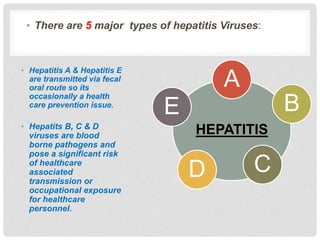
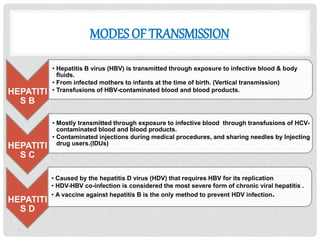
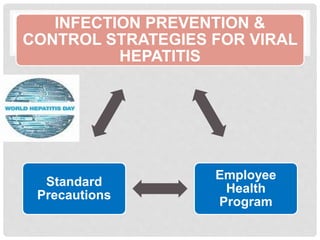
World Hepatitis Day is observed annually on July 28th to raise global awareness of viral hepatitis. The objectives are to involve people in focusing on hepatitis, raise awareness of the types and transmission, educate about prevention, diagnosis and control, and increase access to vaccines, treatment and skilled healthcare workers. Viral hepatitis B and C affect 325 million people globally and are among the leading causes of liver cancer and death. Standard precautions and employee health programs are key infection control strategies in healthcare facilities to prevent the transmission of hepatitis viruses.