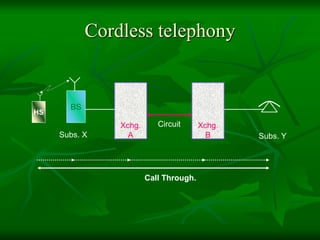
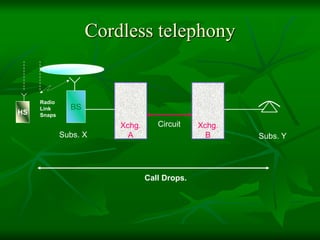
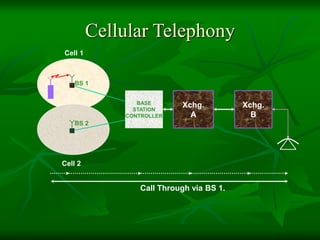
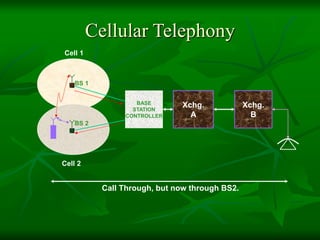
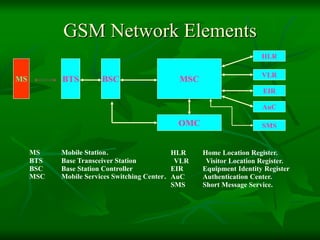
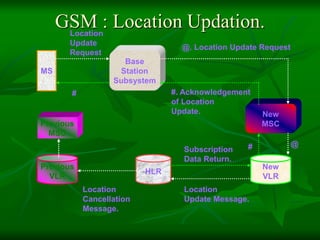
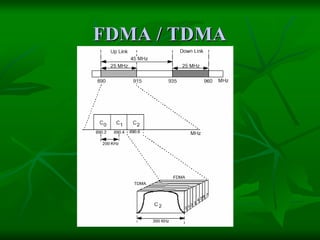
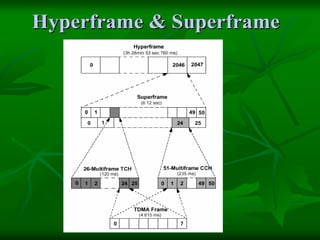
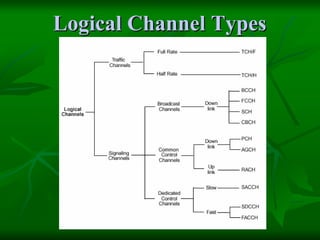
The document provides a comprehensive overview of GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) standards, detailing its objectives, services, and network elements such as mobile stations, base transceiver stations, and various registers. It describes functionalities like call handling, data services, and subscriber authentication, while also outlining the architecture and operation of GSM networks. Key components include the management of speech quality, international roaming, and security measures for mobile communications.