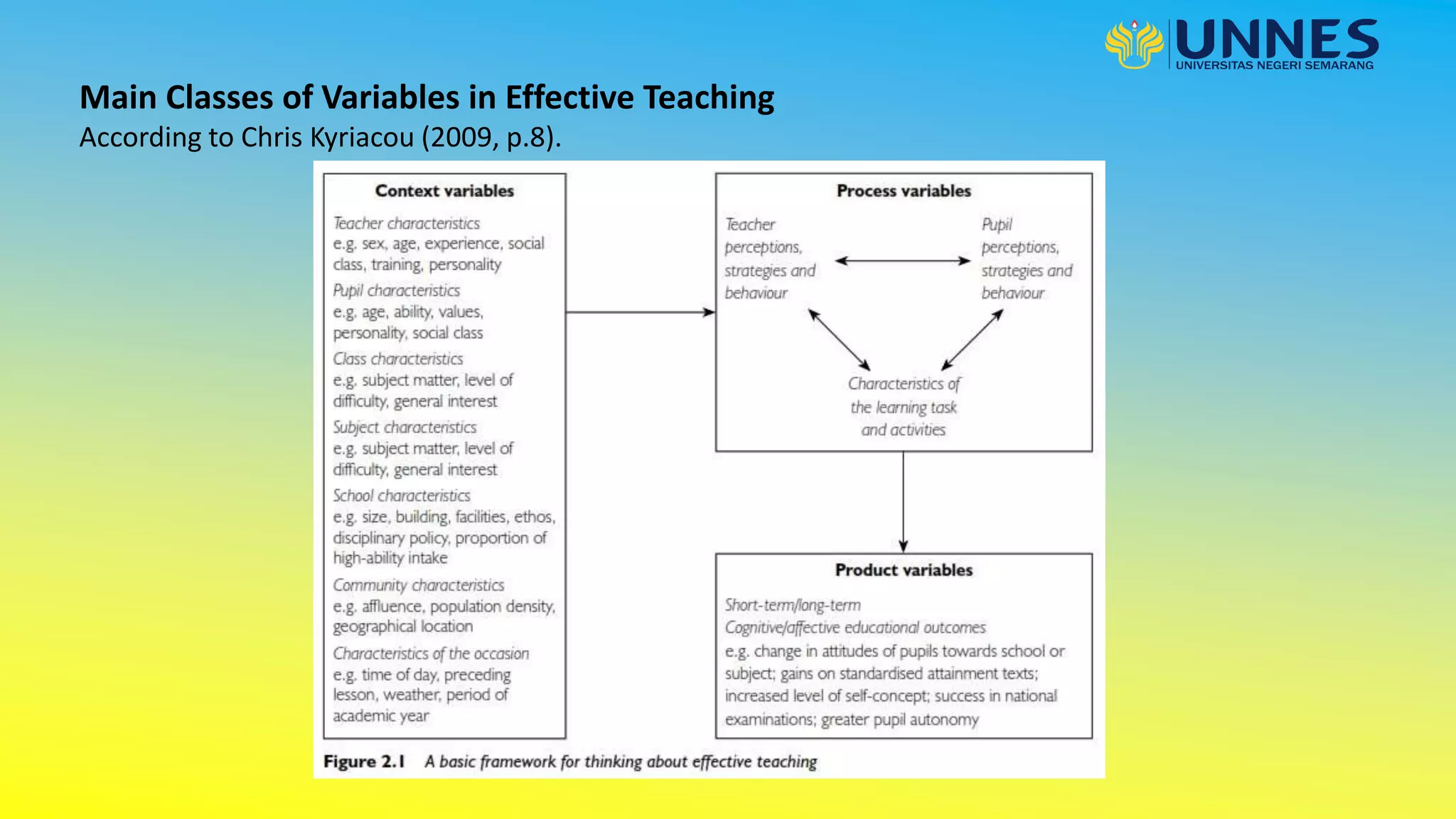
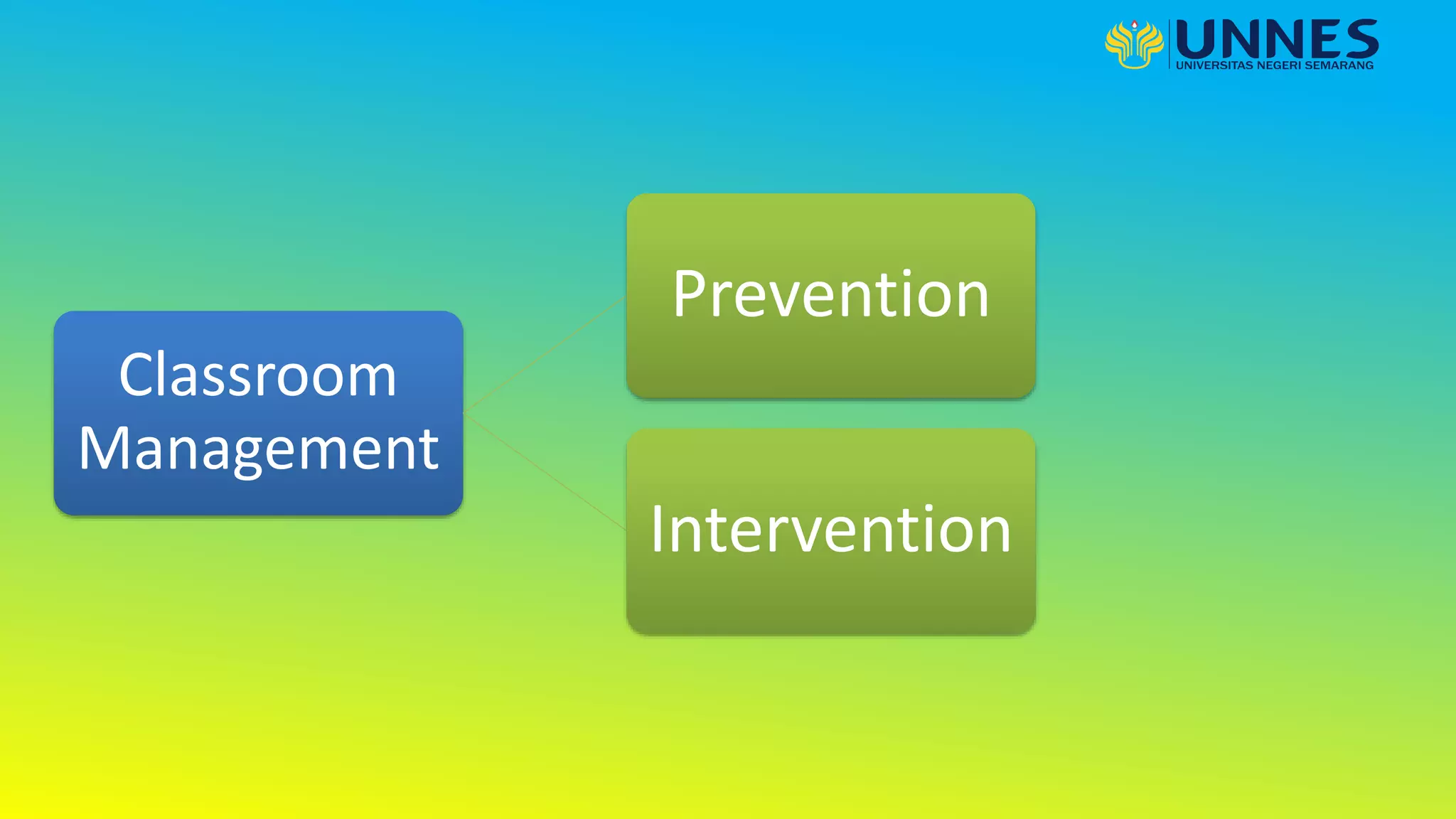
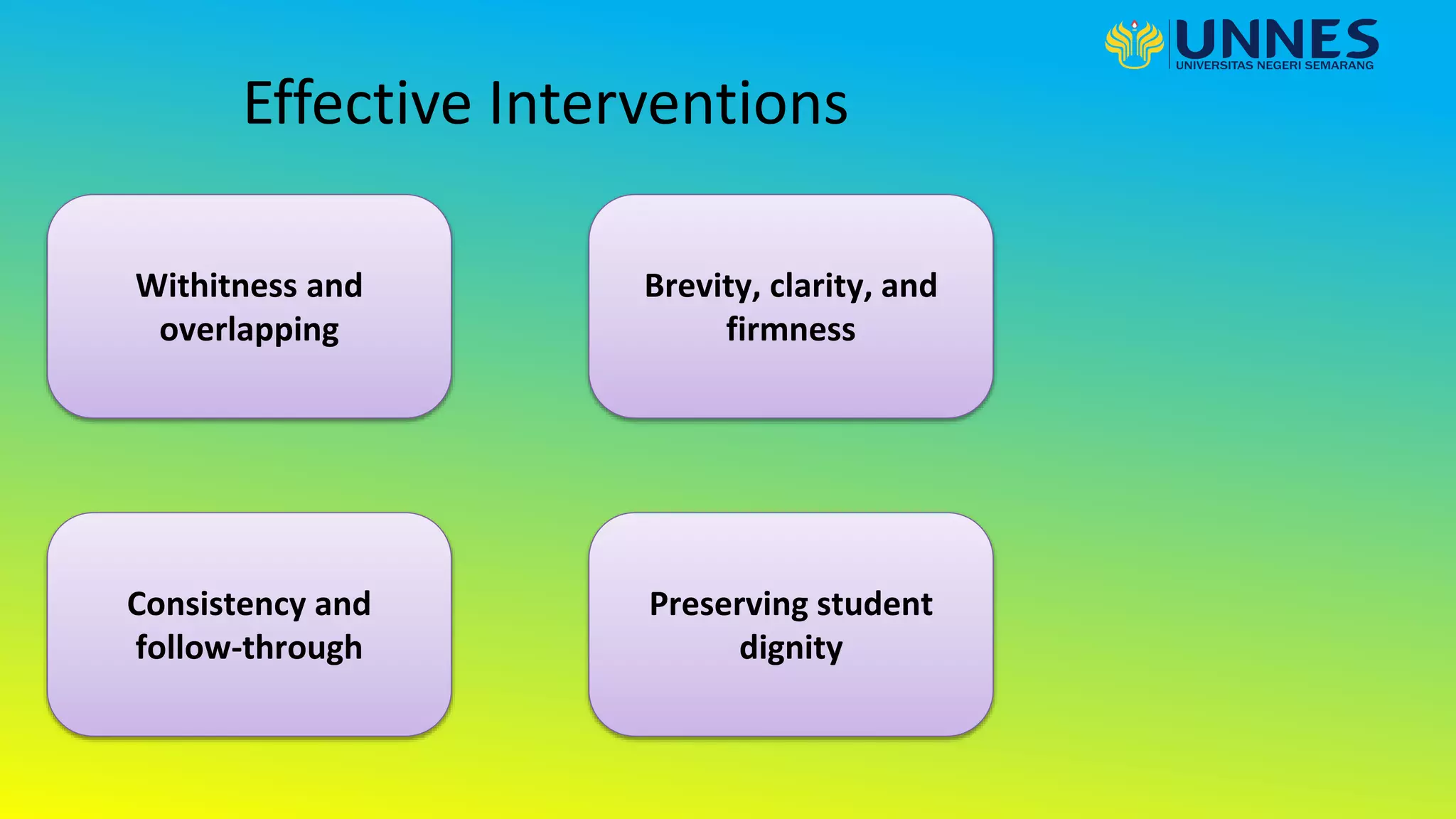
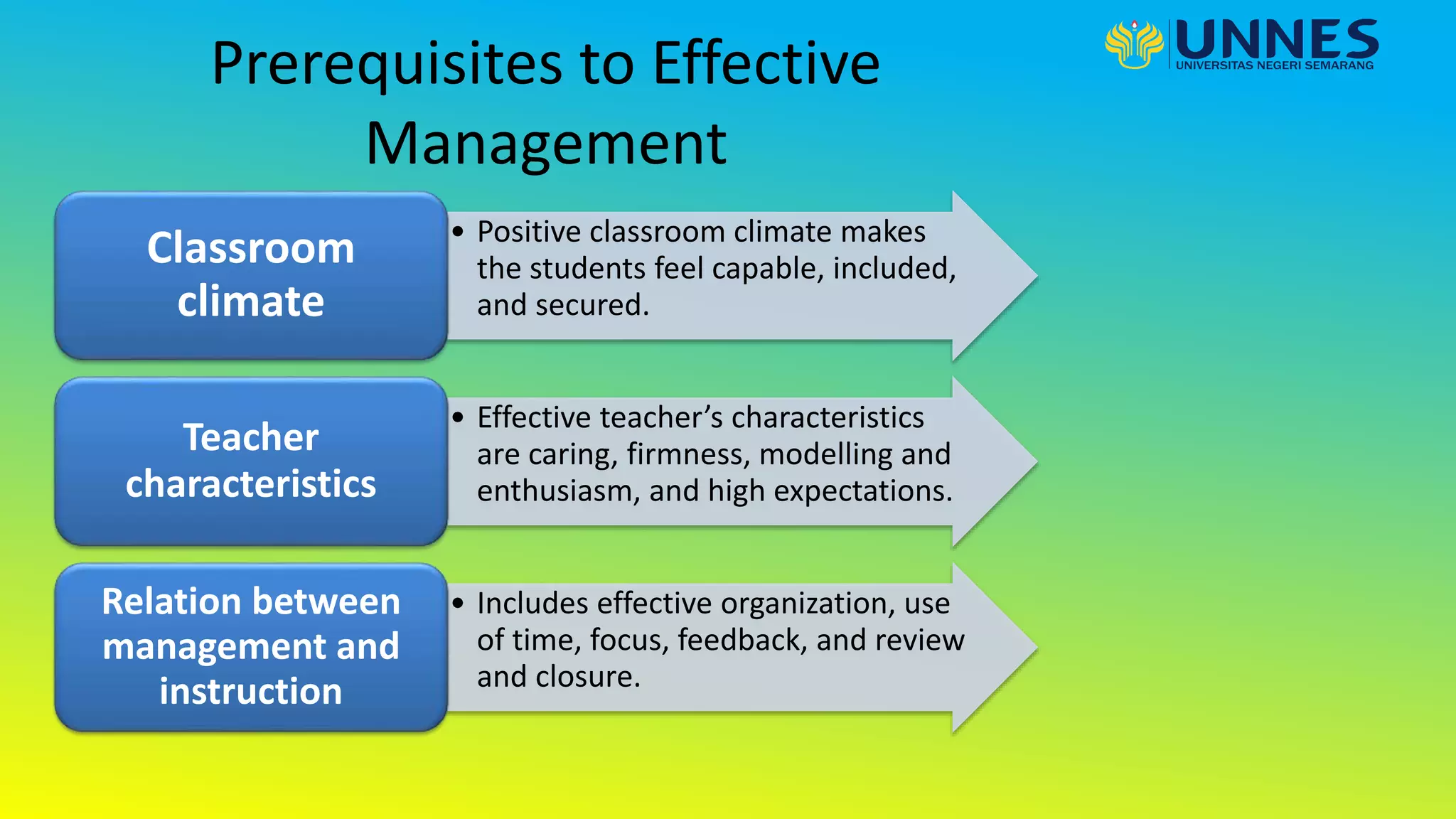
This document discusses effective teaching. It begins by defining effective teaching and listing some of its key features. It then discusses early research on effective teaching which focused on teacher attributes. More recent research examines classroom processes and interactions between teachers and students. Key elements of effective teaching practice include having high expectations, acknowledging individual differences, using a range of pedagogies, encouraging student responsibility, having content mastery, providing a safe environment, monitoring progress and feedback, and building positive relationships. The document also discusses effective classroom management strategies and the role of technology in education.