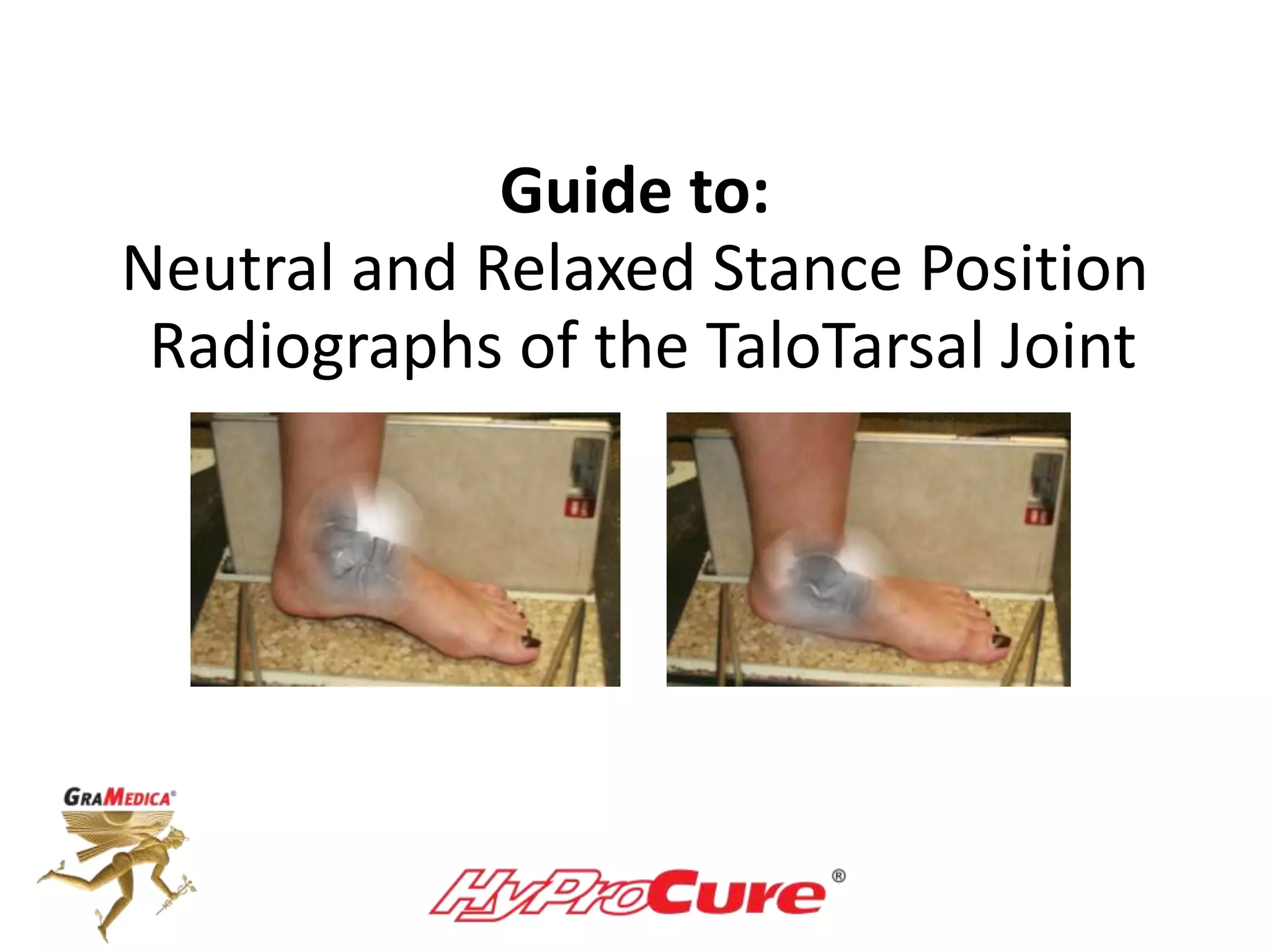
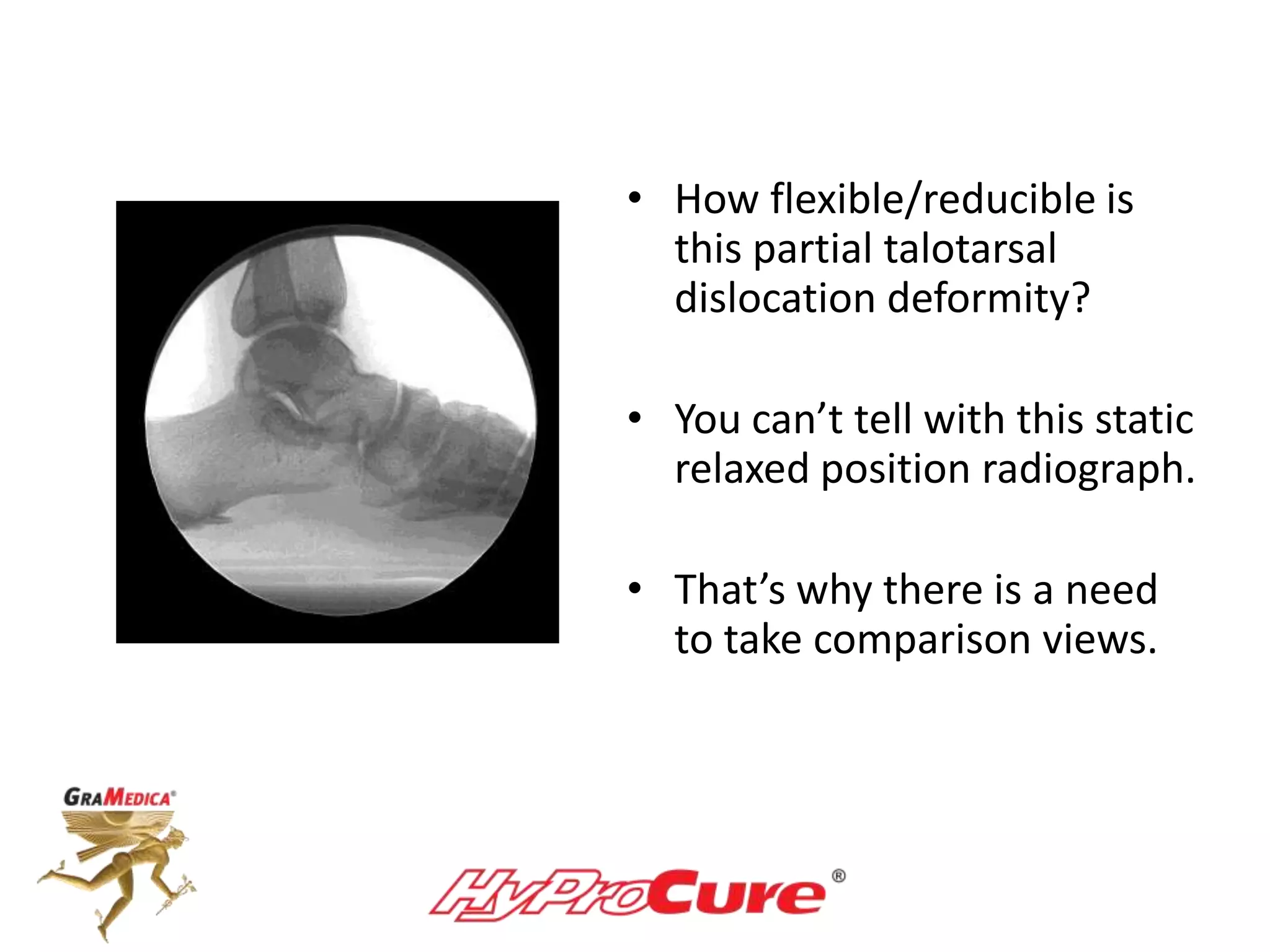
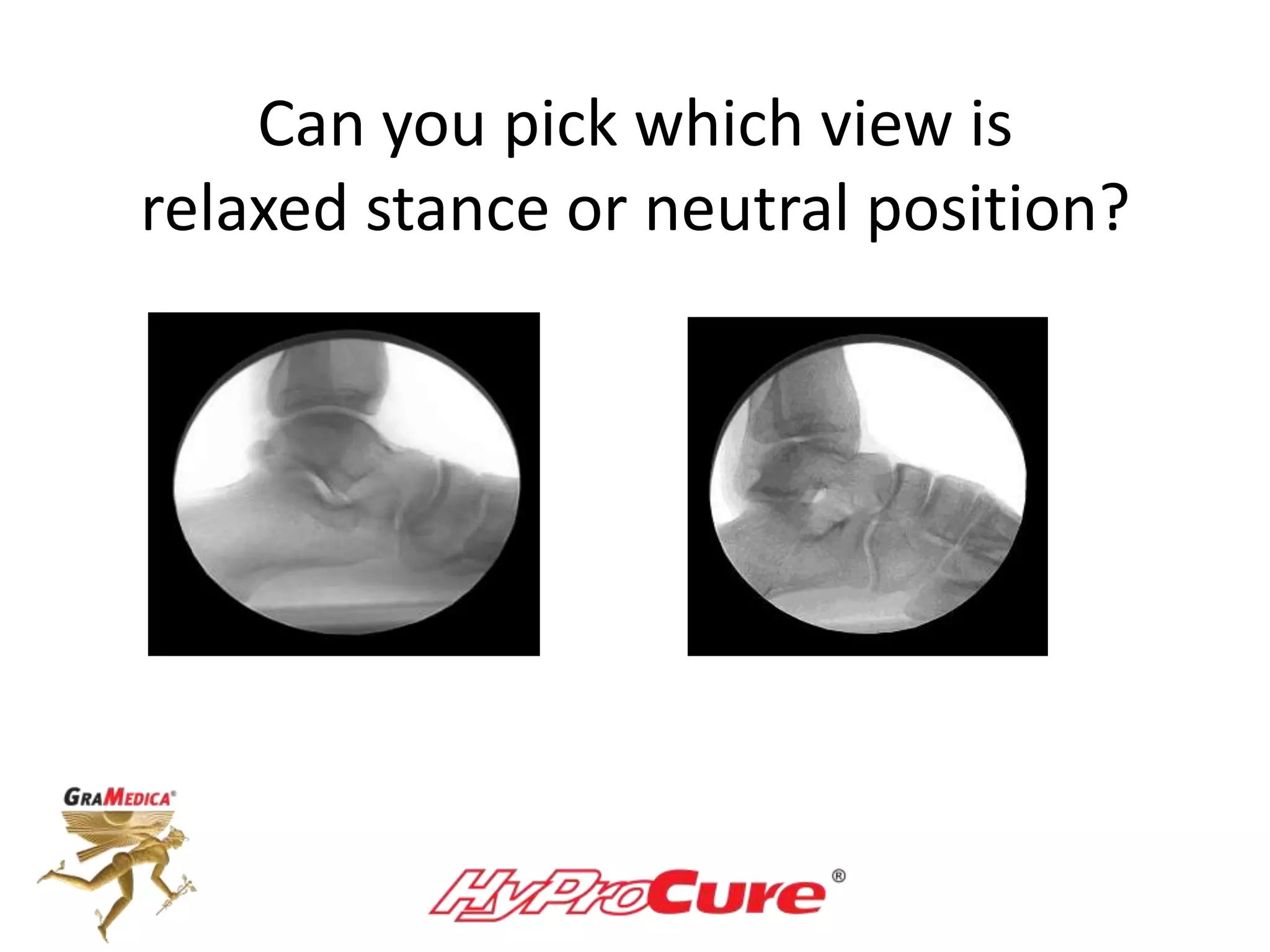
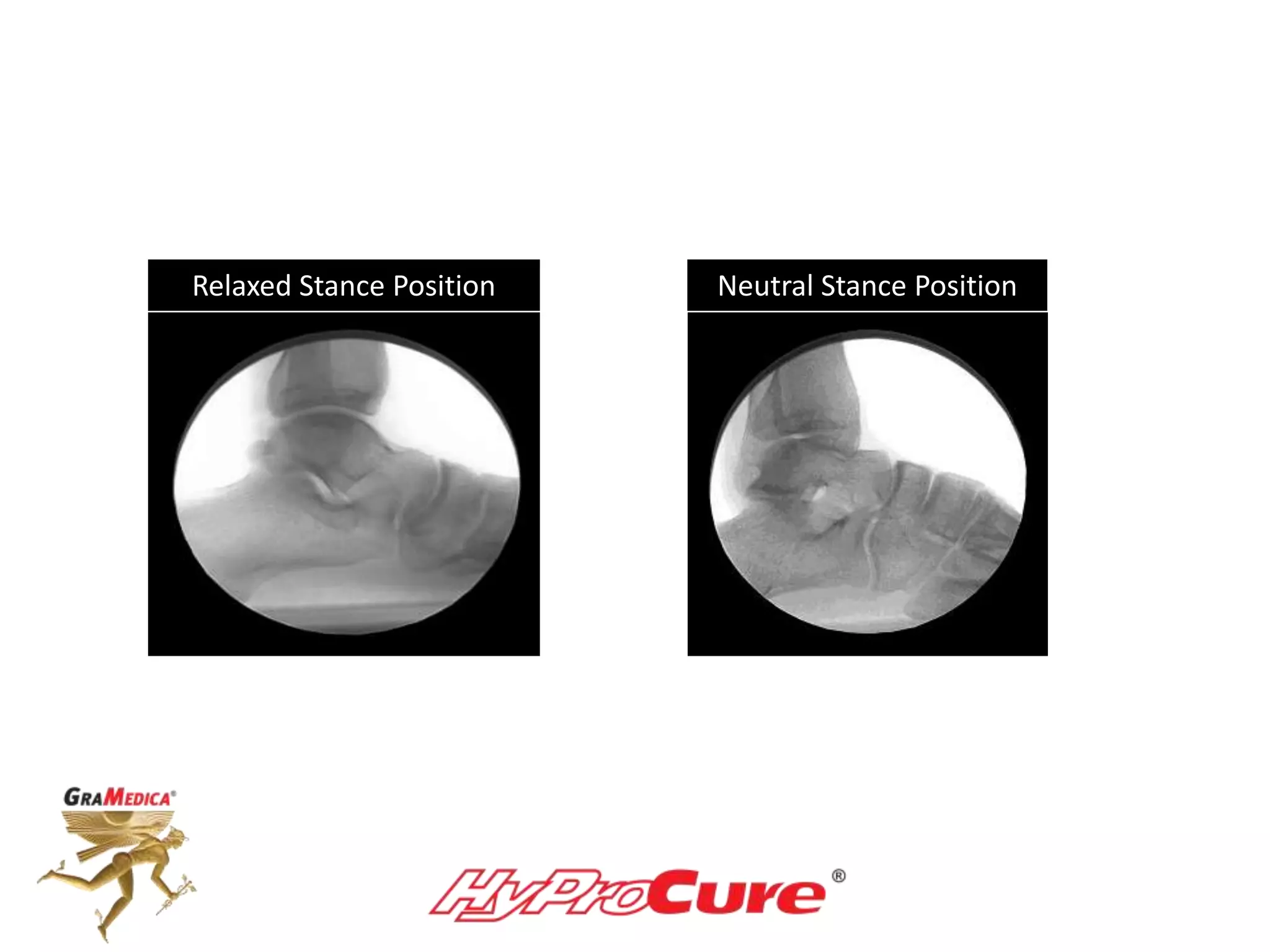
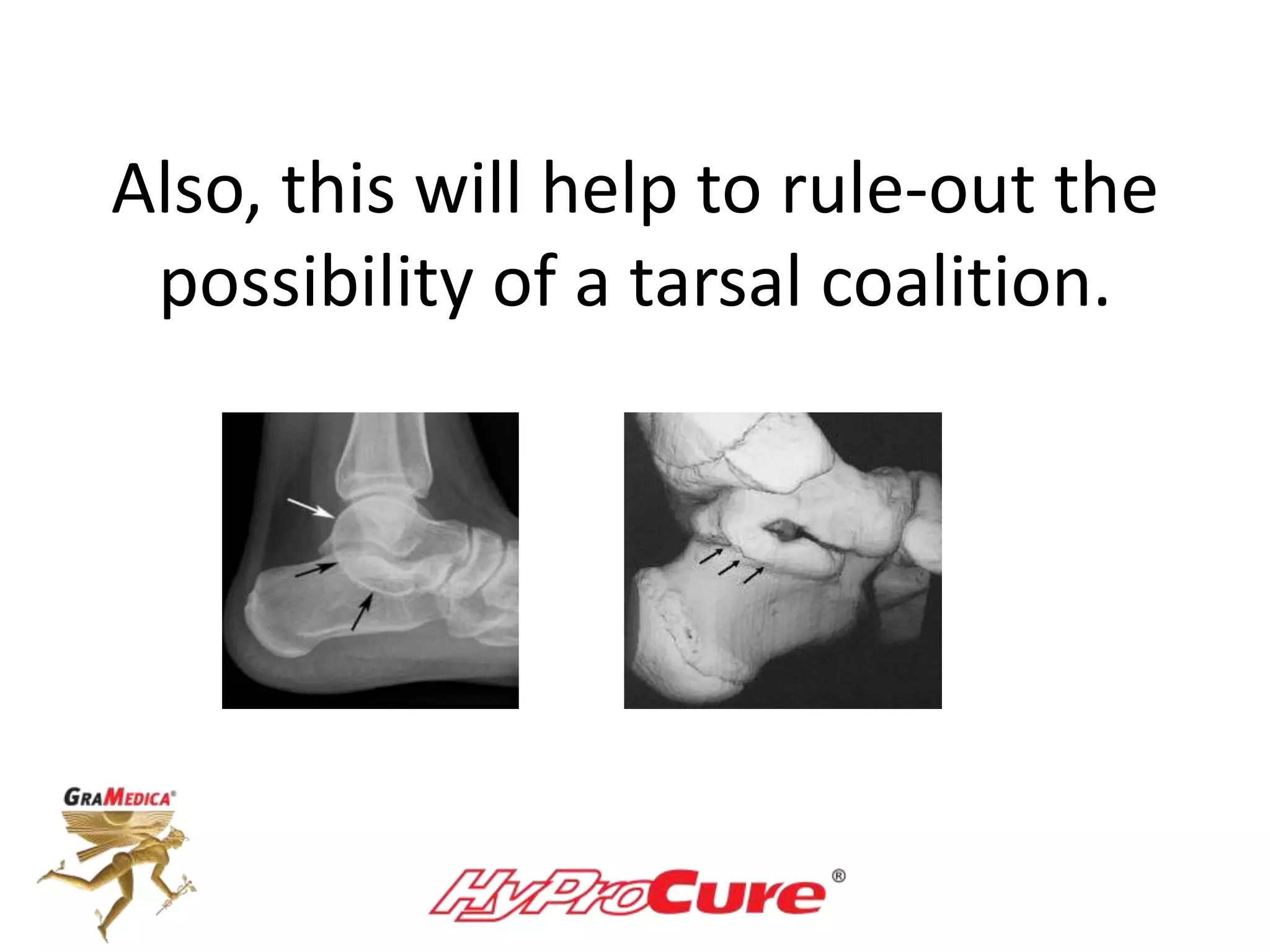
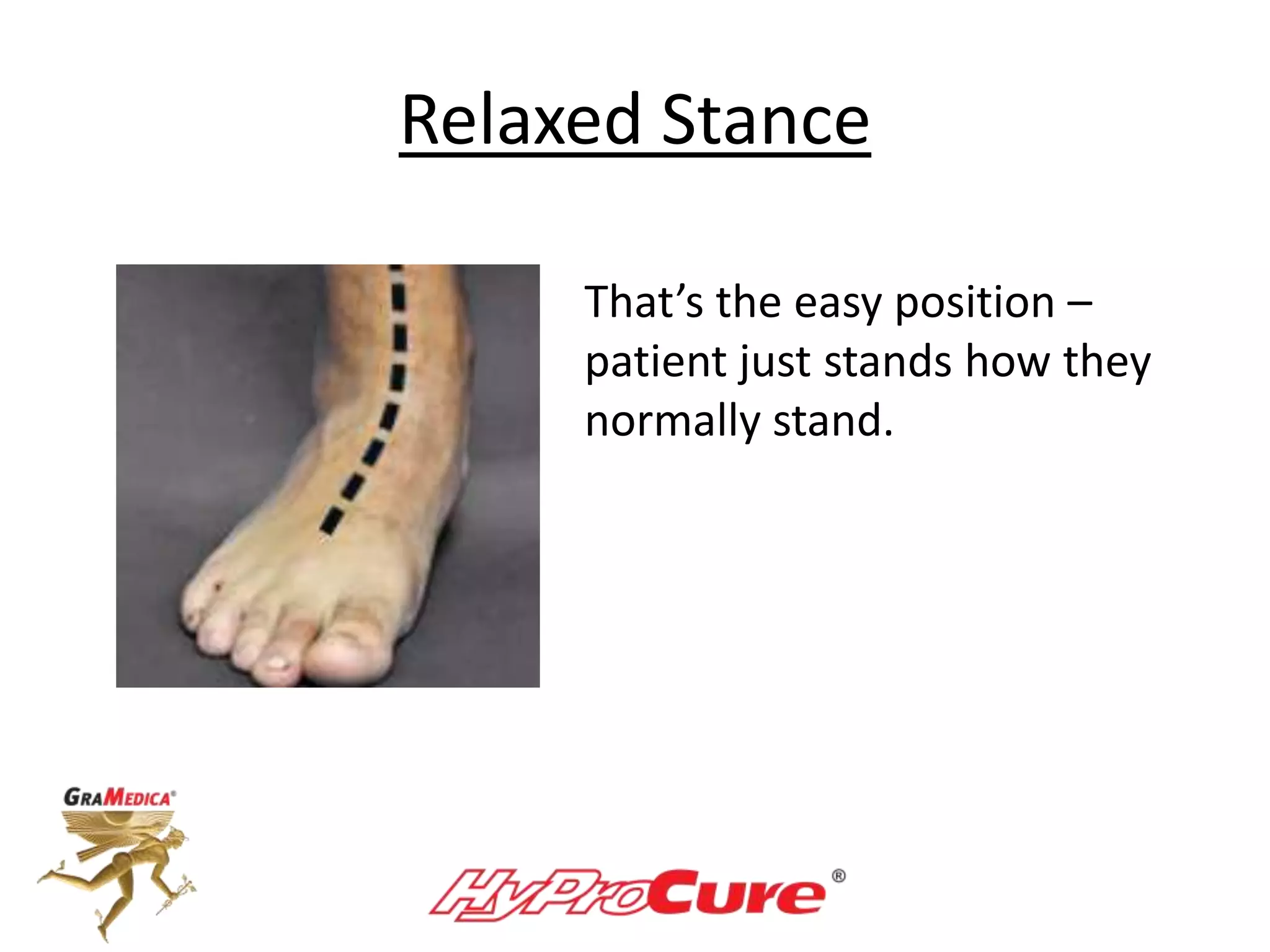
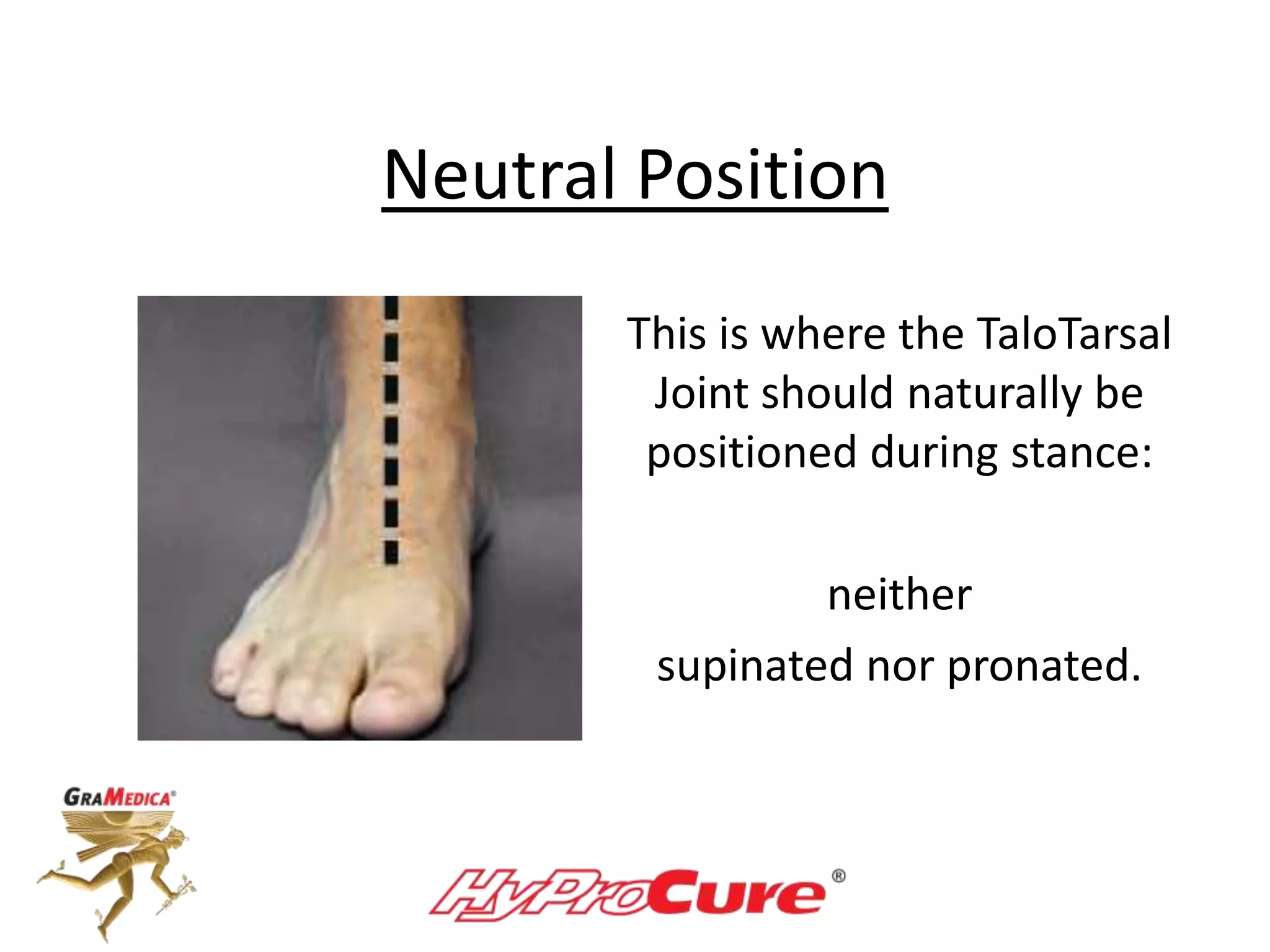
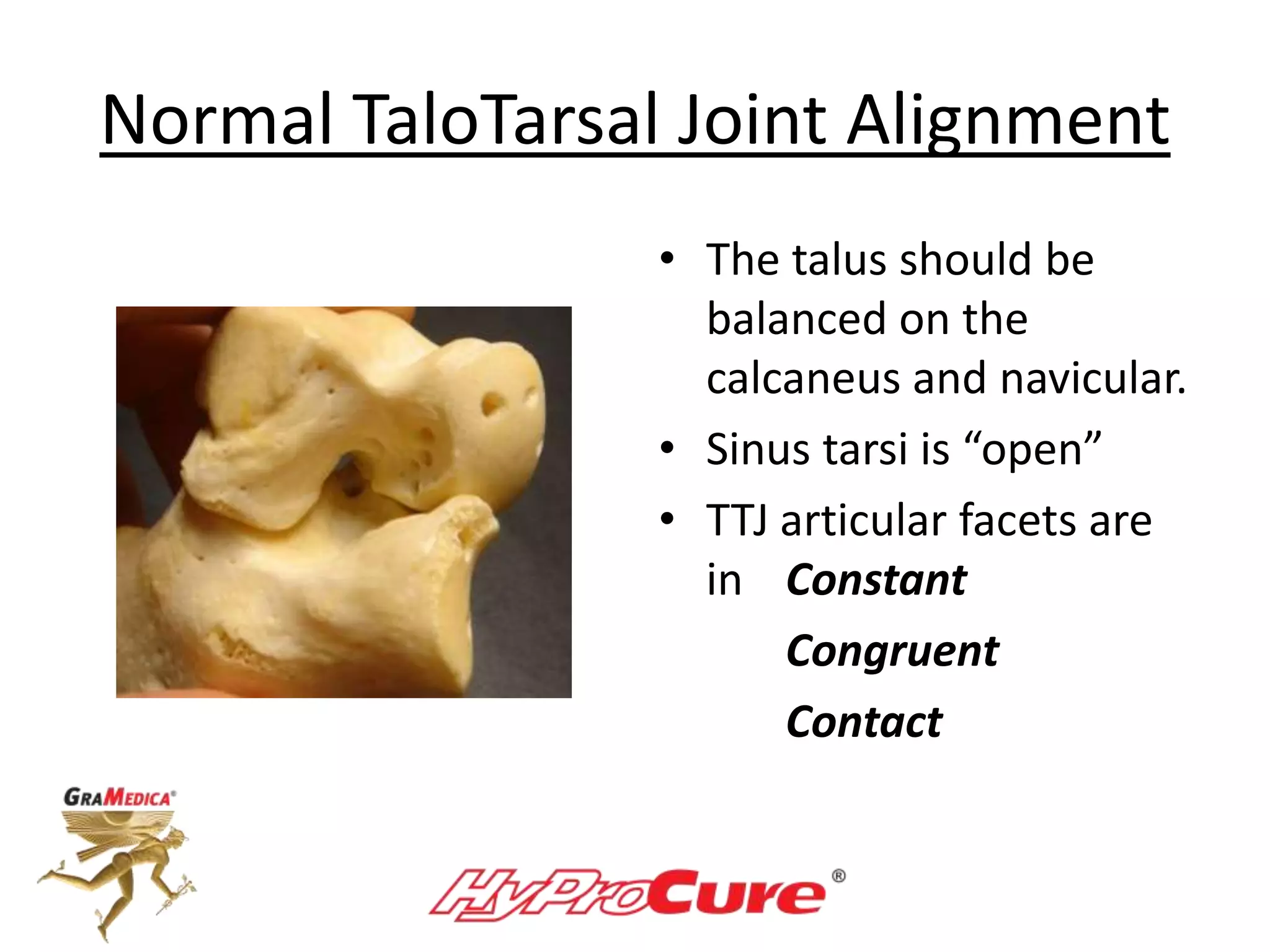
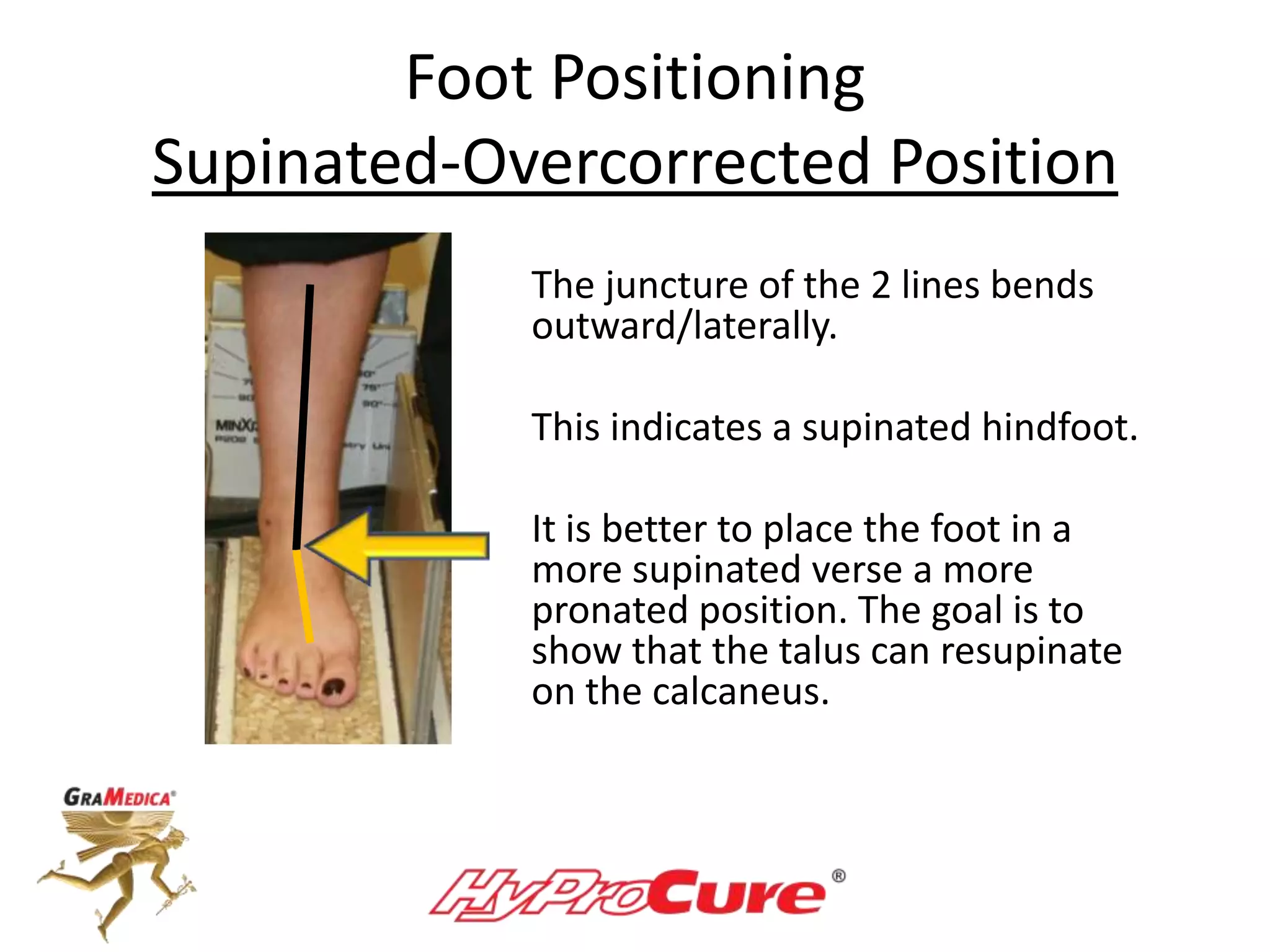
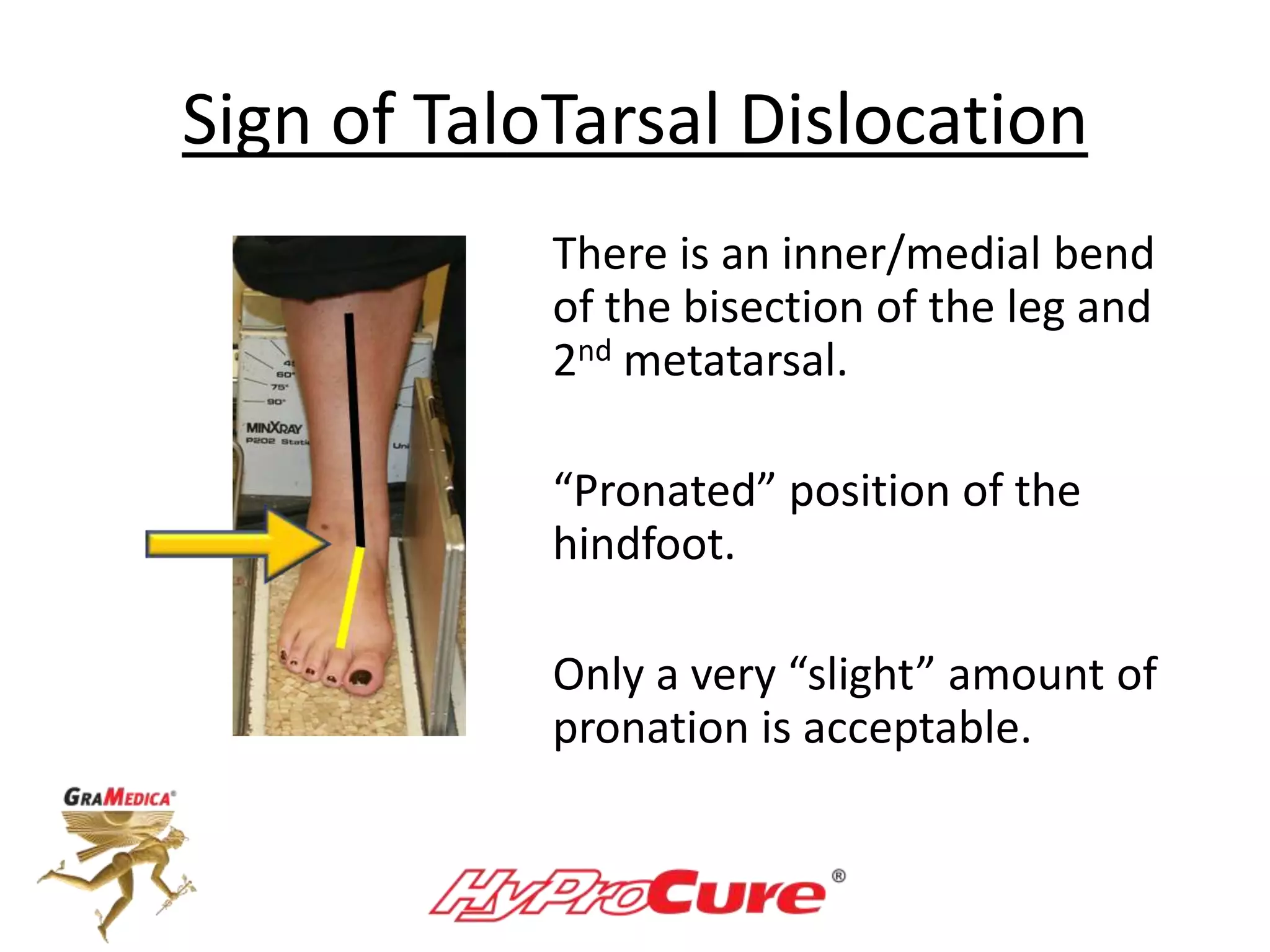
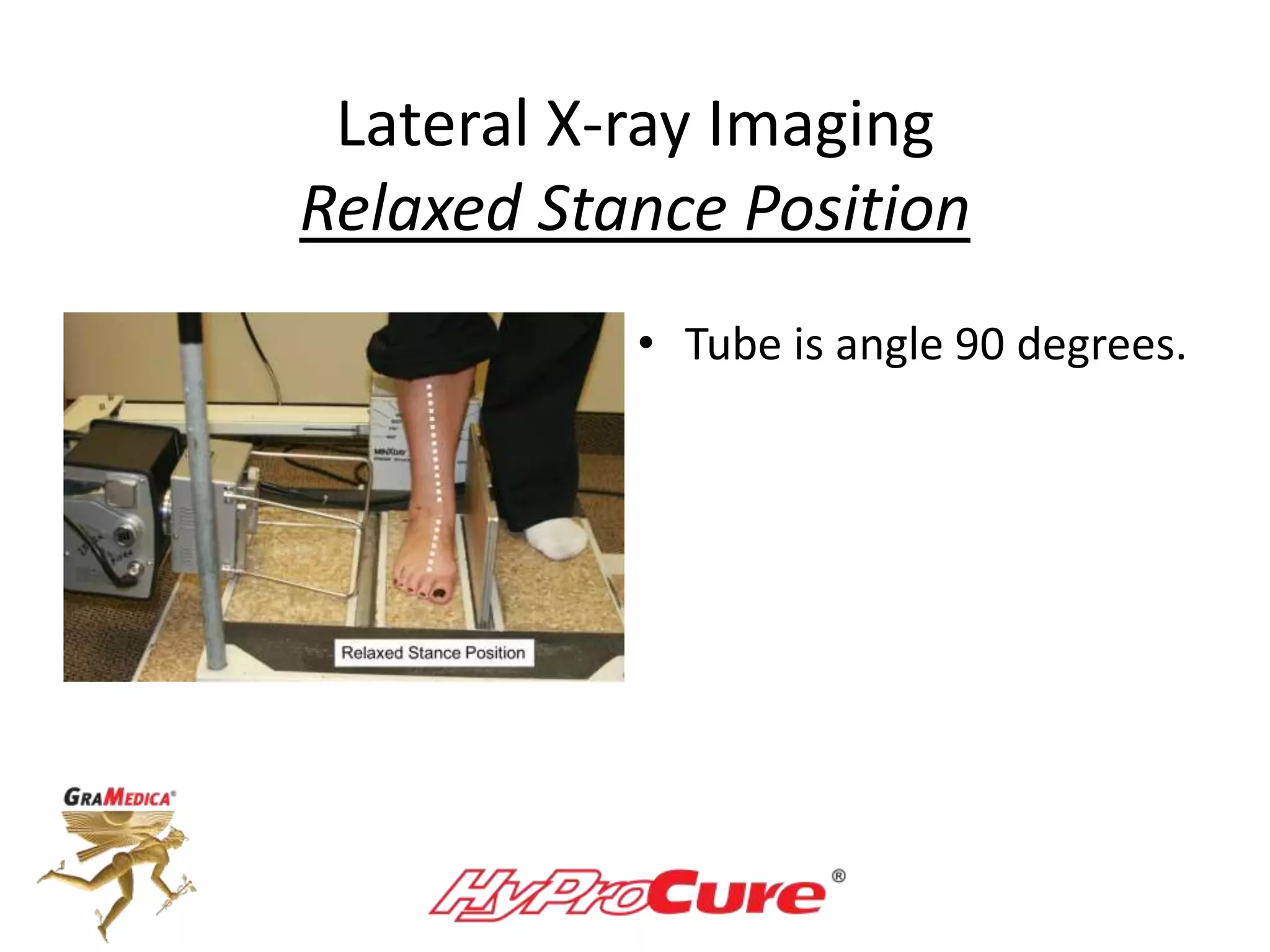
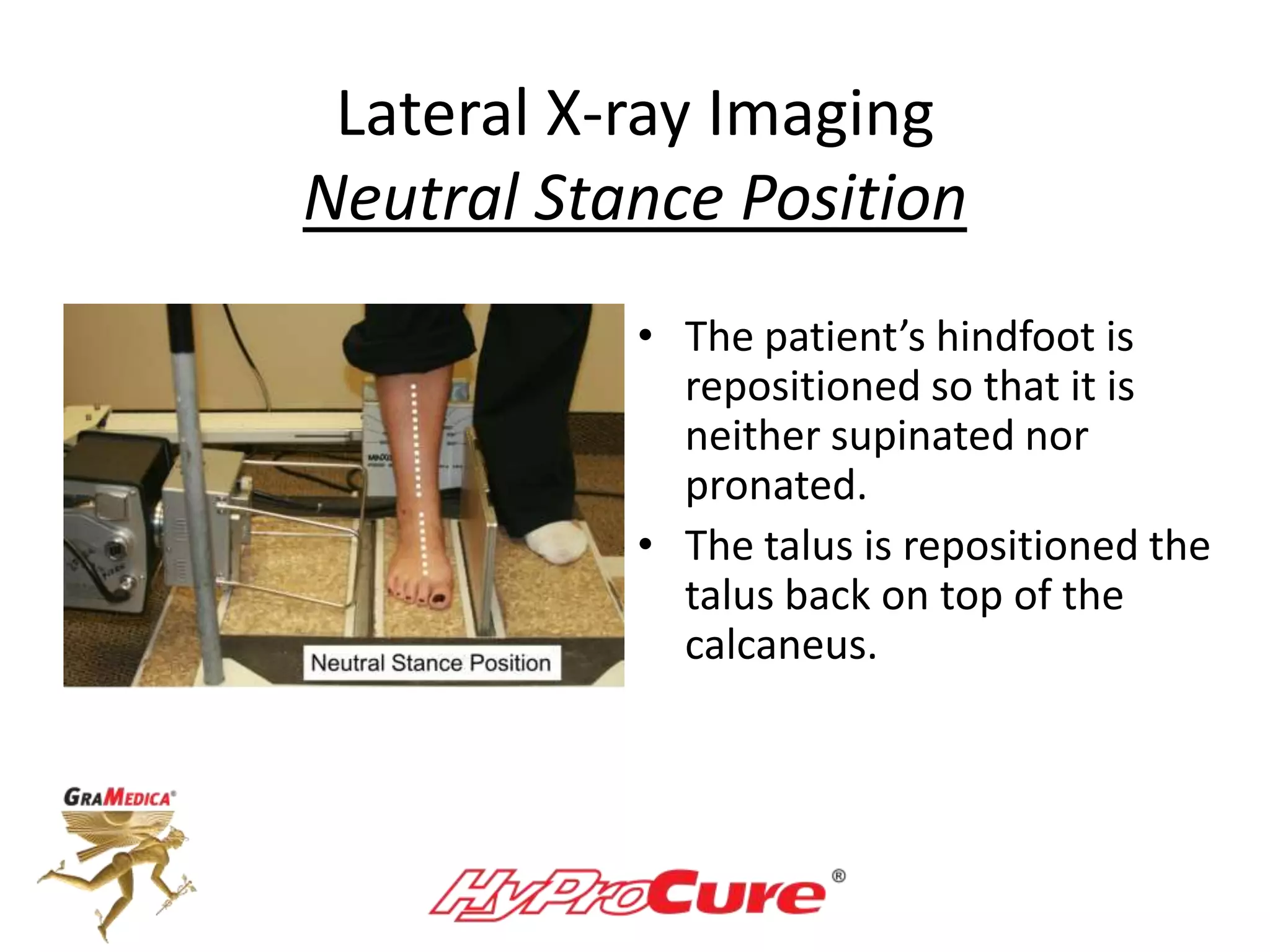
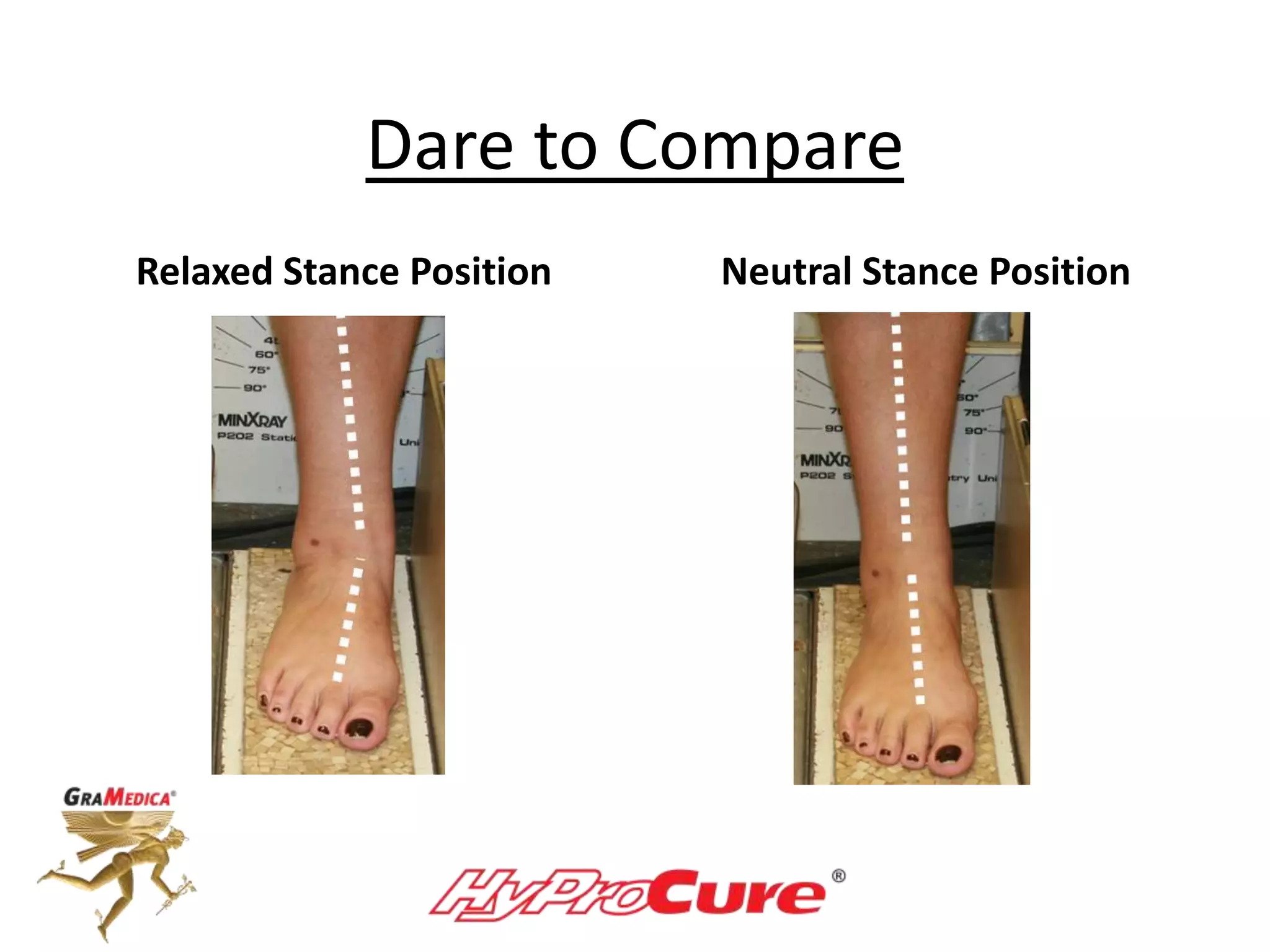
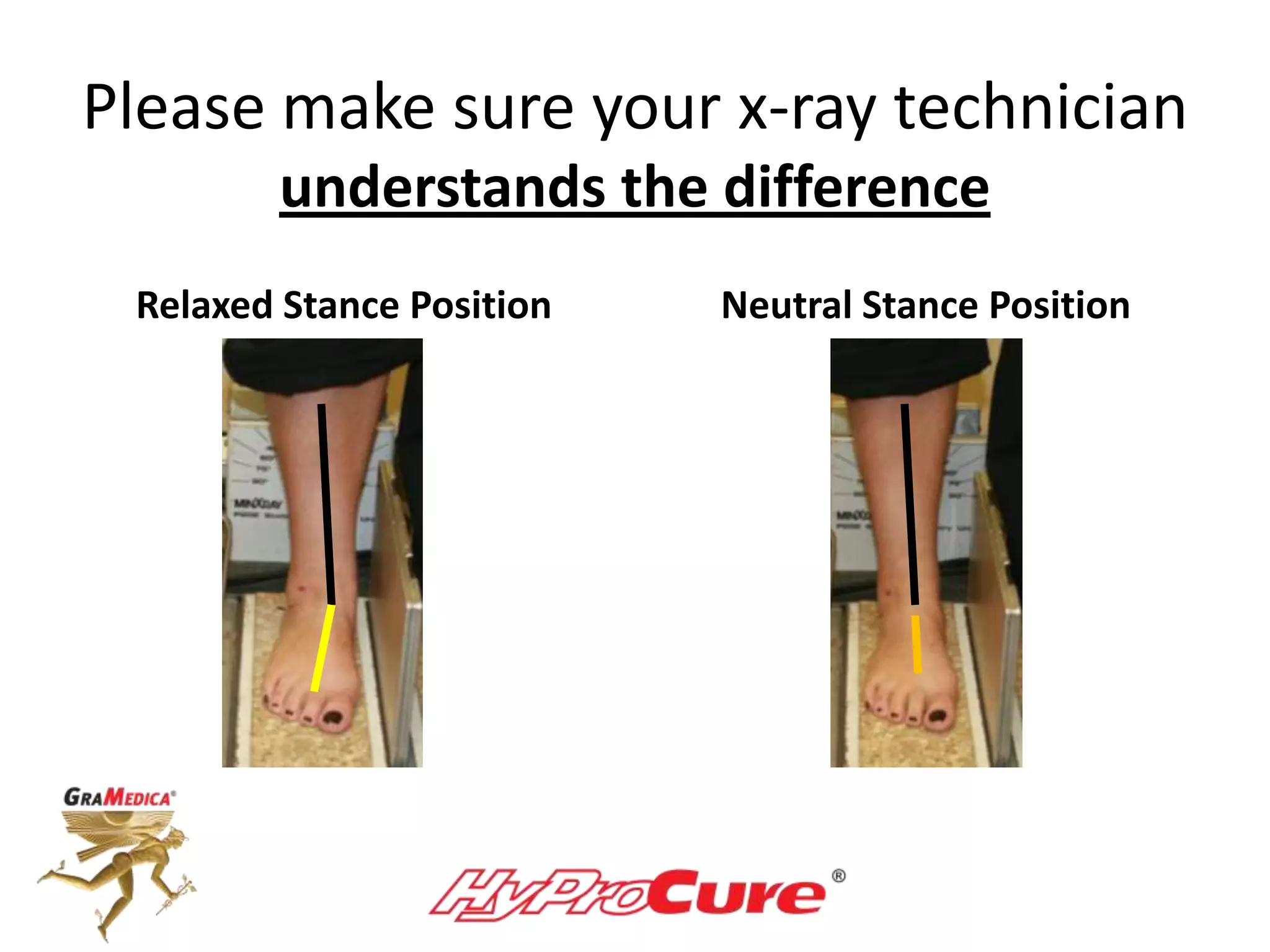
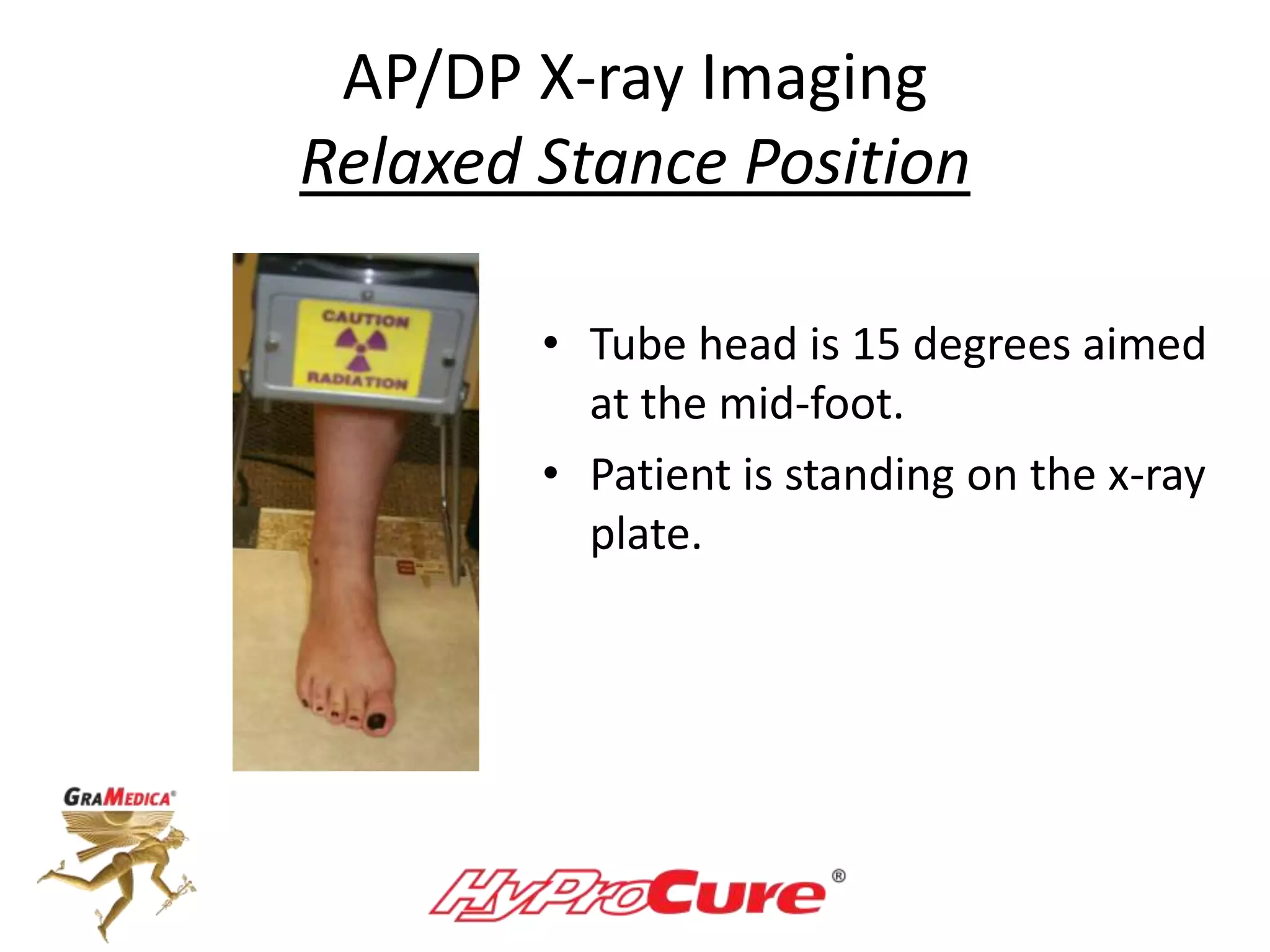
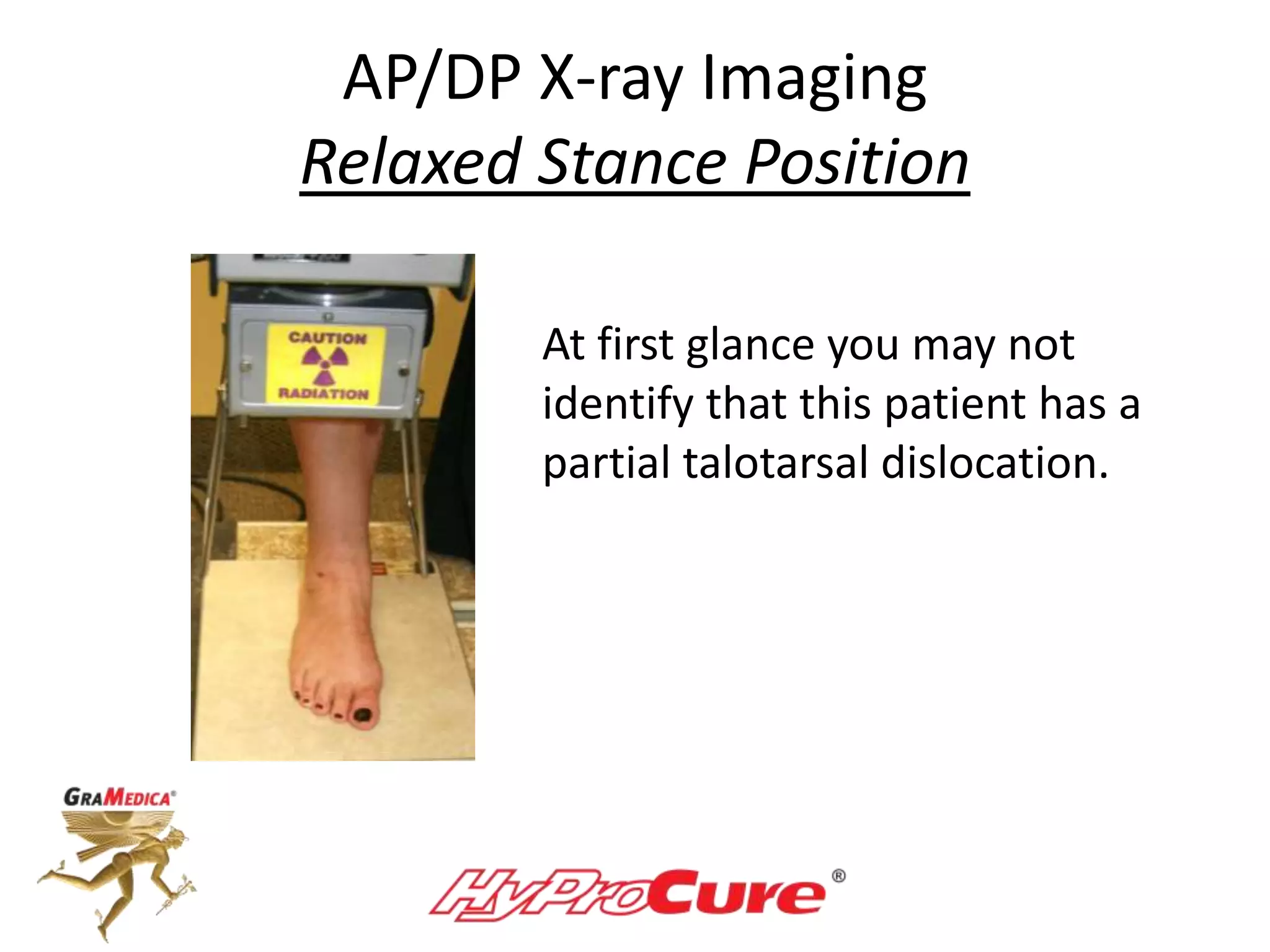
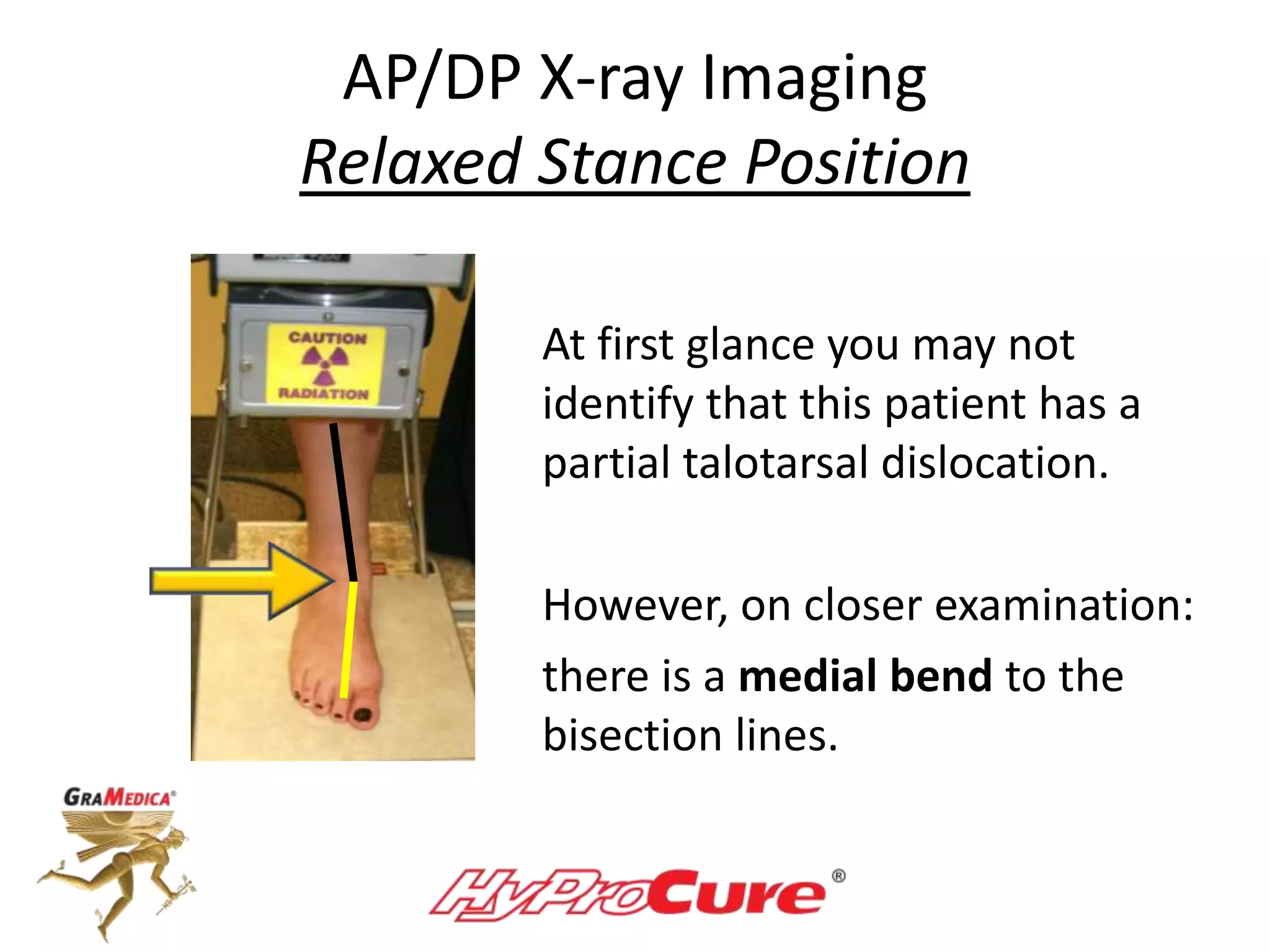
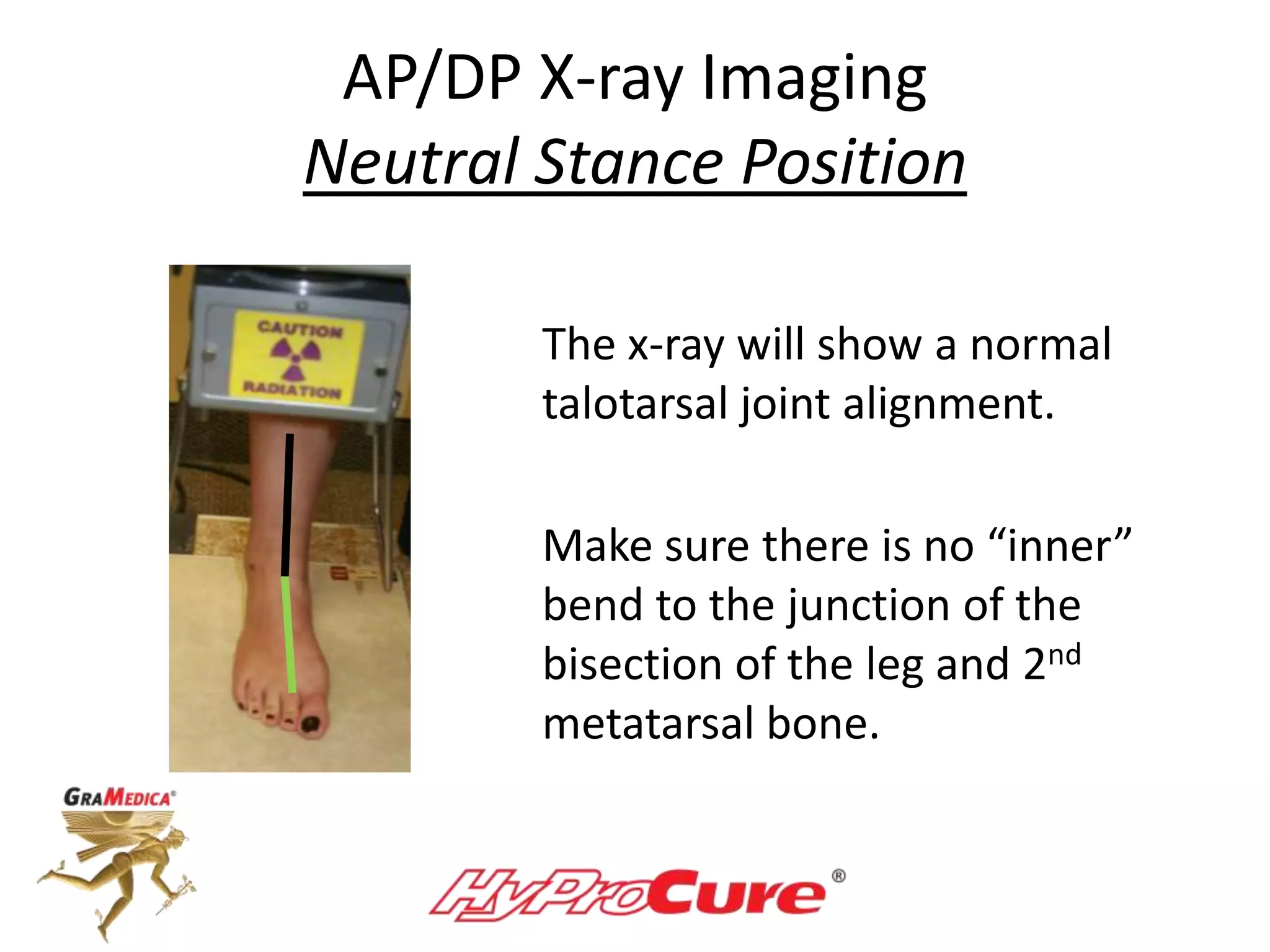
This document provides a guide on obtaining neutral and relaxed stance radiographs of the talotarsal joint to diagnose talotarsal dislocation. It emphasizes the importance of taking comparison views to assess the malleability of the deformity and to rule out secondary issues like tarsal coalition. Clear foot positioning and correct x-ray techniques are crucial for obtaining accurate images to aid in treatment recommendations.