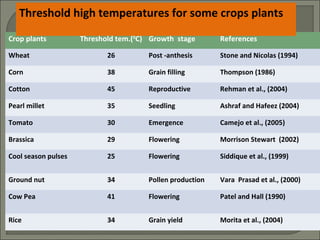
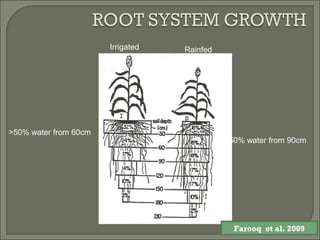
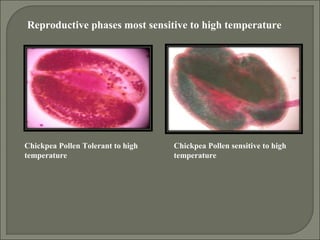
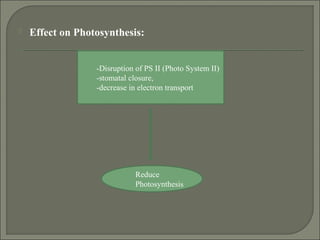
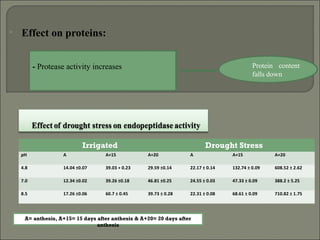
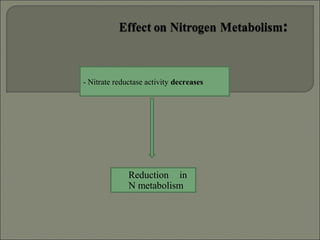
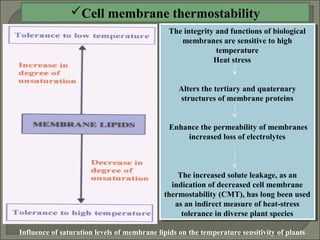
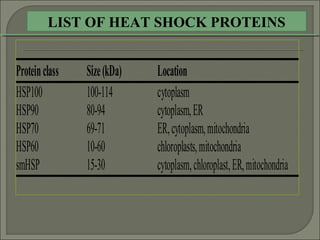
Heat stress can damage plant growth and development by disrupting key processes like photosynthesis, membrane integrity, and protein function. Plants have developed several responses to heat stress including:
1) Producing heat shock proteins and antioxidants to protect cellular functions from heat damage.
2) Altering their morphology, anatomy, and phenology like earlier flowering to reduce heat exposure during sensitive periods.
3) Adjusting physiological processes like accumulating osmolytes to maintain water relations and membrane stability under heat stress.
4) Modulating hormones like ABA and ethylene that help regulate stress responses and signaling. Understanding these adaptation mechanisms can help improve crop heat tolerance through breeding.