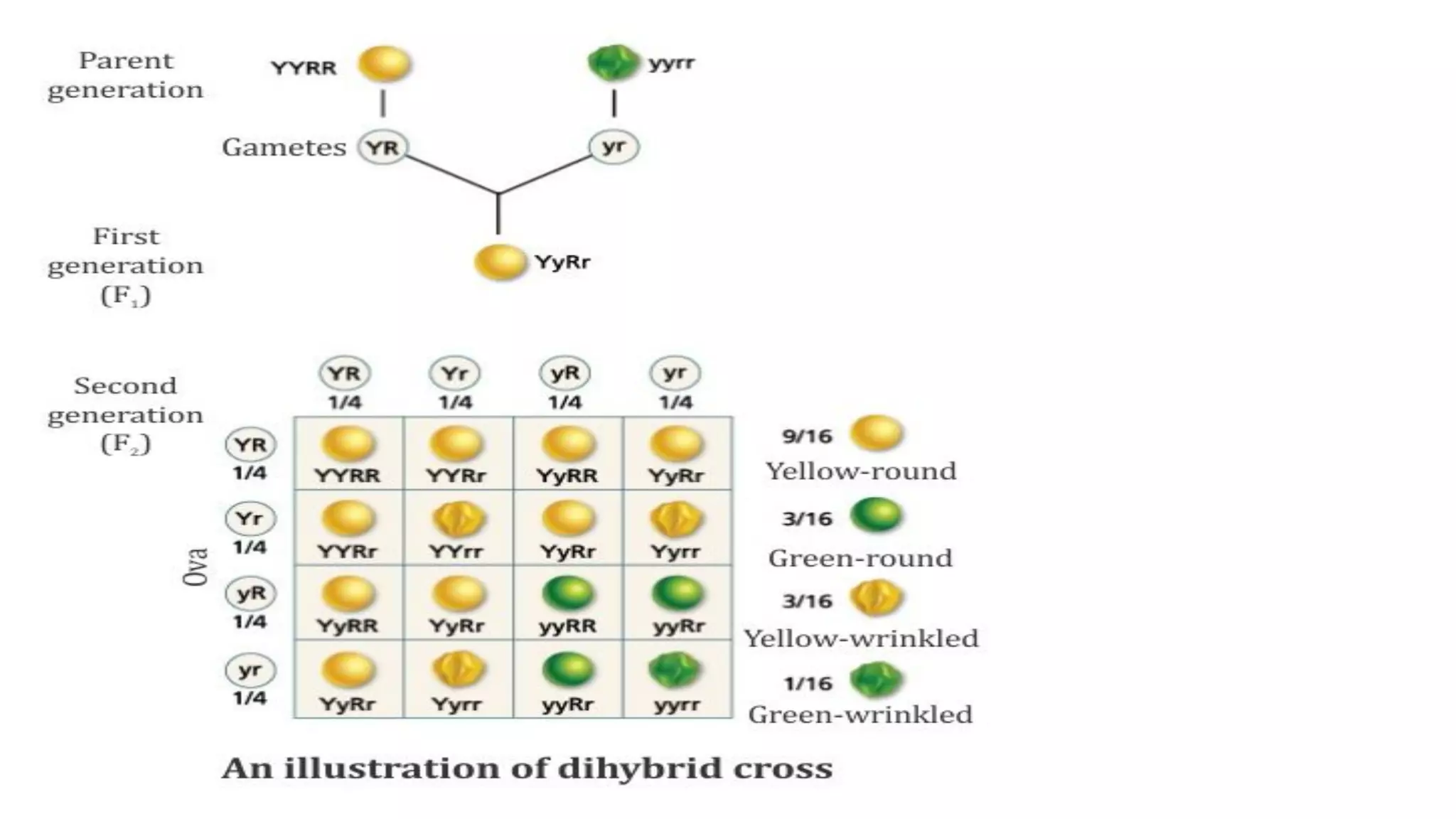
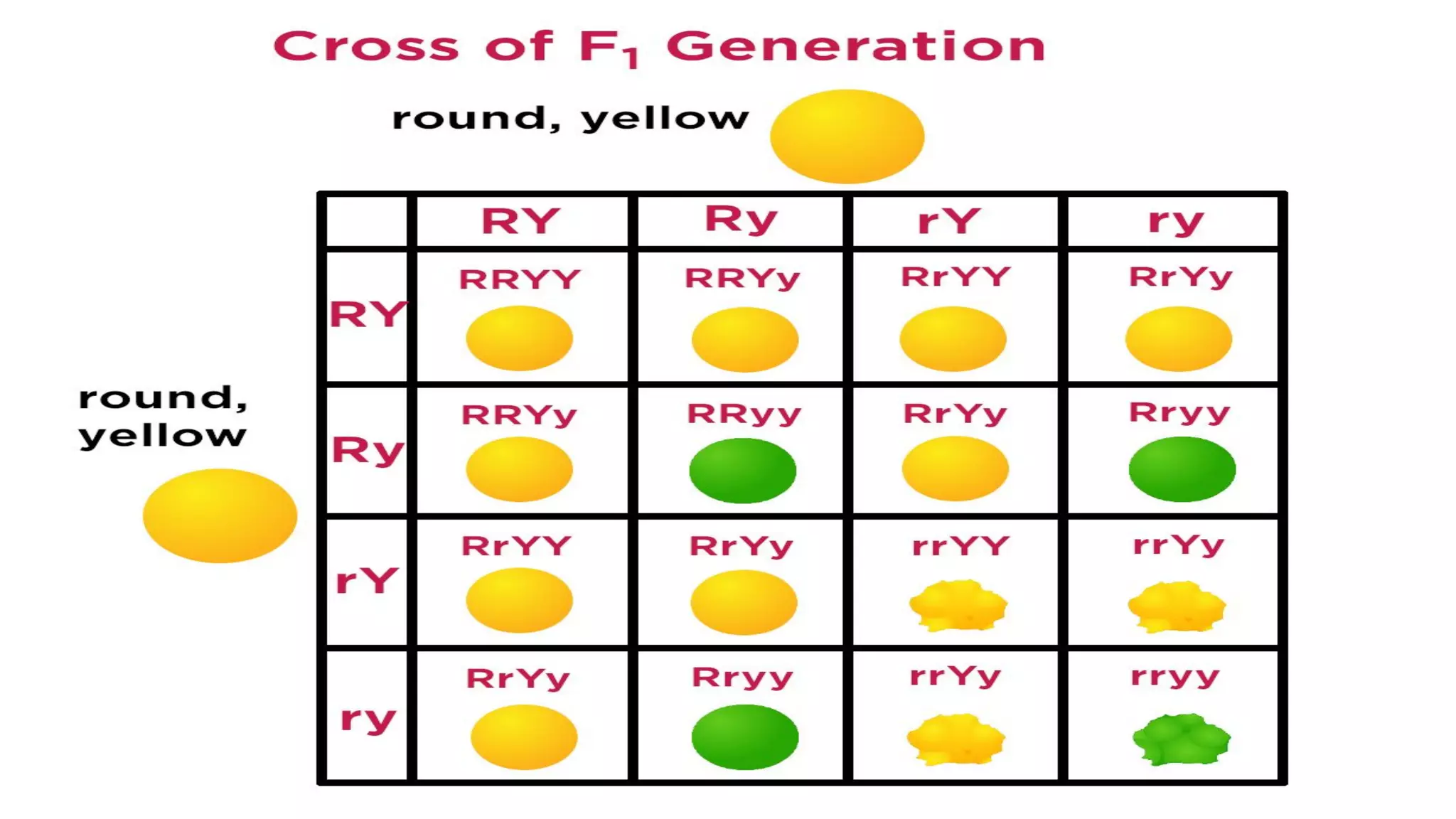
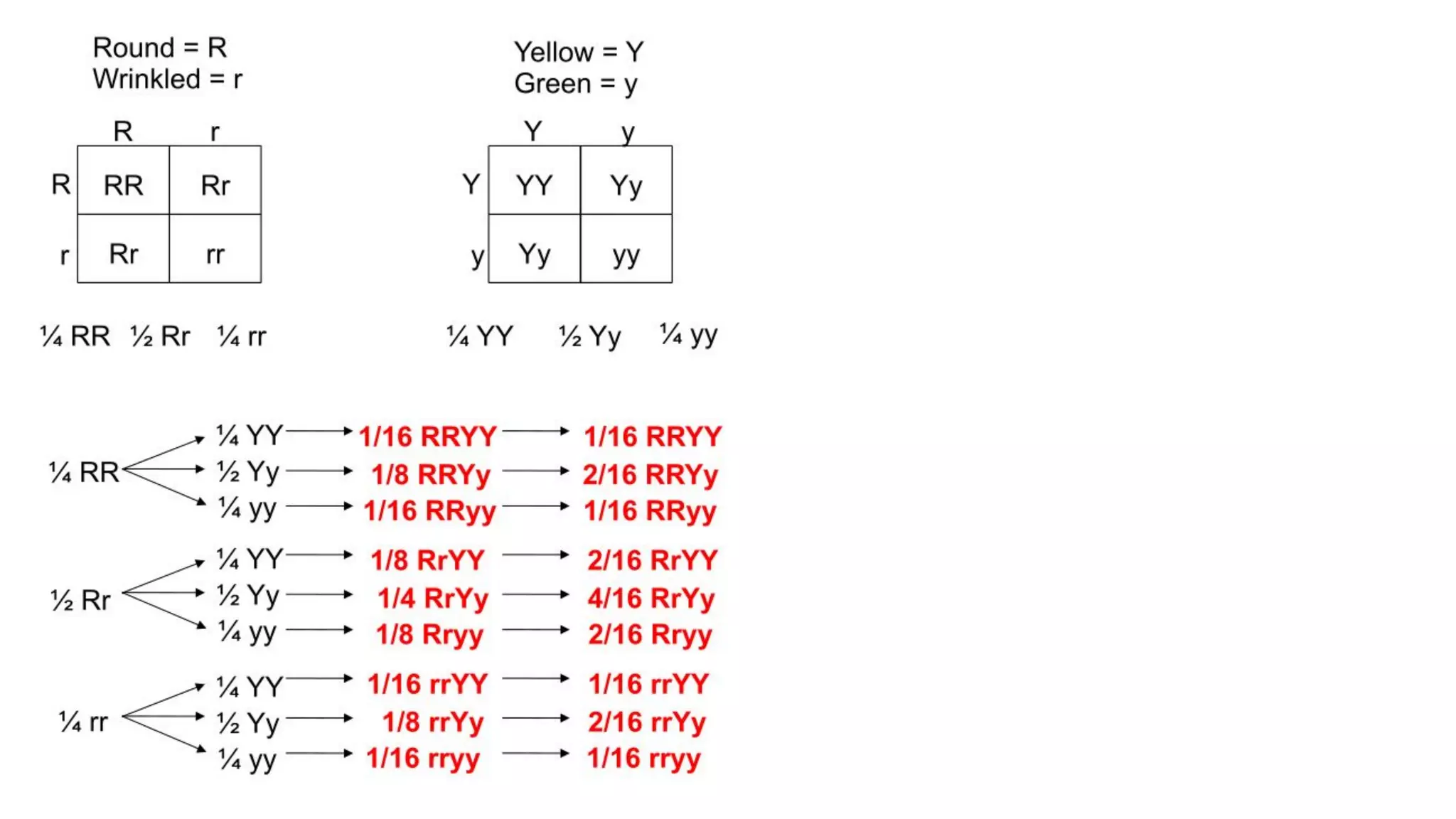
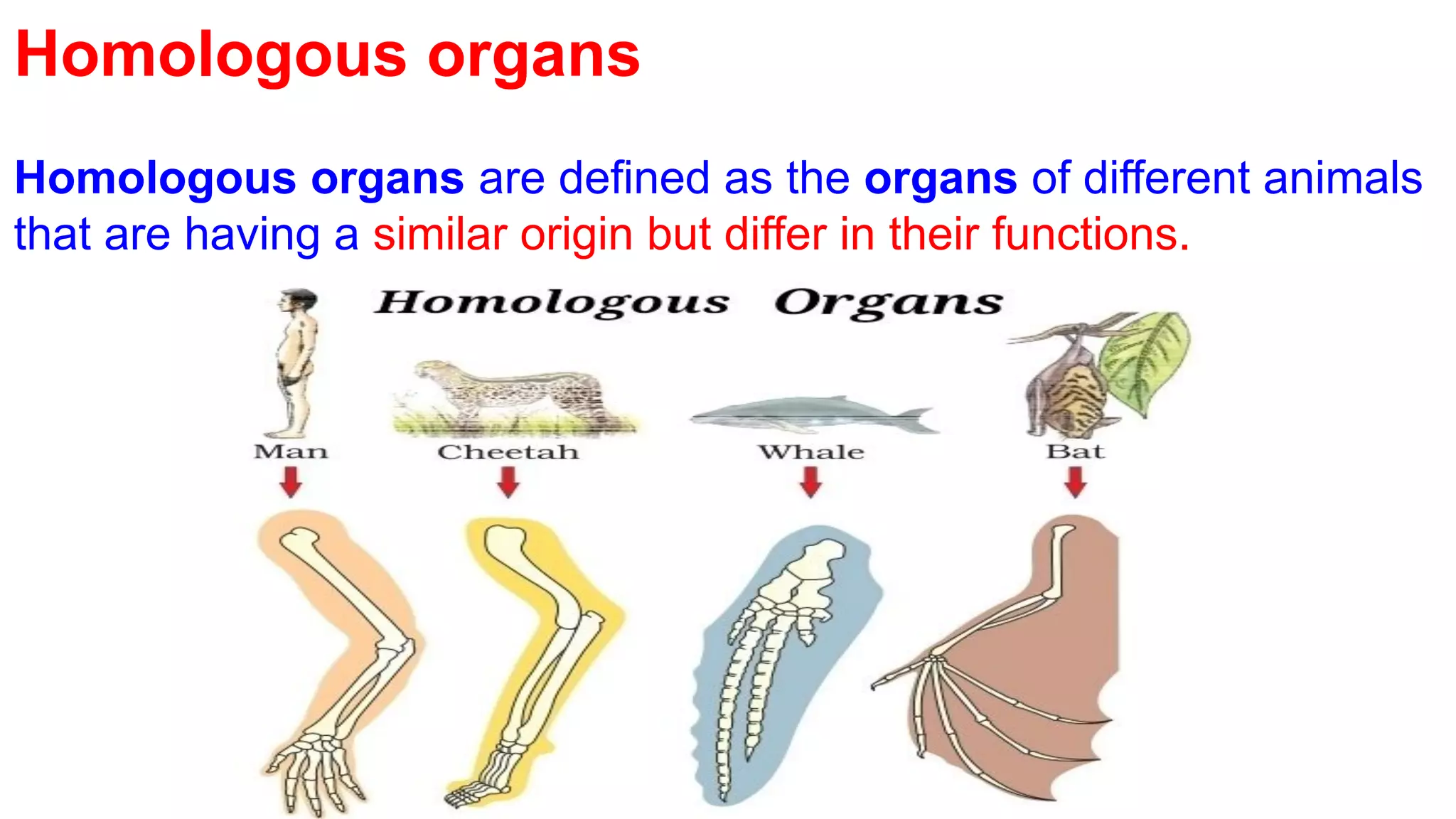
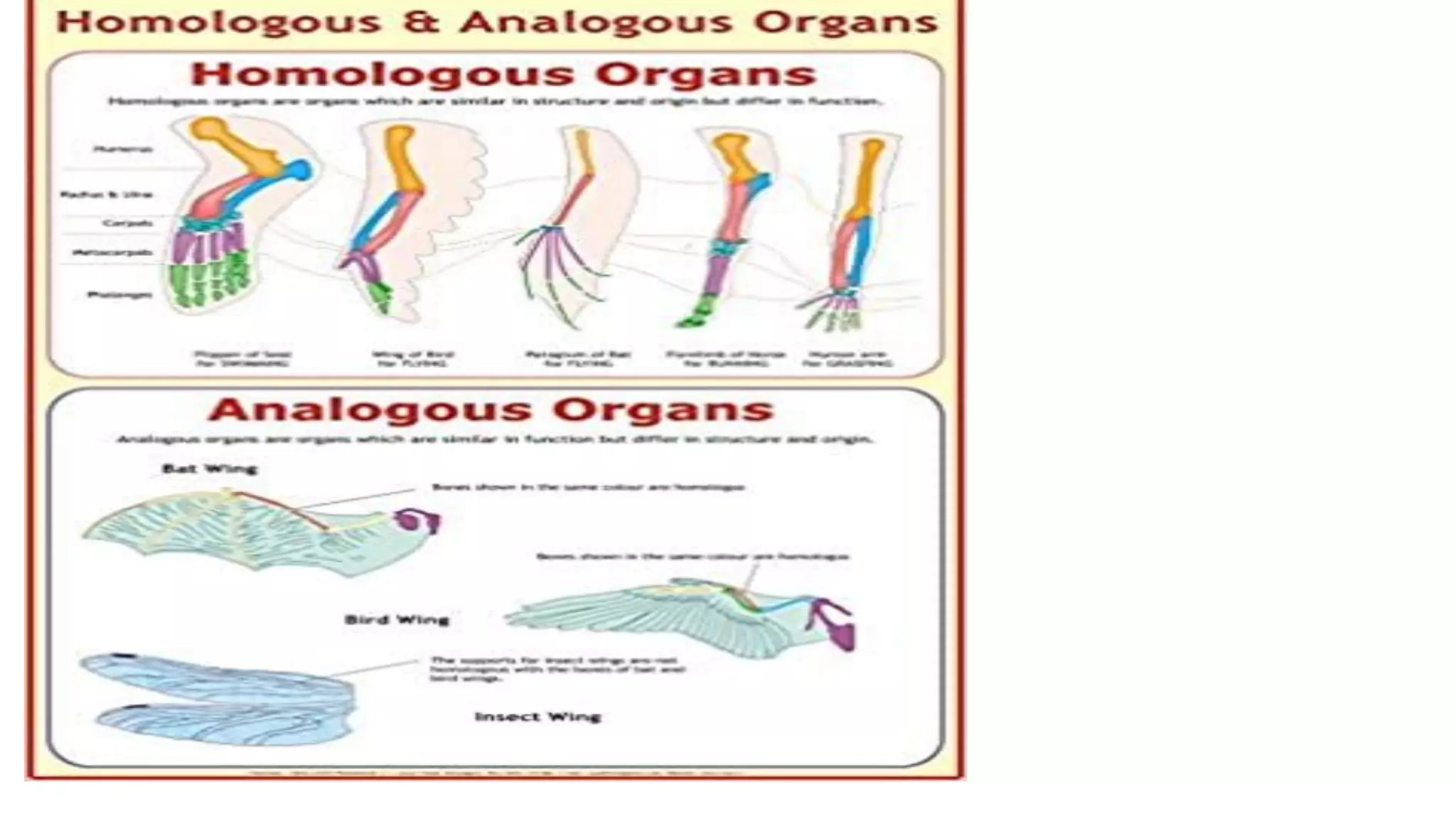
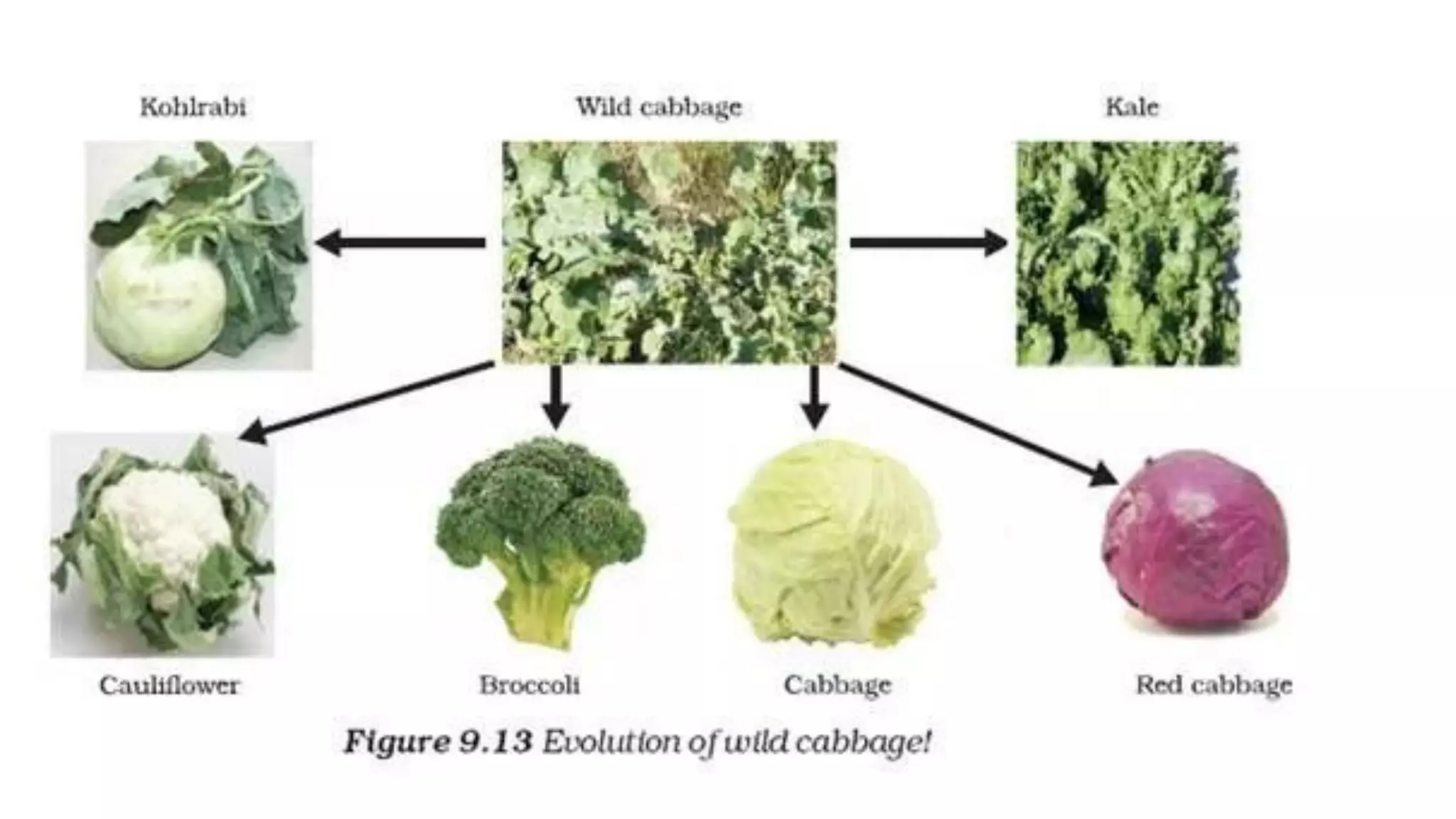
Heredity refers to the genetic traits passed down from parents to offspring. Traits can be physical characteristics like eye color or diseases. Genetics is the study of heredity and variations. Gregor Mendel conducted experiments in the 19th century that showed traits are passed to offspring through discrete units (now known as genes) rather than a blending of parents' traits. His work established the foundations of classical genetics, including the laws of segregation, dominance and independent assortment.