To get practical exposure in field level
To get a glimpse of our future working environment
To develop our communication and managerial skills for field practice
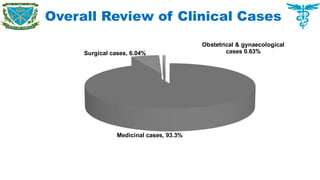
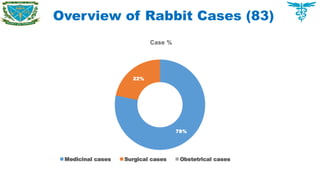
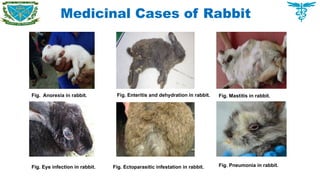
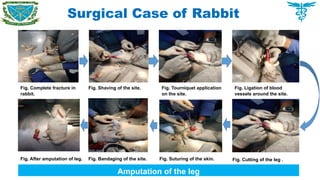
To have an overview of current cases commonly found in different areas
To improve our skills in farm management
To improve our confidence level and skills
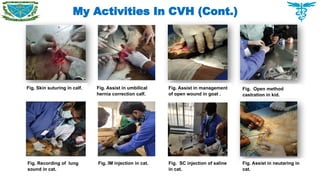
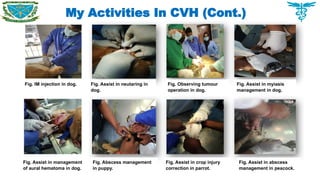
Handling and restraining of pet animals
Therapeutic management of common diseases
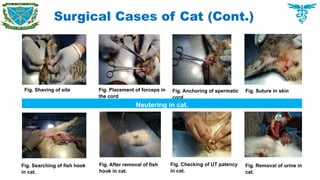
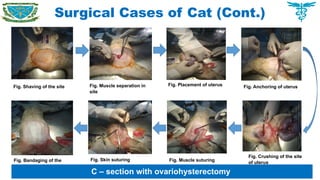
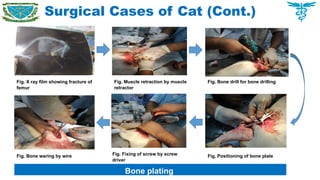
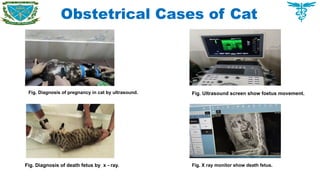
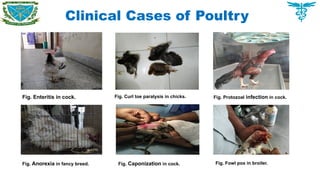
Handling clinical and surgical cases of dogs, cats, rabbits, birds as well as farm animals
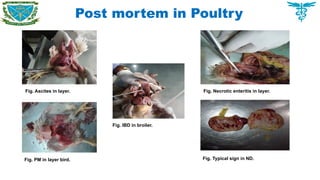
Post mortem of chicken
Discussion sessions
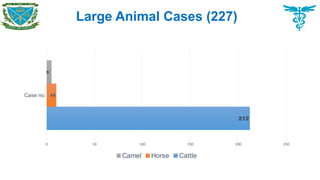
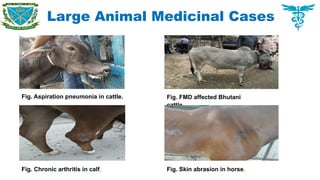
Large animal cases
Cattle, Horse, Camel
Small ruminant cases
Goat, Sheep
Small animal cases
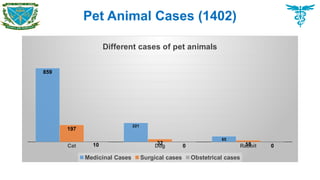
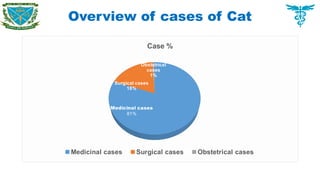
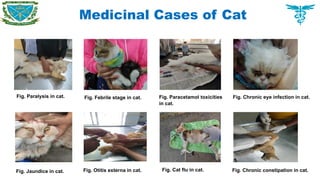
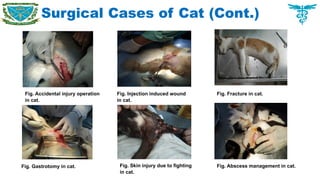
Pet animals
Cat, Dog, Rabbit
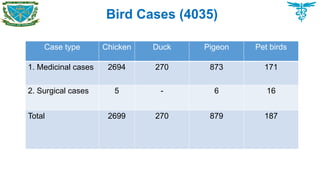
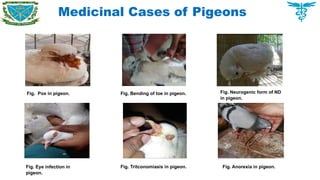
Birds cases
Poultry species
Chickens, Duck, Pigeon
Pet birds
Parrot, Burgerigard, Cockertail, Moyna etc.
Others
Peacock, Turtle
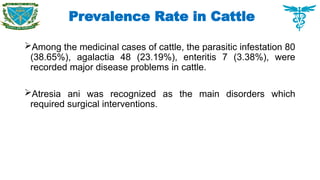
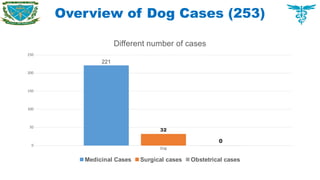
Among the medicinal cases of cattle, the parasitic infestation 80 (38.65%), agalactia 48 (23.19%), enteritis 7 (3.38%), were recorded major disease problems in cattle.
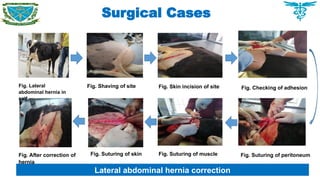
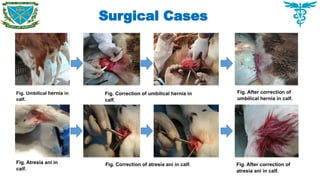
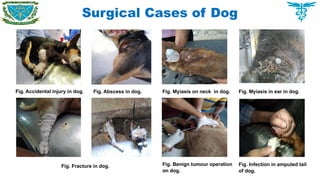
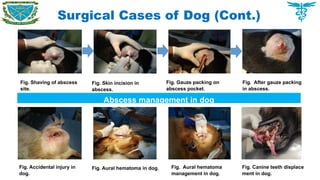
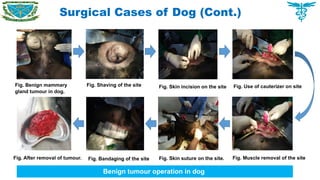
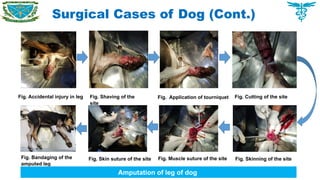
Atresia ani was recognized as the main disorders which required surgical interventions.
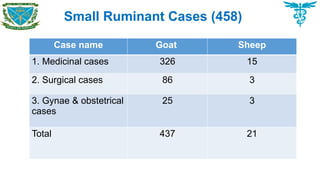
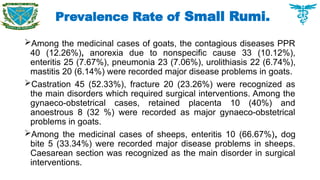
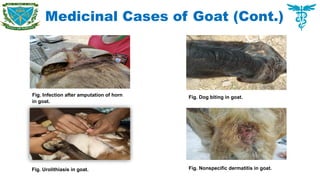
Among the medicinal cases of goats, the contagious diseases PPR 40 (12.26%), anorexia due to nonspecific cause 33 (10.12%), enteritis 25 (7.67%), pneumonia 23 (7.06%), urolithiasis 22 (6.74%), mastitis 20 (6.14%) were recorded major disease problems in goats.
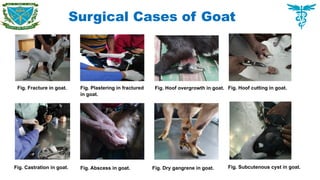
Castration 45 (52.33%), fracture 20 (23.26%) were recognized as the main disorders which required surgical interventions. Among the gynaeco-obstetrical cases, retained placenta 10 (40%) and anoestrous 8 (32 %) were recorded as major gynaeco-obstetrical problems in goats.
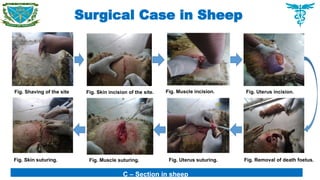
Among the medicinal cases of sheeps, enteritis 10 (66.67%), dog bite 5 (33.34%) were recorded major disease problems in sheeps. Caesarean section was recognized as the main disorder in surgical interventions.