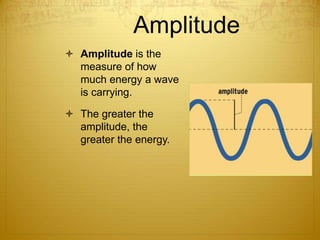
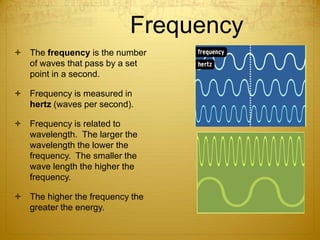
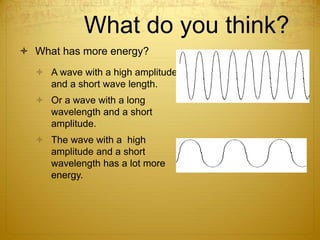
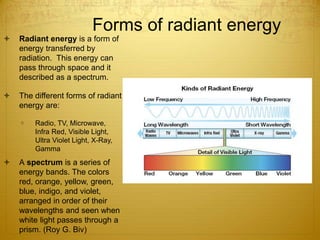
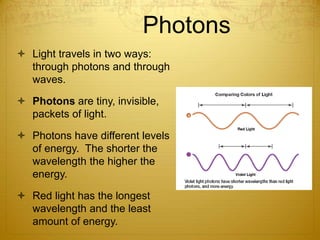
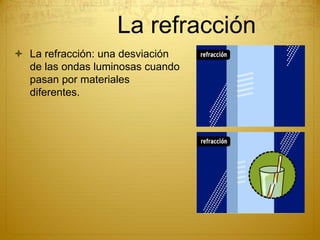
Energy can take many forms, including heat, light, and sound. Heat is the total energy of moving molecules, while temperature measures average molecular motion. Light and sound are forms of energy that travel in waves. Light waves can be electromagnetic or travel via photons, and different frequencies of light appear as different colors. Sound waves require a medium and produce pitch and loudness. Heat can be transferred through conduction, convection, and radiation. Radiation uses electromagnetic waves to transfer energy through space.