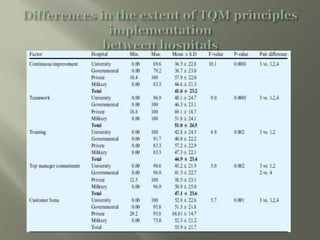
This document discusses a study on the implementation of total quality management (TQM) principles in hospitals. The study used a cross-sectional survey design to collect data from nurses across four hospitals representing different health sectors. Factor analysis identified five key TQM principles being implemented: continuous improvement, teamwork, training, top management commitment, and customer focus. The study found that private hospitals have implemented TQM more than other sectors, while implementation was not related to nurse demographics except for the availability of a dedicated TQM unit.