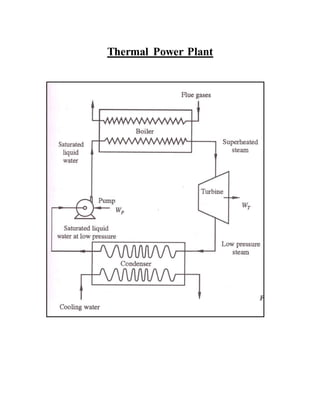
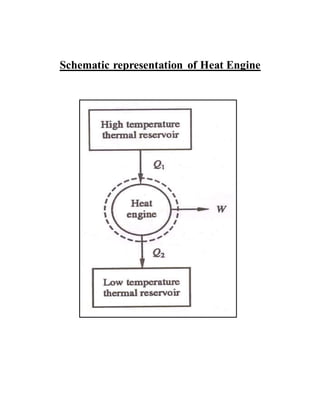
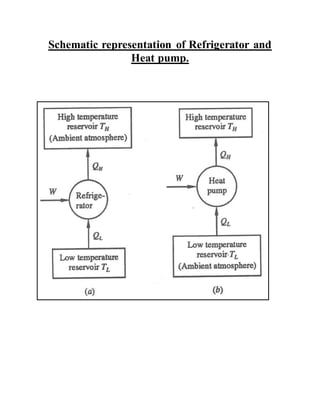
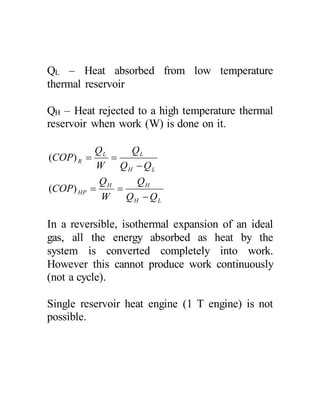
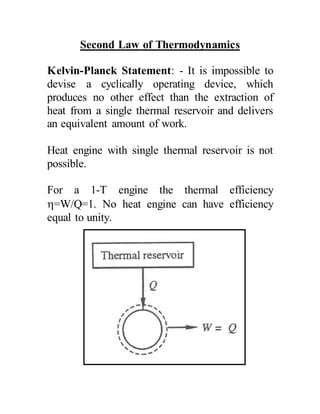
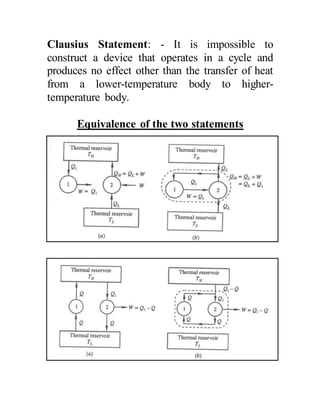
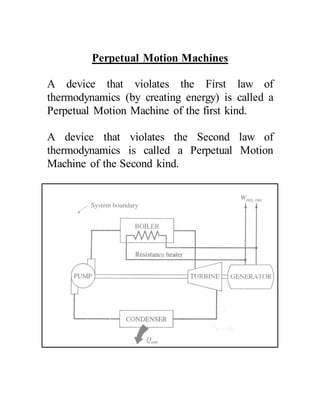
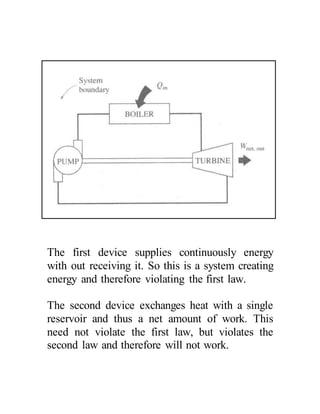
The document discusses the limitations of the first and second laws of thermodynamics, illustrating that energy conservation alone does not guarantee process occurrence, and emphasizes the role of thermal reservoirs, heat engines, and the inefficacy of perpetual motion machines. It defines reversible and irreversible processes, providing examples of irreversibilities that preclude reversibility in systems. The document concludes with a discussion on the equivalence of the Kelvin-Planck and Clausius statements concerning heat transfer and work, asserting that no heat engine can have perfect efficiency.