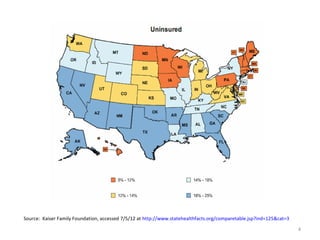
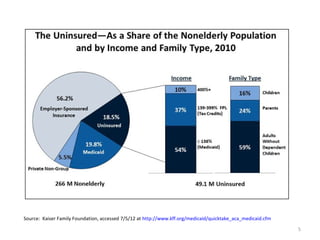
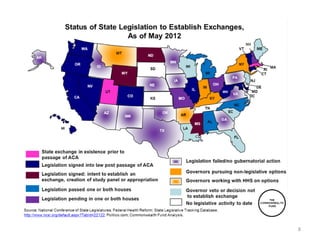
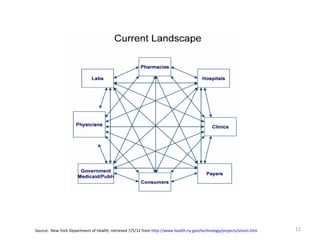
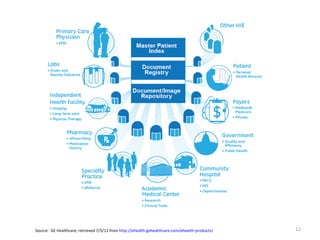
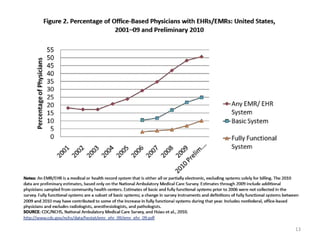
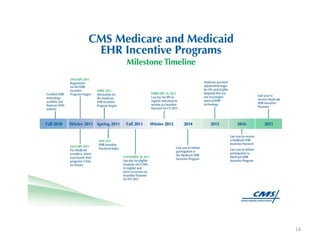
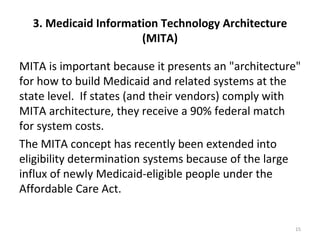
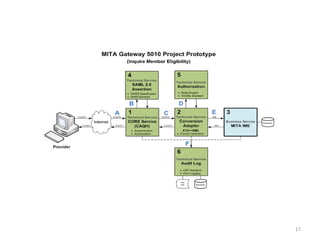
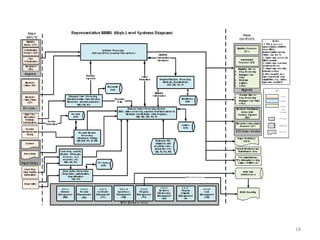
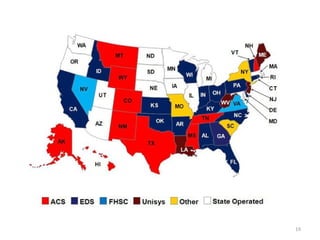
The document discusses key changes in health and human services driven by the Affordable Care Act, which mandates states to set up health insurance exchanges. It also covers the HITECH Act, requiring the implementation of health information exchanges to facilitate patient information sharing among healthcare providers. Lastly, it addresses the Medicaid Information Technology Architecture (MITA), which outlines system construction for Medicaid and offers financial incentives for adherence.