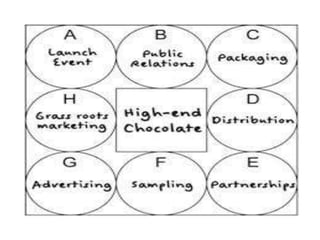
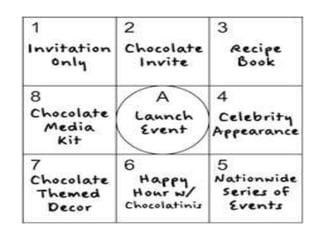
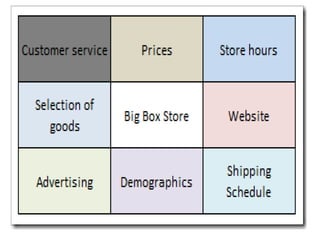
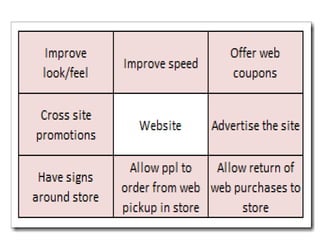
Group discussions are used for recruitment, decision making, and problem solving. They involve an exchange of ideas among individuals in a group setting. Key aspects of effective group discussions include setting guidelines, allowing all members to participate, maintaining focus on the topic, and reaching consensus or a decision. Leadership roles include facilitating participation, ensuring no one dominates, and summarizing discussions. Common techniques used in group discussions are brainstorming, where many ideas are generated, and the Delphi method, which uses anonymous questionnaires with experts.