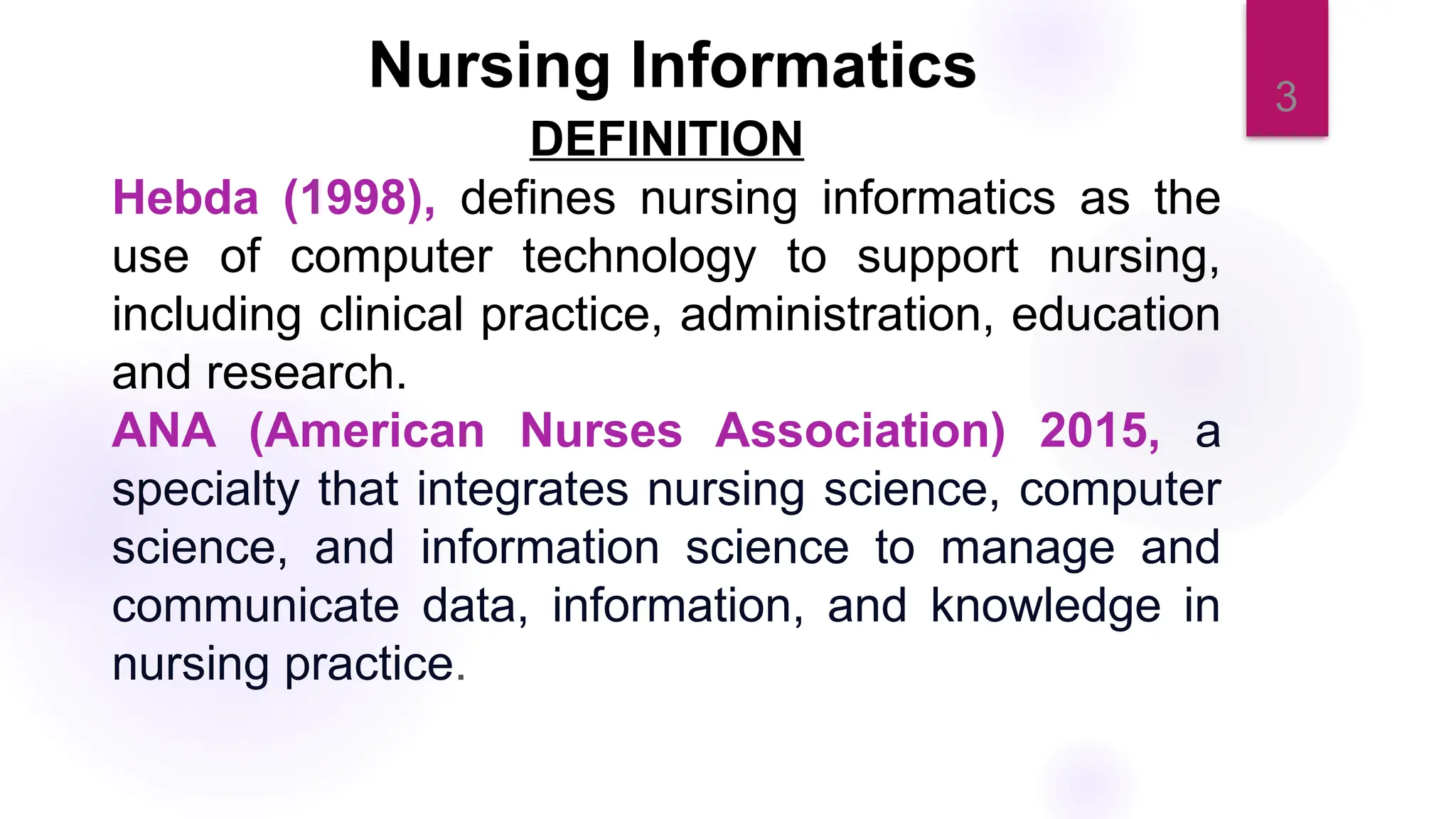
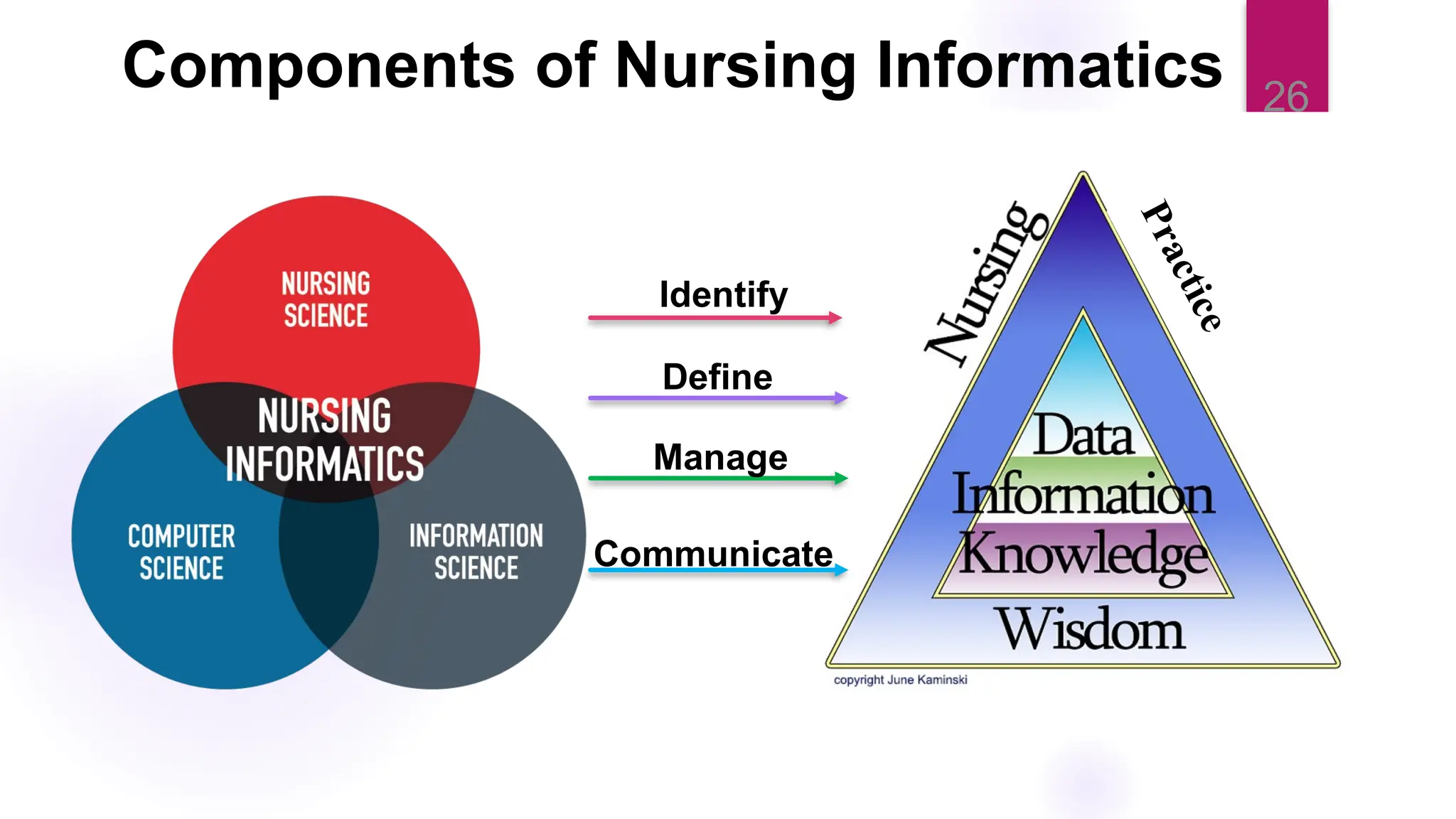
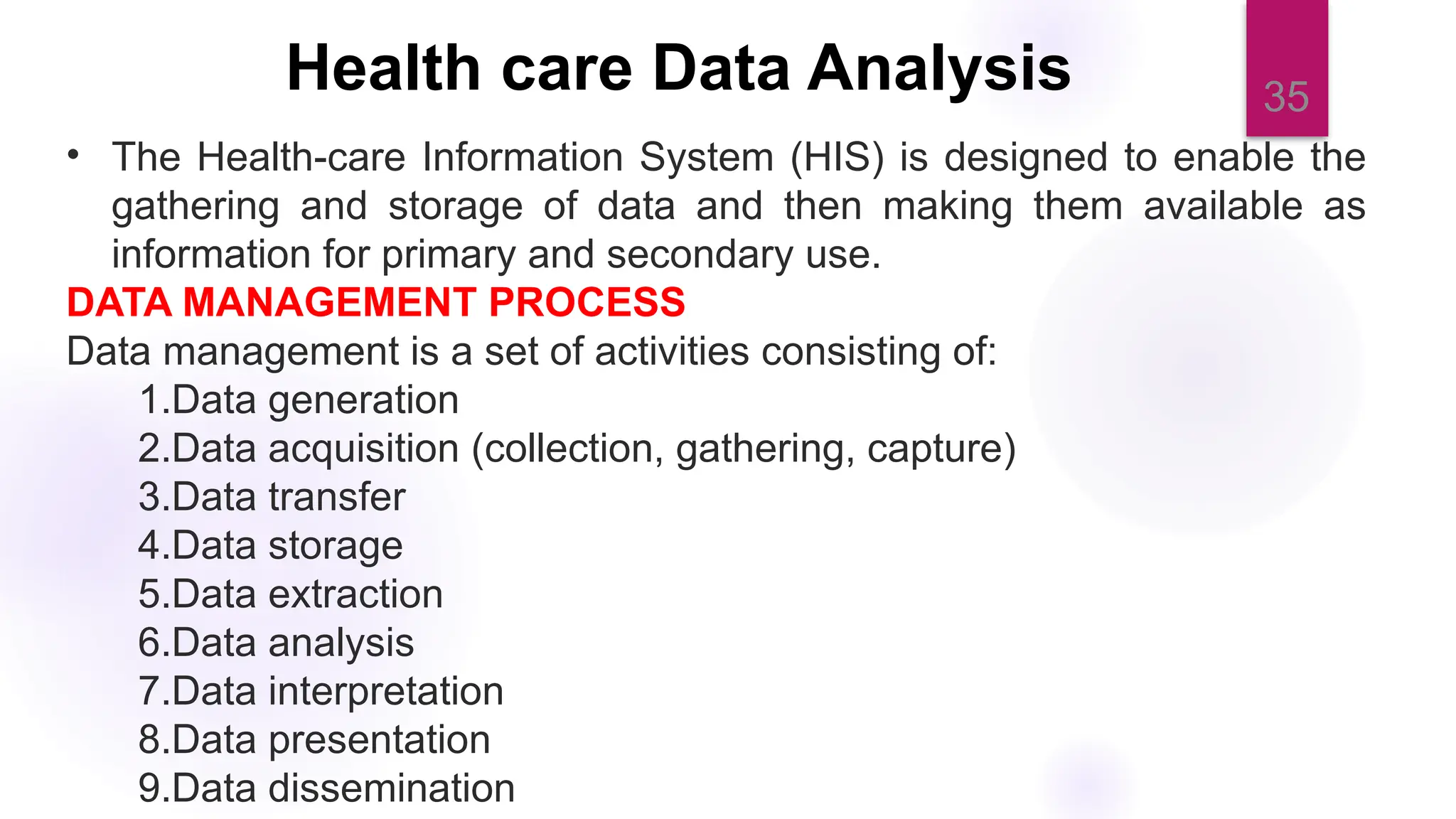
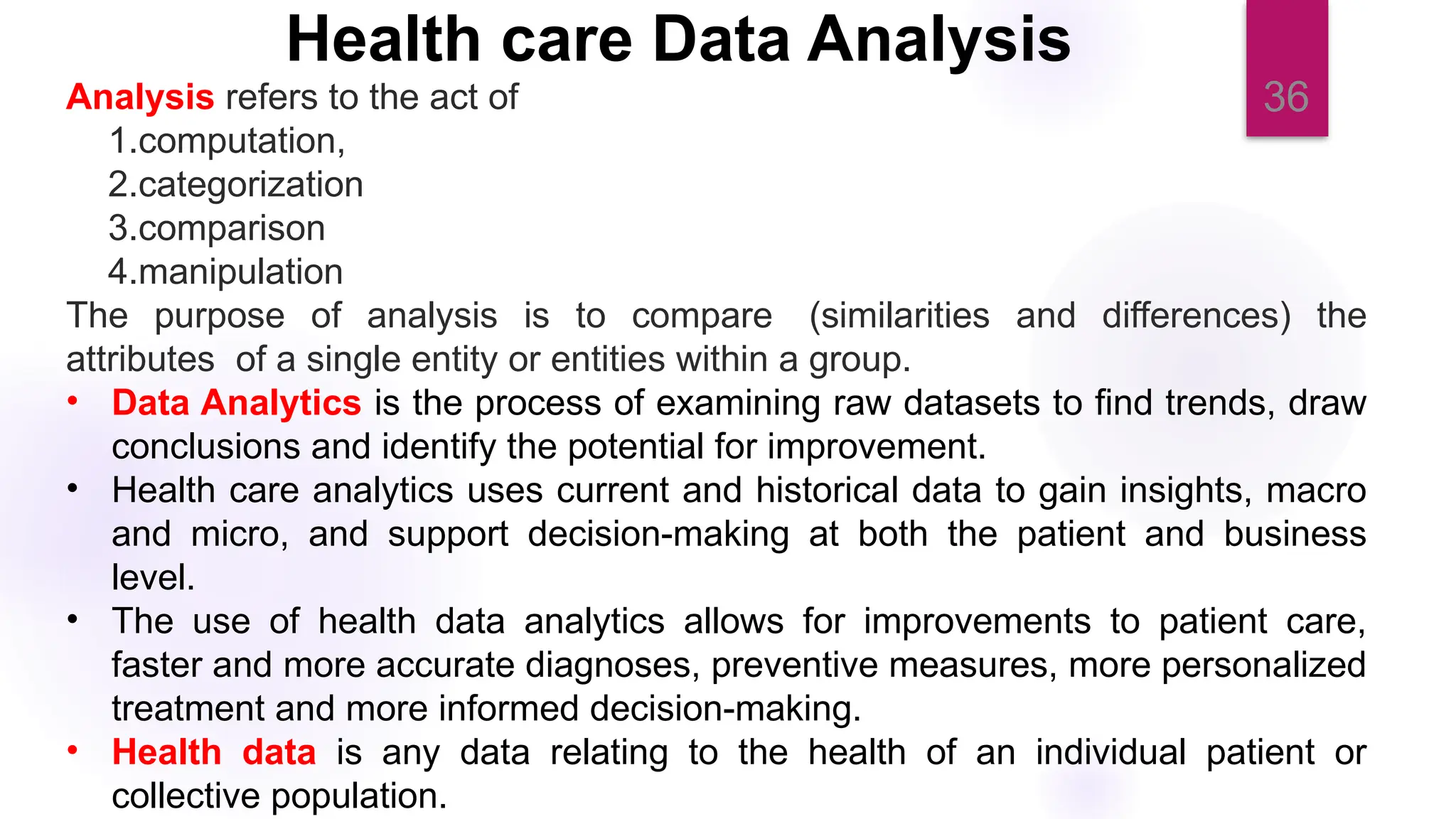
The document discusses nursing informatics as the integration of nursing science with information and communication technologies to enhance healthcare delivery and improve patient outcomes. It emphasizes the importance of data management and analytics within nursing practice, including how emerging technologies like telehealth are transforming care. Additionally, it outlines the essential competencies and benefits related to the effective use of nursing informatics in various healthcare settings.