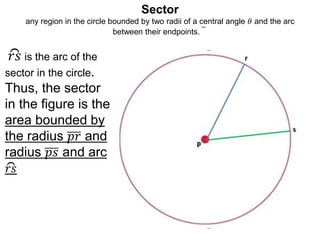
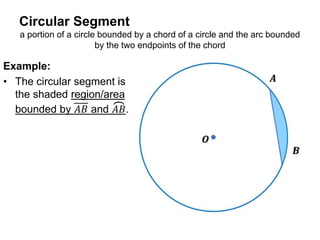
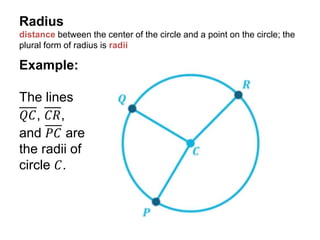
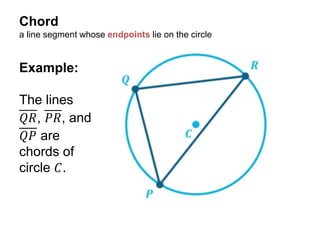
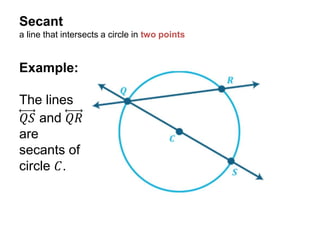
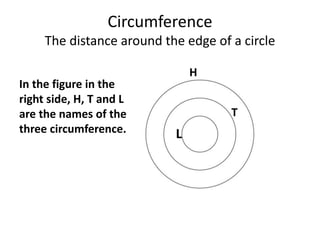
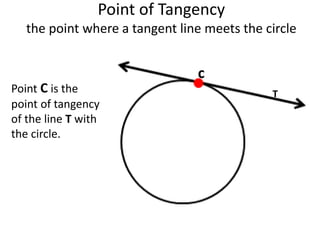
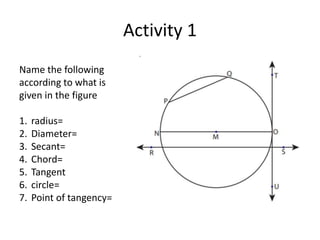
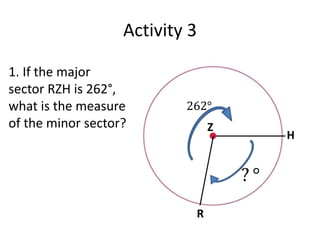
This document defines and provides examples of key terms used in geometry to describe parts of a circle, including radius, diameter, chord, secant, tangent, sector, arc, circular segment, circumference, point of tangency, and circle. It also includes example problems asking the reader to name these parts based on diagrams and calculate values like the measure of an angle or area of a segment.