Embed presentation
Download to read offline

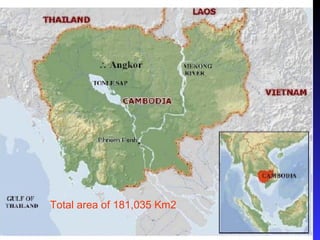








Over 20 years, Cambodia faced significant suffering due to wars and internal conflicts, leading to vulnerabilities and development issues. The Cambodian government is focused on providing access to clean water, improving rural water supply, and addressing challenges related to climate change and water management. Key challenges include an inadequate infrastructure for water management, reliance on foreign support, and maintaining resources for both human and ecosystem needs.








