This document provides an overview of Spanish grammar topics including:
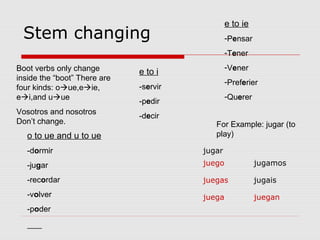
1. Nationalities and stem-changing verbs
2. Uses of the preposition "para" including purpose, reaction, destination, and indicating being ready
3. Indirect object pronouns and their placement before conjugated verbs or with infinitives
4. Rules for pronoun placement with infinitives, gerunds, and commands
5. The construction of "gustar" and forming likes/dislikes
6. Affirmative and negative words in Spanish
7. Forming Spanish superlatives with "-ísimo"
8. Uses of reflexive verbs and placement of reflexive pronou