1. Plants can experience either chilling stress from temperatures between 0-15°C or freezing stress from temperatures below 0°C. Chilling can disrupt metabolic processes while freezing can cause either vitrification or ice crystal formation within plant tissues and cells.
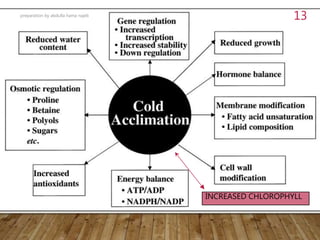
2. Cold hardening allows plants to acclimate to cold temperatures by modifying membrane lipids and lowering optimal temperatures for photosynthesis. Other protections include soil banking, wrapping tree trunks, sprinkling, fogging, and using wind machines or warm water circulation.
3. Symptoms of freezing injury include foliage desiccation, water-soaked areas developing into necrotic spots, and apparent wilting from damaged roots or conductive tissues. Cold stress response is complex and involves