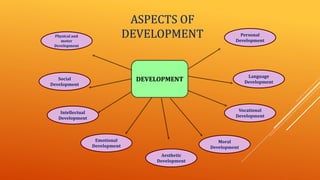
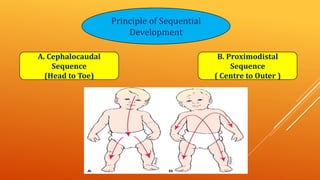
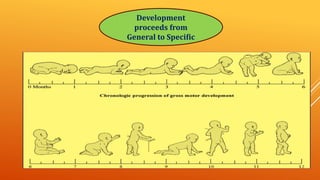
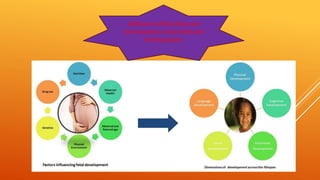
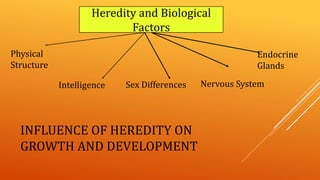
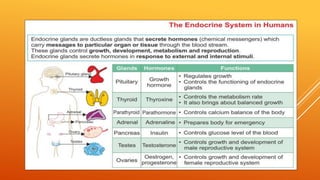
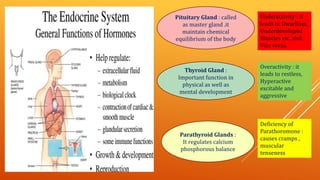
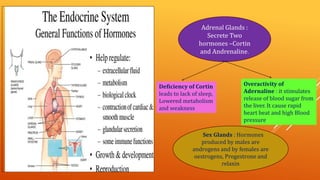
This document discusses growth and development. It defines growth as an increase in size, height, and weight, while development refers to orderly changes towards maturity. Growth is a quantitative change and one aspect of development, whereas development involves qualitative changes and is a continuous, integrated process influenced by both heredity and environment. Some key principles of growth and development discussed are sequential progression from head to toe and general to specific; constancy of individual differences; continuity; interaction between heredity and environment; and development being a product of maturation and learning. The roles of various endocrine glands like the pituitary, thyroid, and sex glands in influencing physical, intellectual, emotional and social development are also summarized.