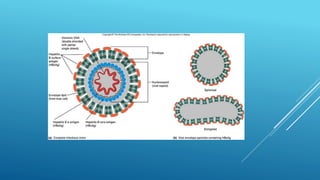
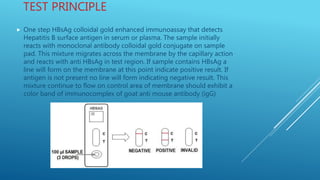
The document describes a rapid test strip method for detecting hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in serum or plasma. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a major cause of liver disease and cancer worldwide. The test works by detecting HBsAg, which appears early in hepatitis B infection, on a strip using monoclonal antibodies and colloidal gold. To use the test, serum is placed on the strip and results are read after 15 minutes, with lines at the test and control regions indicating a positive result. The test is designed to quickly detect HBsAg qualitatively but has limitations if antigen levels are low or interfering substances are present.