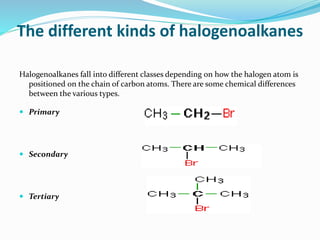
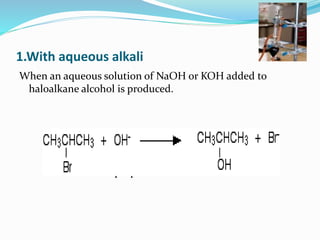
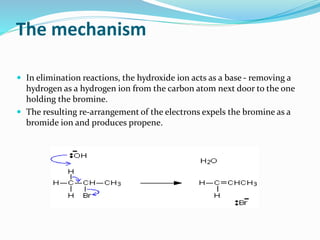
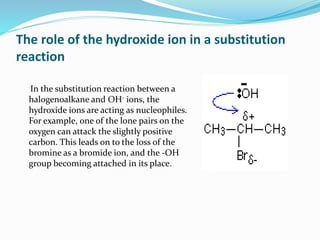
Halogenoalkanes are compounds formed when hydrogen atoms in alkanes are replaced by halogen atoms, classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary based on the halogen's position. They undergo nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions, with nucleophiles such as hydroxide ions playing key roles in these reactions. The document details several reactions involving halogenoalkanes with examples, including the production of alcohols, amines, and propene.