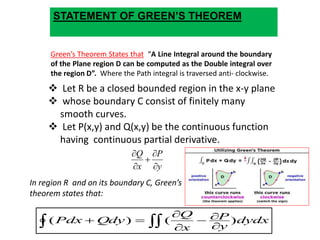
Green's theorem relates a line integral around a simple closed curve C to a double integral over the plane region D bounded by C. It states that a line integral around the boundary of a plane region D can be computed as the double integral over region D, with the path integral traversed counterclockwise. The theorem is proved by dividing the bounding curve C into two parts and expressing the line integrals around each part in terms of their bounding functions, showing they are equal to the double integral over region D.