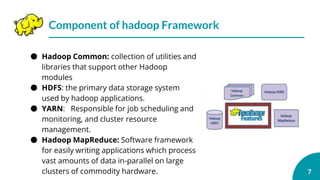
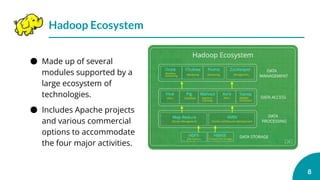
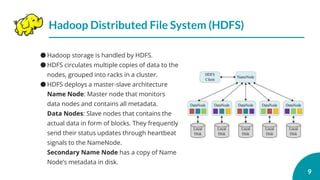
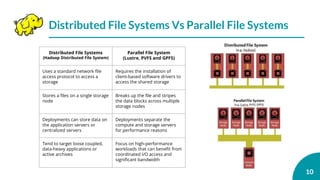
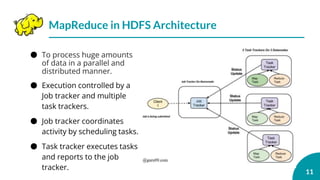
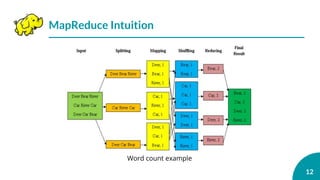
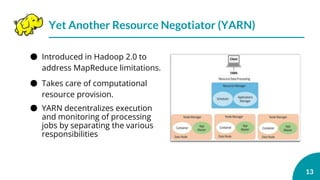
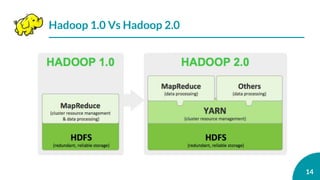
This document is an outline for a presentation on advanced topics in computer science focusing on big data and Hadoop. It introduces big data and Hadoop, describing Hadoop's features like HDFS and MapReduce. It discusses how companies use big data and Hadoop, components of the Hadoop framework, and compares distributed and parallel file systems. The document also covers YARN, shortcomings of Hadoop, and its future directions.