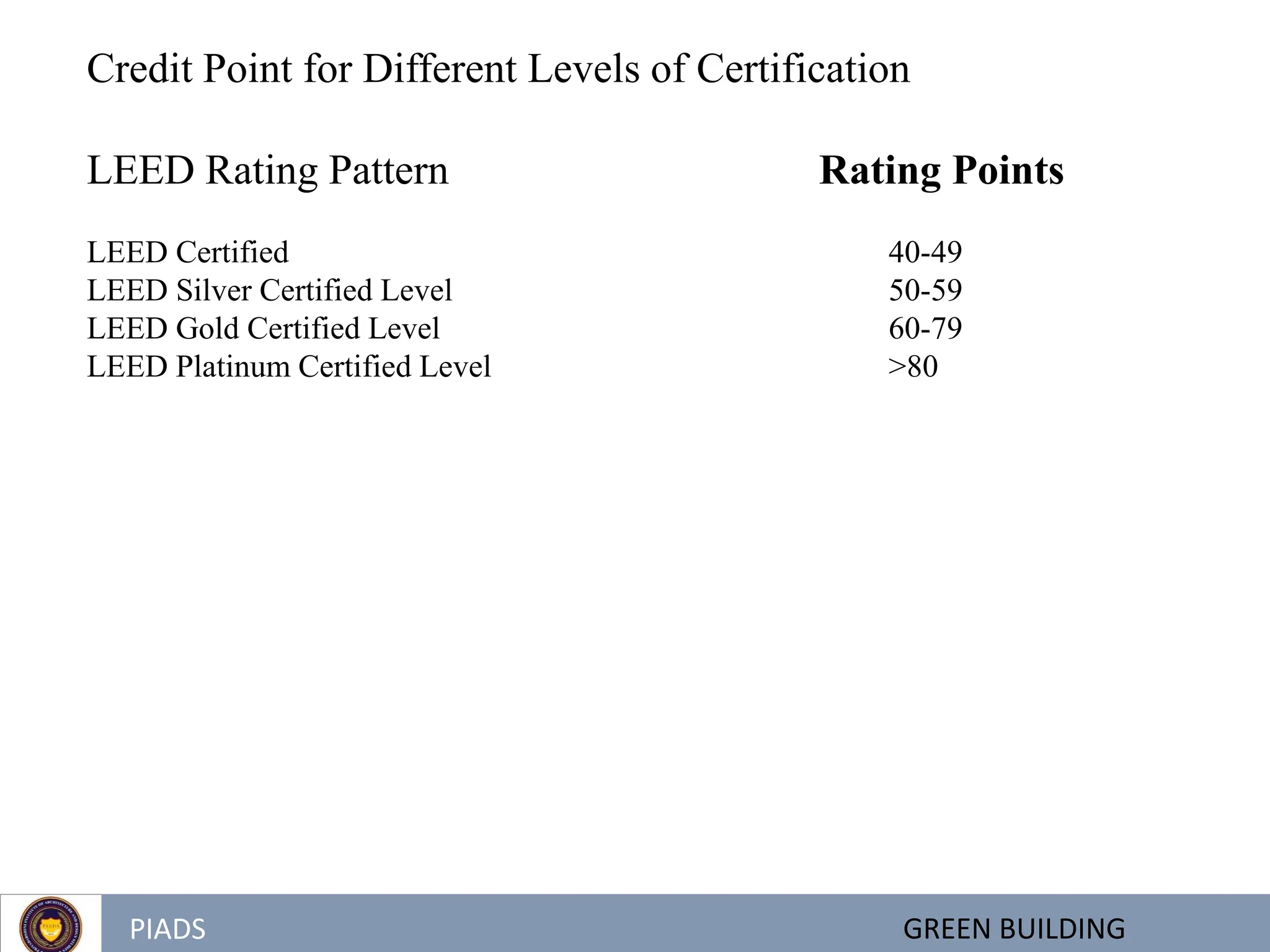
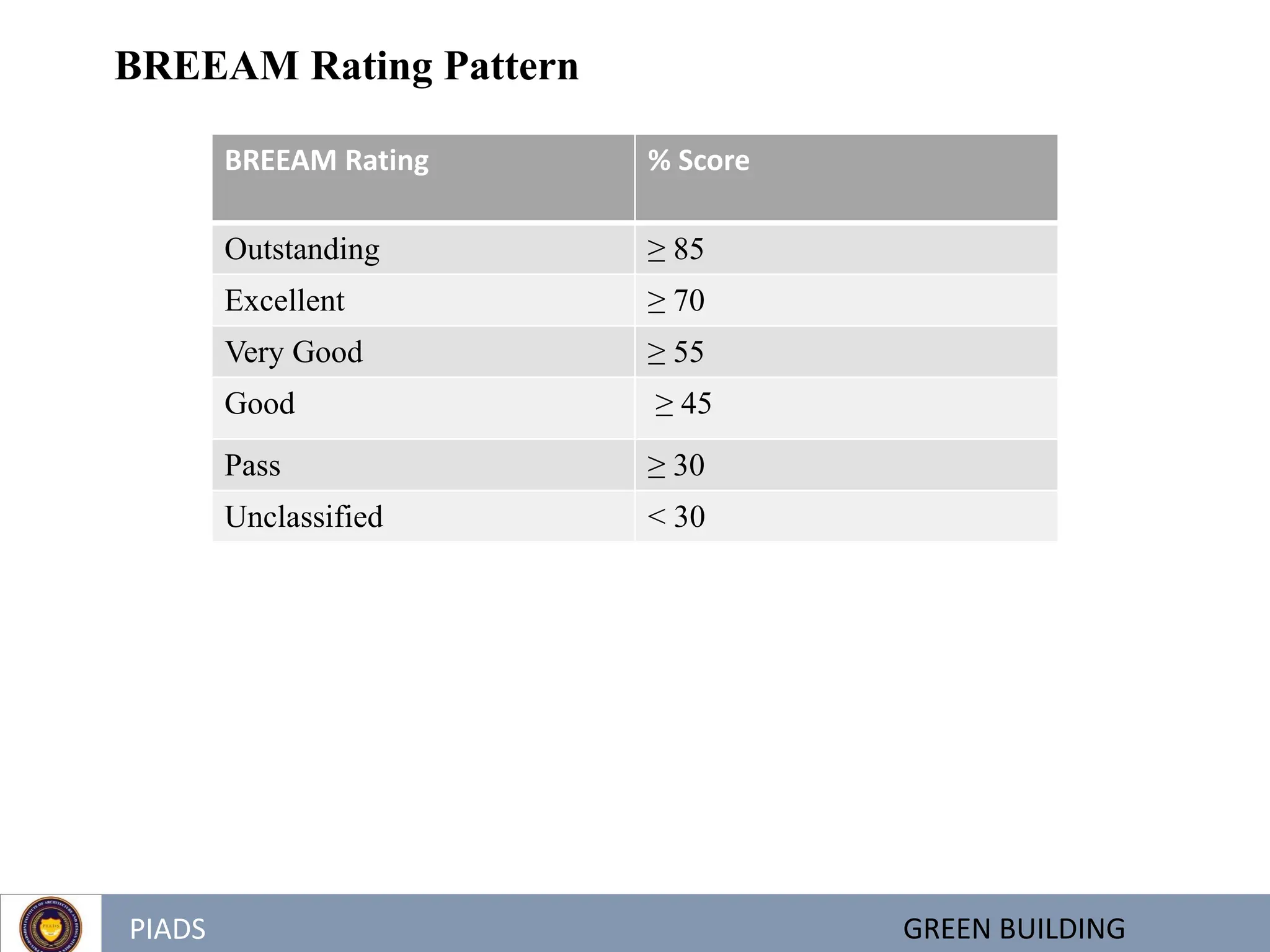
The document discusses green buildings and defines them as structures that use less water and energy, conserve natural resources, generate less waste, and provide healthier spaces compared to conventional buildings. It outlines various green building rating systems used globally like LEED and BREEAM, and in India like GRIHA. The benefits of green buildings are reduced costs, improved occupant health and productivity, and minimized environmental impacts. The goals of green building are to make the earth more sustainable by reducing disruption to natural habitats from construction. India is seeing rapid growth in construction but also needs to reduce its environmental impacts through sustainable building practices.