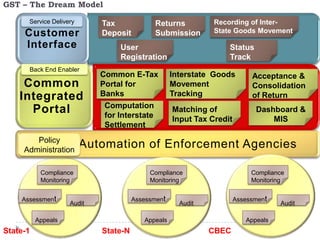
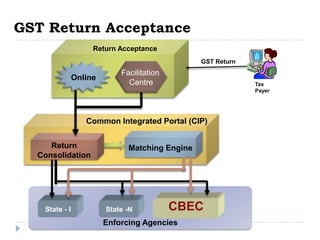
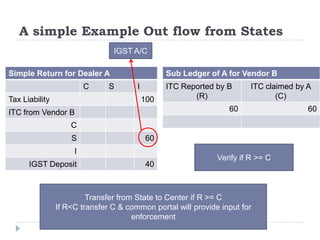
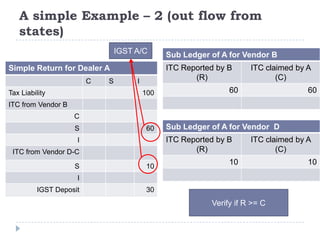
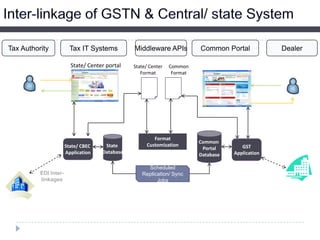
This document provides an overview of GST in India. It discusses the current indirect tax system and its challenges. An ideal GST model is proposed with a single rate across states, a common portal, and integrated ICT solution. The current GST implementation involves a dual GST with CGST and SGST for intra-state and CGST and IGST for inter-state transactions. Significant ICT development is underway including the GSTN portal for registration, returns, and settlement between states. Several policy and technical aspects still need to be decided for full implementation.