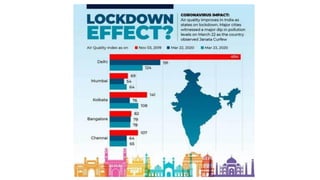
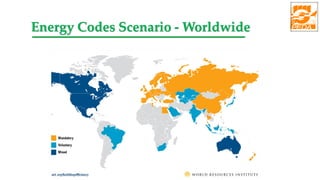
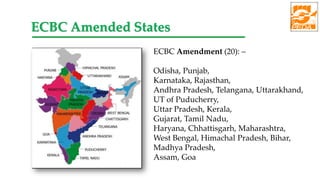
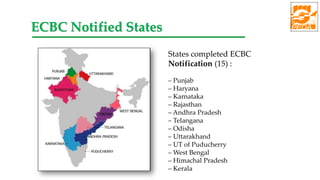
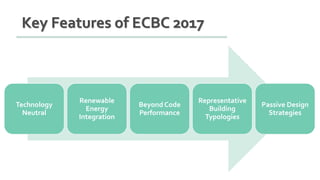
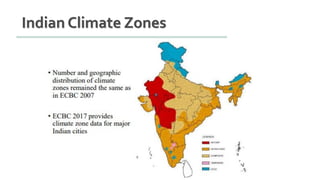
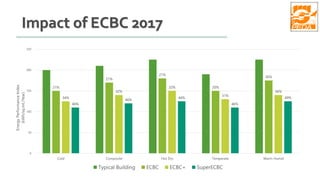
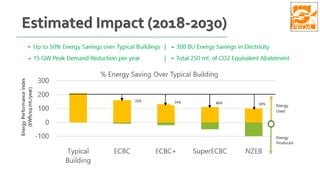
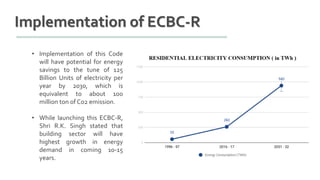
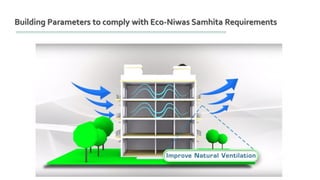
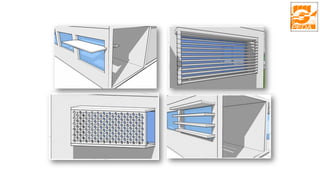
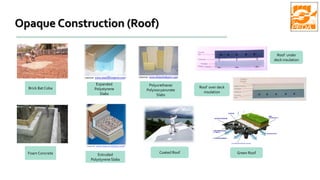
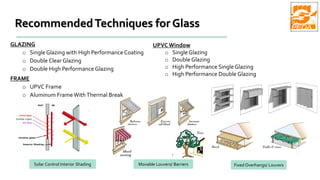
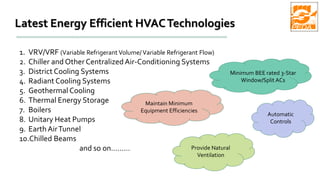
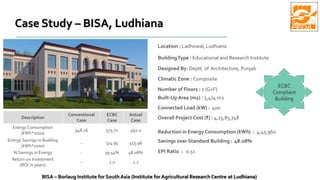
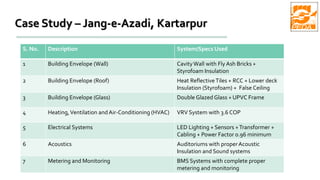
The document provides information about ECBC (Energy Conservation Building Code), which specifies energy performance requirements for commercial buildings in India. It discusses key aspects of ECBC such as its objectives, scope, components, impact in reducing energy consumption, implementation in various states, and case studies of ECBC compliant buildings showing significant energy savings. ECBC aims to minimize energy use and carbon emissions from buildings through passive design strategies and efficient technologies.