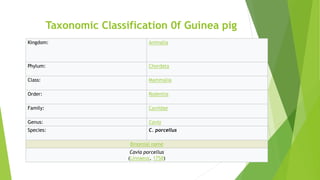
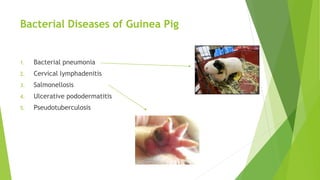
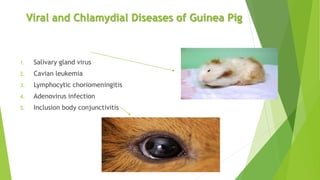
The document discusses the guinea pig, including its taxonomy, history, common varieties, anatomy, physiology, reproduction, housing, feeding, behavior, diseases, and care. It provides details on the taxonomic classification of guinea pigs, listing them in the order Rodentia and family Caviidae. It also outlines the identification of male and female guinea pigs and describes the gestation period and litter sizes of guinea pigs.