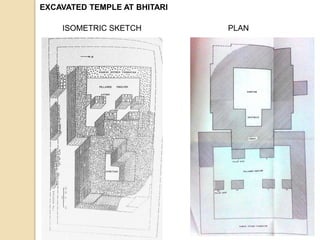
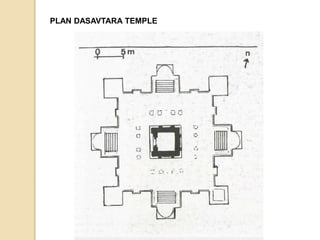
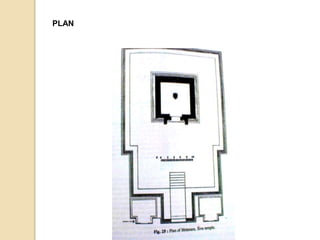
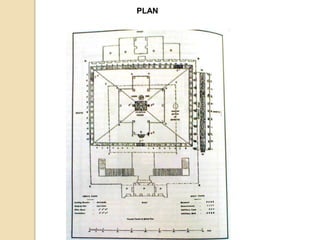
The Gupta Empire was a golden age of India founded by Maharaja Sri Gupta. Key rulers like Chandragupta I and Samudragupta expanded the empire across northern India. The Guptas achieved notable advancements in fields like science, administration, art, and literature. Some of their most famous architectural and artistic works include the Ajanta Caves, Ellora Caves, and temples at Deogarh and Bhitari.