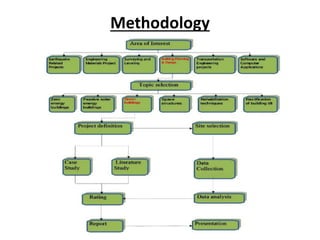
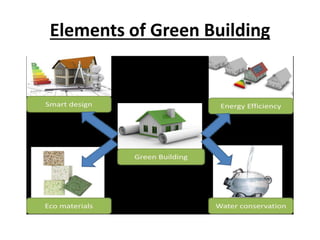
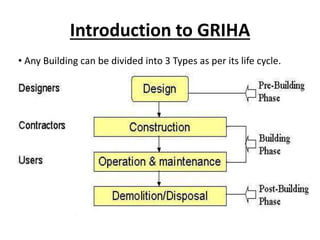
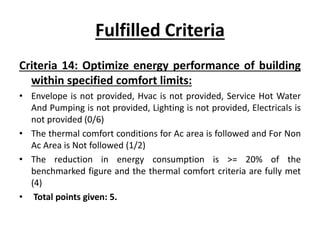
The document presents a project on modifying the R.K. College building to improve its green rating according to GRIHA guidelines, defining green buildings and their sustainable practices. It outlines the benefits, goals, and methodologies related to green building, including various rating systems and their criteria. The evaluation focuses on the building's lifecycle, detailing criteria fulfilled and points scored for various aspects of green architecture and construction efficiency.