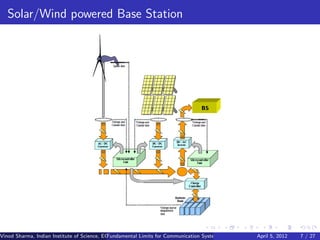
This document discusses communication systems powered by renewable energy sources. It presents three key points:
1) Wireless networks consume a significant amount of energy, motivating the need for green communication techniques.
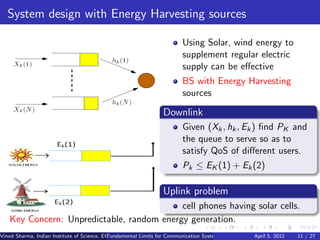
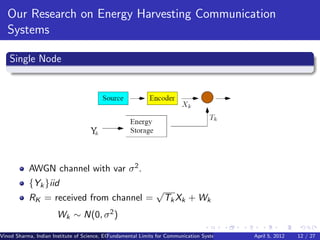
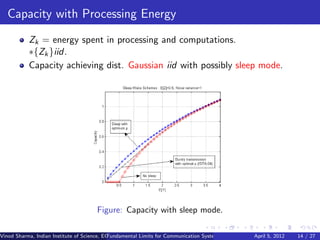
2) Fundamental limits on communication are explored for single nodes and networks powered by unpredictable renewable sources like solar and wind.
3) MAC protocols, scheduling, and routing algorithms are proposed to maximize throughput in energy harvesting multihop networks.








![Single Node: Capacity
Theorem:
When energy is consumed only in transmission,
the capacity = 0.5log (1 + E [Y ]/σ 2 )
Comments
1 Limiting capacity achieving distribution is iid N(0, E [Y ])
2 Capacity is same as that of an AWGN channel with average power
constraint E [Y ].
Vinod Sharma, Indian Institute of Science, ECE ()
Fundamental Limits for Communication Systems with Renewable Energy Sources 13 / 27
April 5, 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinodsharmagreentelecomit-120420001617-phpapp02/85/Green-Telecom-IT-Vinod-sharma-Green-Telecom-13-320.jpg)
![Single Node with Data Buffer
{Xk } stationary, ergodic
{YK } stationary, ergodic
TK = min(EK , E [Y ] − ), > 0 (1)
Theorem:
If E [X ] < g (E [Y ] − ), g cont., non decreasing, concave then data queue
is stable.
(1) is throughput optimal policy.
But it is not delay optimal
Vinod Sharma, Indian Institute of Science, ECE ()
Fundamental Limits for Communication Systems with Renewable Energy Sources 15 / 27
April 5, 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinodsharmagreentelecomit-120420001617-phpapp02/85/Green-Telecom-IT-Vinod-sharma-Green-Telecom-15-320.jpg)
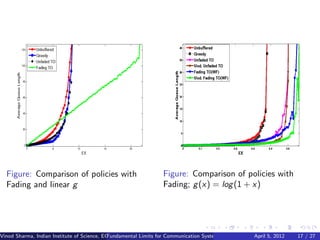
![Single Node
Greedy Policy
Tk = min(Ek , g −1 (qk )) (2)
Theorem
If E [X ] < E [g (Y )] and energy buffer is finite, then under (2) data queue
is stable.
Theorem
If g is linear then (2) is delay optimal and throughput optimal.
Vinod Sharma, Indian Institute of Science, ECE ()
Fundamental Limits for Communication Systems with Renewable Energy Sources 16 / 27
April 5, 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinodsharmagreentelecomit-120420001617-phpapp02/85/Green-Telecom-IT-Vinod-sharma-Green-Telecom-16-320.jpg)
![Combining Queing Theory and Information Theory
Theorem
Reliable Communication with stable data queue is possible iff
E [A] < 1 log 1 + Eσ2 ] .
2
[Y
Vinod Sharma, Indian Institute of Science, ECE ()
Fundamental Limits for Communication Systems with Renewable Energy Sources 18 / 27
April 5, 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinodsharmagreentelecomit-120420001617-phpapp02/85/Green-Telecom-IT-Vinod-sharma-Green-Telecom-18-320.jpg)
![Information Theoretic Capacity
1 E [Y (1)]
R1 log 1+
2 σ2
1 E [Y (2)]
R2 log 1+
2 σ2
1 E [Y (1) + E [Y (2)]
R1 + R2 log 1+
2 σ2
Vinod Sharma, Indian Institute of Science, ECE ()
Fundamental Limits for Communication Systems with Renewable Energy Sources 20 / 27
April 5, 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinodsharmagreentelecomit-120420001617-phpapp02/85/Green-Telecom-IT-Vinod-sharma-Green-Telecom-20-320.jpg)
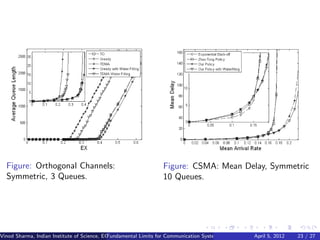
![Opportunistic Scheduling for Fading Channels: Orthogonal
Channels
Hk (i) = channel gain of Qi in slot k
Throughput optimal policy:
Choose queue with index
∗
ik = argmax(qk (i)gi (Hk (i)(fracE [Y (i)] − α(i))))
∗
E [Y (ik )]−
and use Tk = ∗
α(ik )
∗ ∗
α(ik ) = fraction of time slots assigned to ik estimated via LMS.
Vinod Sharma, Indian Institute of Science, ECE ()
Fundamental Limits for Communication Systems with Renewable Energy Sources 21 / 27
April 5, 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinodsharmagreentelecomit-120420001617-phpapp02/85/Green-Telecom-IT-Vinod-sharma-Green-Telecom-21-320.jpg)
![Opportunistic Scheduling: CDMA
Zigbee, WIFI use CSMA.
Choose backoff timer of Qi as
f (qk (i)gi (hk (i) E [Y (i)]− ))
α(i)
f non-increasing
Vinod Sharma, Indian Institute of Science, ECE ()
Fundamental Limits for Communication Systems with Renewable Energy Sources 22 / 27
April 5, 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinodsharmagreentelecomit-120420001617-phpapp02/85/Green-Telecom-IT-Vinod-sharma-Green-Telecom-22-320.jpg)