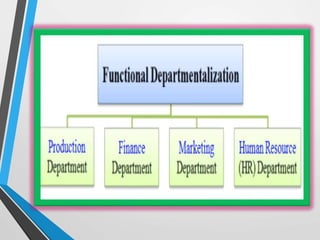
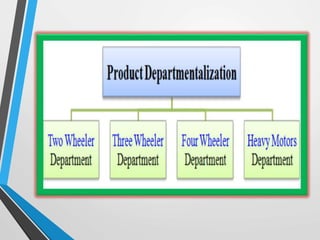
This presentation introduces departmentalization, which is the process of grouping jobs into departments. There are four main types of departmentalization: functional, product, customer, and location. Functional departmentalization groups activities by function, product departmentalization groups by product line, customer departmentalization groups by type of customer, and location departmentalization groups by geography. The presentation provides examples of each type and discusses other considerations for departmentalization, concluding that managers should understand the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches.