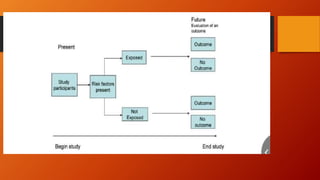
Quantitative designs involve systematically gathering numerical data to investigate phenomena. They can be experimental, involving interventions, or non-experimental via descriptive, analytical, cohort, case-control, cross-sectional, or ecological studies. Quantitative designs are used to test theories, develop models, and identify relationships between variables through statistical analysis. They provide reliable, generalizable data but require large sample sizes and may not explain behaviors.