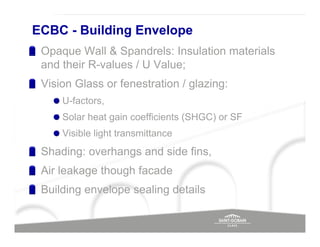
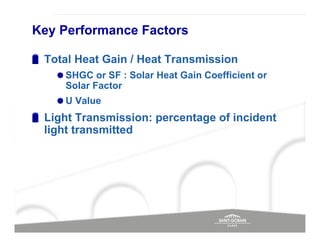
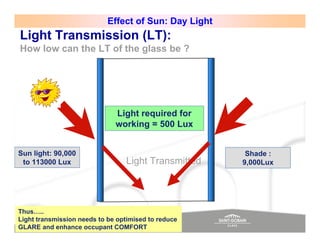
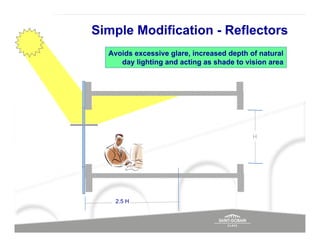
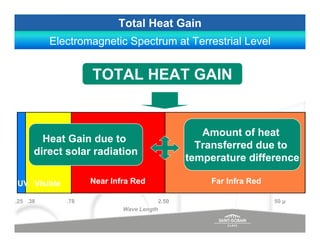
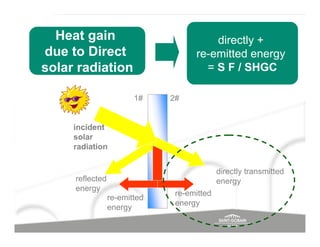
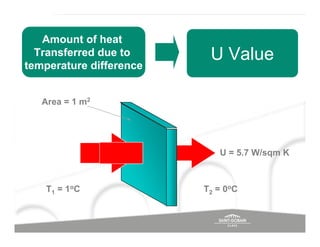
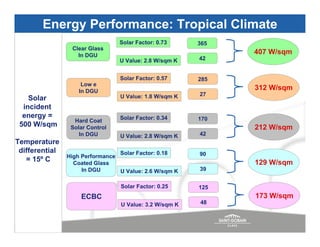
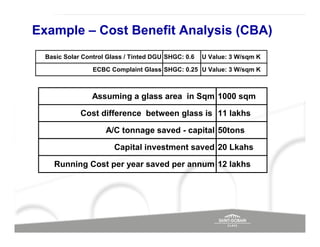
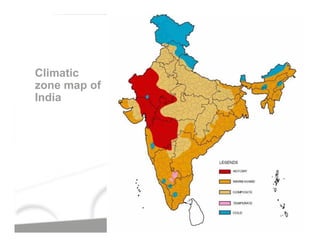
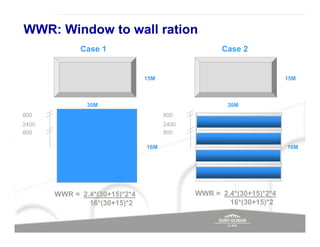
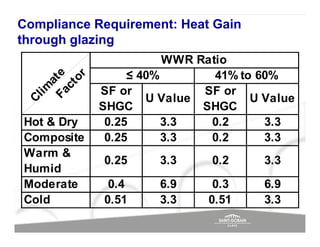
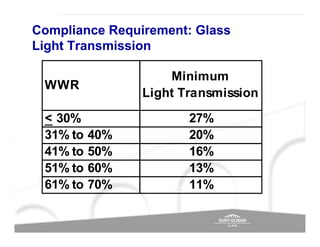
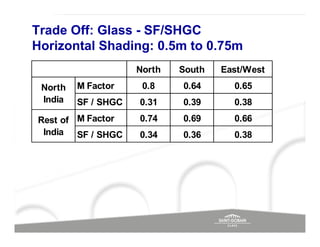
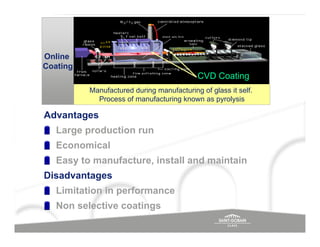
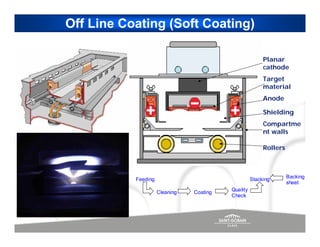
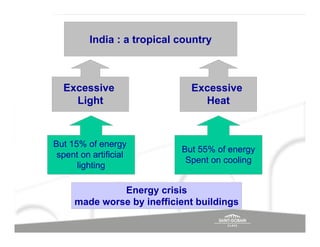
The document discusses energy efficient building envelopes from the perspective of the Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC) in India. It covers key factors related to the building envelope that impact energy efficiency, such as opaque walls and spandrels, vision glass or fenestration, shading, and air leakage. Specific parameters discussed include insulation R-values, U-values, solar heat gain coefficients (SHGC), visible light transmittance, and building envelope sealing details. The benefits of using glass systems in construction are outlined. Key performance factors for glass like total heat gain, light transmission, and strategies to control daylight and energy are summarized.