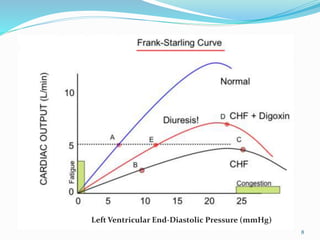
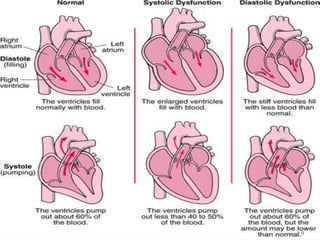
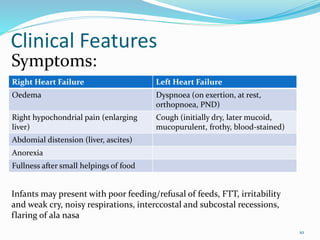
Dr. Eke Eghosasere Paul gave a presentation on pediatric heart failure to the Nelson Club on September 15, 2014. The presentation covered the epidemiology, etiology, pathophysiology, clinical signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of heart failure in children. Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot meet the body's metabolic needs due to reduced cardiac output. Compensatory mechanisms initially help maintain function but eventually become ineffective, leading to worsening clinical symptoms. Proper diagnosis and management of the underlying cause are important for treatment.